ASP.NET 运行时详解 揭开请求过程神秘面纱
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ASP.NET 运行时详解 揭开请求过程神秘面纱相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
对于ASP.NET开发,排在前五的话题离不开请求生命周期。像什么Cache、身份认证、Role管理、Routing映射,微软到底在请求过程中干了哪些隐秘的事,现在是时候揭晓了。抛开乌云见晴天,接下来就一步步揭开请求管道神秘面纱。
上篇回顾
在介绍本篇内容之前,让我们先回顾下上一篇《ASP.NET运行时详解 集成模式和经典模式》的主要内容。在上一篇随笔中,我们提到ASP.NET运行时通过Application的InitInternal方法初始化运行管道。ASP.NET运行时提供了两种初始化管道模式,集成模式和经典模式。随后又分别介绍了两种模式下管道的初始化过程。那么,每个管道具体是做什么事以及管道具体是怎么执行的?接下来,本篇的内容会围绕着两个问题进行讲解。另外,上篇还遗留了页面的生命周期介绍。所以,本篇也会对页面生命周期做介绍。
管道步骤
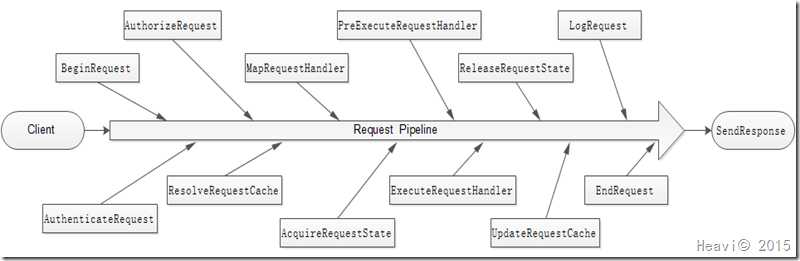
什么是请求管道?请求管道就是把Application的一系列事件串联成一条线,这些事件按照排列的先后顺序依次执行,事件处理的对象包括HttpModule、HttpHandler、ASP.NET Page。那么,在管道中具体包括哪些事件?下图概括了ASP.NET请求管道中包括的事件。
现在我们知道了管道包含的执行事件,但每个事件具体执行哪些操作?下面的列表简要列举了每个事件的执行的工作:
序号 事件 说明 1 BeginRequest 请求管道的第一个事件,当ASP.NET相应一个请求时就会被触发。 2 AuthenticateRequest 验证请求,开始检查用户身份,一般是获取请求的用户信息。 3 AuthorizeRequest 用户权限检查,未通过一般跳转到EndRequest事件。 4 ResolveRequestCache 当权限验证通过后,通过缓存模块提供服务,检查请求是否存在缓存,存在则直接返回缓存结果。 5 MapRequestHandler ASP.NET 基础结构使用 MapRequestHandler 事件来确定用于当前请求的请求处理程序。 6 AcquireRequestState 获取请求状态。 7 PreExecuteRequestHandler 在ASP.NET执行处理事件handler之前执行。 8 ExecuteRequestHandler 执行具体的Handler。 9 ReleaseRequestState 当 ASP.NET执行完请求的Handler后, State模块保存当前的状态数据。 10 UpdateRequestCache 缓存模块存储相应,提供给后面的请求缓存。 11 LogRequest 在ASP.NET生成日志之前触发。 12 EndRequest 结束当前请求。 13 SendResponse 发送请求响应。
列表简单的描述了管道中包含的事件,每个事件都可以通过HttpModule进行扩展。其实上面这些事件只是一个空架子,而实际干活的还是上一篇随笔中我们提到的HttpModule,ASP.NET默认实现了很多IHttpModule类,而这些类就是处理篇头提出的像Cache、身份认证、Role、Rounting等操作。接下来我们就One By One的分析这些Module具体做了什么操作。
之前我们有列举出了ASP.NET自身提供的IHttpModule,下表包含了ASP.NET自身提供的IHttpModule以及对应的类型:
序号 名称 类型 1 OutputCacheModule System.Web.Caching.OutputCacheModule 2 Session System.Web.SessionState.SessionStateModule 3 WindowsAuthentication System.Web.Security.WindowsAuthenticationModule 4 FormsAuthentication System.Web.Security.FormsAuthenticationModule 5 DefaultAuthentication System.Web.Security.DefaultAuthenticationModule 6 RoleManager System.Web.Security.RoleManagerModule 7 UrlAuthorization System.Web.Security.UrlAuthorizationModule 8 FileAuthorization System.Web.Security.FileAuthorizationModule 9 AnonymousIdentification System.Web.Security.AnonymousIdentificationModule 10 UrlMappingsModule System.Web.UrlMappingsModule 11 ServiceModel-4.0 System.ServiceModel.Activation.ServiceHttpModule, System.ServiceModel.Activation 12 UrlRoutingModule-4.0 System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule 13 ScriptModule-4.0 System.Web.Handlers.ScriptModule, System.Web.Extensions 列表中的Module会被安插到管道的事件步骤上,但每个Module具体安插到哪一个管道事件上,我们还是不清楚。要了解清楚这些,我们不得不分析这13个Module的源代码。
13个IHttpModule源代码分析
为了不影响整篇的阅读效果,我把13个IHttpModule代码的详细介绍放在了附录。我们不需要全部了解,但是像处理缓存的OutputCacheModule、身份认证的FormsAuthenticationModule、授权Url地址的UrlAuthorizationModule、处理路由映射的UrlRoutingModule等Module是有必要了解的。详细请查看附录中的源代码介绍。
统一管道生厂线
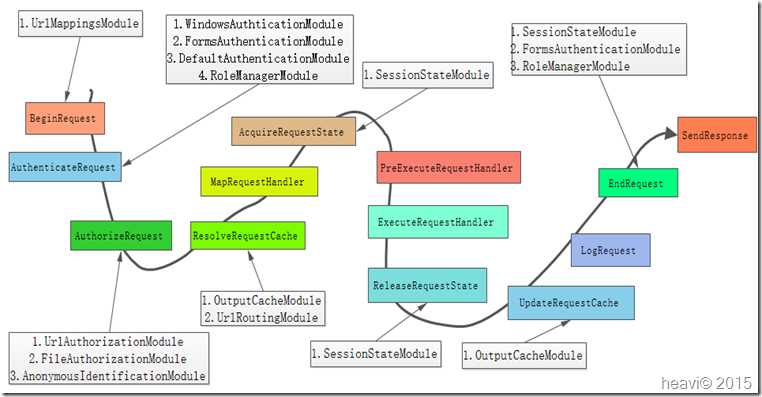
13个Module分析完了,我们也大概知道每个HttpModule应该安插在哪个管道事件上了。上面介绍的IHttpModule,我们通过一张流程图直观的展现出来。流程图如下:
到目前为止,我已经知道了管道中的IHttpModule。但是,只有这些IHttpModule,一次请求的完整流程还是跑不通的。例如,UrlRoutingModule生成了IHttpHandler,但在哪个管道步骤上调用IHttpHandler生成请求页面我们还是不知道。一个请求的完成流程可以归纳为MHPM。什么事MHPM呢?先看看下面的流程图:
图中的MHPM分别表示:IHttpModule、IHttpHandler、Page、IHttpModule。从图中可以看出,有些IHttpModule在处理IHttpHandler之前执行,而有些IHttpModule在生成页面Page之后执行。分析了所有的IHttpModule,但我们还是没看到执行IHttpHandler的ExecuteRequestHandler管道上有任何附加操作。回想上一篇随笔,我们还记得集成模式的管道类PipelineStepManager有一个BuildSteps方法,部分代码如下:
internal override void BuildSteps(WaitCallback stepCallback) { HttpApplication.IExecutionStep step2 = new HttpApplication.CallHandlerExecutionStep(app); app.AddEventMapping("ManagedPipelineHandler", RequestNotification.ExecuteRequestHandler, false, step2); }
代码中实例化了一个执行步骤step2,然后把step2映射到管道的ExecuteRequestHandler步骤。CallHandlerExecutionStep实现了管道步骤接口IExecutionStep。通过实现接口的Execute方法执行IHttpHandler的ProcessRequest方法。Execute代码如下:
void HttpApplication.IExecutionStep.Execute() { HttpContext context = this._application.Context; IHttpHandler handler = context.Handler; if (handler == null) { this._sync = true; } else if (handler is IHttpAsyncHandler) { IAsyncResult result; bool flag; bool flag2; IHttpAsyncHandler handler2 = (IHttpAsyncHandler)handler; this._sync = false; this._handler = handler2; Func<HttpContext, AsyncCallback, object, IAsyncResult> func = AppVerifier.WrapBeginMethod<HttpContext>(this._application, new Func<HttpContext, AsyncCallback, object, IAsyncResult>(handler2.BeginProcessRequest)); result = func(context, this._completionCallback, null); this._asyncStepCompletionInfo.RegisterBeginUnwound(result, out flag, out flag2); if (flag) { handler2.EndProcessRequest(result); } } else { this._sync = true; handler.ProcessRequest(context); } }代码首先对handler做判断,判断handler是否是异步类IHttpAsyncHandler。如果是,则执行Handler的异步方法:BeginProcessRequest;如果不是,则直接调用handler的同步方法ProcessRequest。
CallHandlerExecutionStep步骤执行完后,ASP.NET就能得到具体的ASP.NET Page页面。在ProcessRequest执行过程中,涉及到页面的生成周期。对于页面的生命周期,我们必须区分WEBFORM页面和MVC页面。两种不同的页面,生命周期也完全不同。WEBFORM是基于事件驱动,但MVC页面已经不再基于事件驱动。ExecuteRequestHandler管道事件上现在也附件的有操作了。目前为止,ASP.NET执行过程的整个管道步骤我们也差不多涉及的有个90%了。了解清楚请求过程的生命周期是非常有必要的。了解清楚了请求过程原理,我们可以设计出更加灵活的ASP.NET系统,并且能基于ASP.NET做更多的自定义扩展。
总结
本篇内容首先分析了ASP.NET执行管道包含哪些事件。但最初这些管道只是一个空架子,而在管道事件上添加具体任务是有IHttpModule完成。微软自己为ASP.NET执行管道实现了13个IHttpModule接口,并且这13个Module分布在不同的管道是事件上。本篇我们也具体介绍了这13个Module具体分布在哪些管道是事件上,以及每个Module在管道事件上具体做了什么操作。
本篇也简单的介绍了ExecuteRequestHandler管道事件上的IHttpHandler任务怎样执行。但没有具体介绍IHttpHandler是怎样生成我们需要的ASP.NET Page页面,也既是页面的生命周期。所以,下一篇随笔的预定内容既是ASP.NET高频话题:ASP.NET页面生命周期。
如果本篇内容对大家有帮助,请点击页面右下角的关注。如果觉得不好,也欢迎拍砖。你们的评价就是博主的动力!下篇内容,敬请期待!
附录
1.OutputCacheModule
所在管道步骤:ResolveRequestCache、UpdateRequestCache。查看OutputCacheModule实现的Init方法,代码如下:
void IHttpModule.Init(HttpApplication app) { if (RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().OutputCache.EnableOutputCache) { app.ResolveRequestCache += new EventHandler(this.OnEnter); app.UpdateRequestCache += new EventHandler(this.OnLeave); } }
通过代码我们能看出它在ResolveRequestCache和UpdateRequestCache这两个管道事件上执行了某些操作。OnEnter事件查看缓存记录是否有缓存,有缓存则直接返回缓存,而不执行之后的管道流程了。代码如下:
internal void OnEnter(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { if (OutputCache.InUse) { switch (request.HttpVerb) { case HttpVerb.GET: case HttpVerb.HEAD: case HttpVerb.POST: { string str; this._key = str = this.CreateOutputCachedItemKey(context, null); object obj2 = OutputCache.Get(str); if (obj2 != null) { response.Cache.ResetFromHttpCachePolicySettings(settings, context.UtcTimestamp); string originalCacheUrl = response2._kernelCacheUrl; if (originalCacheUrl != null) { response.SetupKernelCaching(originalCacheUrl); } PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.OUTPUT_CACHE_RATIO_BASE); PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.OUTPUT_CACHE_HITS); this._key = null; this._recordedCacheMiss = false; application.CompleteRequest(); return; } return; } } } }其实OnEnter里边的代码比我粘贴出来的多很多,但主流程是一致的。都是先通过请求的上下文信息(例如RequestPath、Method参数等)获取缓存主键,然后通过缓存主键到缓存队列里边去查看是否有主键对应的缓存。如果有缓存,则直接把缓存输出到Response.Output中,然后整个流程请求流程结束;如果没有缓存,则按管道流程执行下一步。
既然在OnEnter里边能取出来缓存,那么肯定有写缓存的地方。写缓存正式通过OutputCacheModule的OnLeave方法写入,OnLeave方法代码如下:internal void OnLeave(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { bool flag = false; if (response.HasCachePolicy) { cache = response.Cache; if (((cache.IsModified() && (response.StatusCode == 200)) && ((request.HttpVerb == HttpVerb.GET) || (request.HttpVerb == HttpVerb.POST))) && response.IsBuffered()) { if (((((cache.GetCacheability() == HttpCacheability.Public) || (cache.GetCacheability() == HttpCacheability.ServerAndPrivate)) || ((cache.GetCacheability() == HttpCacheability.Server) || flag3)) && ((!cache.GetNoServerCaching() && !response.ContainsNonShareableCookies()) && (cache.HasExpirationPolicy() || cache.HasValidationPolicy()))) && ((!cache.VaryByHeaders.GetVaryByUnspecifiedParameters() && (cache.VaryByParams.AcceptsParams() || ((request.HttpVerb != HttpVerb.POST) && !request.HasQueryString))) && (!cache.VaryByContentEncodings.IsModified() || cache.VaryByContentEncodings.IsCacheableEncoding(context.Response.GetHttpHeaderContentEncoding())))) { flag = true; } } } if (flag) { CachedVary vary; string str; string[] varyByParams; this.RecordCacheMiss(); HttpCachePolicySettings currentSettings = cache.GetCurrentSettings(response); string[] varyByContentEncodings = currentSettings.VaryByContentEncodings; string[] varyByHeaders = currentSettings.VaryByHeaders; if (this._key == null) { this._key = this.CreateOutputCachedItemKey(context, null); } DateTime noAbsoluteExpiration = Cache.NoAbsoluteExpiration; TimeSpan noSlidingExpiration = Cache.NoSlidingExpiration; if (currentSettings.SlidingExpiration) { noSlidingExpiration = currentSettings.SlidingDelta; } else if (currentSettings.IsMaxAgeSet) { DateTime time2 = (currentSettings.UtcTimestampCreated != DateTime.MinValue) ? currentSettings.UtcTimestampCreated : context.UtcTimestamp; noAbsoluteExpiration = time2 + currentSettings.MaxAge; } if (noAbsoluteExpiration > DateTime.UtcNow) { HttpRawResponse snapshot = response.GetSnapshot(); string kernelCacheUrl = response.SetupKernelCaching(null); Guid cachedVaryId = (vary != null) ? vary.CachedVaryId : Guid.Empty; CachedRawResponse rawResponse = new CachedRawResponse(snapshot, currentSettings, kernelCacheUrl, cachedVaryId); CacheDependency dependencies = response.CreateCacheDependencyForResponse(); OutputCache.InsertResponse(this._key, vary, str, rawResponse, dependencies, noAbsoluteExpiration, noSlidingExpiration); } } }代码首先检查请求头和响应头,看看是否符合写缓存的条件,例如检查缓存是否修改、返回状态是否为200等。接下来创建缓存主键、设置缓存周期。最后一步就是通过OutputCache.InsertResponse方法把结果缓存到OutputCache中。
2. SessionStateModule
所在管道步骤:AcquireRequestState、ReleaseRequestState、EndRequest。SessionStateModule的Init方法调用了InitModuleFromConfig方法,从配置文件中读取配置,初始化状态存储。在Web.config配置中我们经常看到<sessionState mode="InProc" cookieless="UseCookies" />配置,mode包括InProc(进程内)、SQLServer(数据库)、StateServer(进程外)、Custom(自定义)、Off(关闭Session)等。我们先看下InitModuleFromConfig方法的代码:
private void InitModuleFromConfig(HttpApplication app, SessionStateSection config) { if (config.Mode != SessionStateMode.Off) { app.AddOnAcquireRequestStateAsync(new BeginEventHandler(this.BeginAcquireState), new EndEventHandler(this.EndAcquireState)); app.ReleaseRequestState += new EventHandler(this.OnReleaseState); app.EndRequest += new EventHandler(this.OnEndRequest); this._partitionResolver = this.InitPartitionResolver(config); switch (config.Mode) { case SessionStateMode.InProc: if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) { s_canSkipEndRequestCall = true; } this._store = new InProcSessionStateStore(); this._store.Initialize(null, null); break; case SessionStateMode.StateServer: if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) { s_canSkipEndRequestCall = true; } this._store = new OutOfProcSessionStateStore(); ((OutOfProcSessionStateStore)this._store).Initialize(null, null, this._partitionResolver); break; case SessionStateMode.SQLServer: this._store = new SqlSessionStateStore(); ((SqlSessionStateStore)this._store).Initialize(null, null, this._partitionResolver); break; case SessionStateMode.Custom: this._store = this.InitCustomStore(config); break; } this._idManager = this.InitSessionIDManager(config); if (((config.Mode == SessionStateMode.InProc) || (config.Mode == SessionStateMode.StateServer)) && this._usingAspnetSessionIdManager) { this._ignoreImpersonation = true; } } }前面的几行代码加载Session事件到执行管道,接下来的switch代码根据Mode的枚举值初始化不同的Session存储介质。 后面还有一行代码调用了InitSessionIDManager方法,生成一个Session的ID管理器。
当管道执行到AcquireRequestState事件时,SessionStateModule中的BeginAcquireState事件被触发,精简后的代码如下:
private IAsyncResult BeginAcquireState(object source, EventArgs e, AsyncCallback cb, object extraData) { this.ResetPerRequestFields(); this._rqContext = ((HttpApplication)source).Context; this._rqAr = new HttpAsyncResult(cb, extraData); this.ChangeImpersonation(this._rqContext, false); this._store.InitializeRequest(this._rqContext); if (this._idManager.InitializeRequest(this._rqContext, false, out this._rqSupportSessionIdReissue)) { //不使用Cookie直接结束 this._rqAr.Complete(true, null, null); return this._rqAr; } this._rqId = this._idManager.GetSessionID(this._rqContext); this._rqExecutionTimeout = this._rqContext.Timeout; this._rqReadonly = this._rqContext.ReadOnlySessionState; if (this._rqId != null) { sessionStateItem = this.GetSessionStateItem(); } else if (!flag3) { bool flag4 = this.CreateSessionId(); this._rqIdNew = true; if (flag4) { if (s_configRegenerateExpiredSessionId) { this.CreateUninitializedSessionState(); } this._rqAr.Complete(true, null, null); return this._rqAr; } } if (sessionStateItem) { this.CompleteAcquireState(); this._rqAr.Complete(true, null, null); } result = this._rqAr; return result; }代码首先调用存储介质_store的InitializeRequest方法,初始化本次请求。然后调用ID管理器_idManager的InitializeRequest初始化请求,InitializeRequest方法会返回一个布尔值,为true表示不使用cookie,直接返回;为false表示使用cookie,继续执行BeginAcquireState接下来的流程。初始化完成后调用_idManager.GetSessionID方法获取SessionID。如果没有获取到SessionID,则调用CreateSessionId生成SessionID。
当管道执行到ReleaseRequestState步骤时,SessionStateModule中的OnReleaseState事件被触发。我们知道在BeginAcquireState事件中已经生成了SessionID。所以,在ReleaseRequestState中我们能够获取到SessionID,然后根据session状态调用_store.RemoveItem方法移除缓存项或者调用_store SetAndReleaseItemExclusive方法插入、更新或者移除缓存项。
当管道执行到EndRequest步骤时,SessionStateModule中的OnEndRequest事件被触发。这里边主要的内容就是初始化请求参数以及重置超时事件,准备接收下一次请求。3. WindowsAuthenticationModule
所在管道步骤:AuthenticateRequest。WindowsAuthticationModule的Init方法在管道的AuthenticateRequest步骤注册OnEnter事件,OnEnter执行的内容比较简单,从上下文中取出用户身份,然后把用户身份设置到上下文的安全实体WindowsPrincipal中。
4. FormsAuthenticationModule
所在管道步骤:AuthenticateRequest、EndRequest。FormsAuthenticationModule的Init方法代码如下:
public void Init(HttpApplication app) { if (!_fAuthChecked) { _fAuthRequired = AuthenticationConfig.Mode == AuthenticationMode.Forms; _fAuthChecked = true; } if (_fAuthRequired) { FormsAuthentication.Initialize(); app.AuthenticateRequest += new EventHandler(this.OnEnter); app.EndRequest += new EventHandler(this.OnLeave); } }代码调用了FormsAuthentication.Initialize()方法对表单验证做初始化操作。Initialize方法代码如下:
public static void Initialize() { AuthenticationSection authentication = RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().Authentication; authentication.ValidateAuthenticationMode(); _FormsName = authentication.Forms.Name; _RequireSSL = authentication.Forms.RequireSSL; _SlidingExpiration = authentication.Forms.SlidingExpiration; if (_FormsName == null) { _FormsName = ".ASPXAUTH"; } _Protection = authentication.Forms.Protection; _Timeout = (int)authentication.Forms.Timeout.TotalMinutes; _FormsCookiePath = authentication.Forms.Path; _LoginUrl = authentication.Forms.LoginUrl; if (_LoginUrl == null) { _LoginUrl = "login.aspx"; } _DefaultUrl = authentication.Forms.DefaultUrl; if (_DefaultUrl == null) { _DefaultUrl = "default.aspx"; } _CookieMode = authentication.Forms.Cookieless; _CookieDomain = authentication.Forms.Domain; _EnableCrossAppRedirects = authentication.Forms.EnableCrossAppRedirects; _TicketCompatibilityMode = authentication.Forms.TicketCompatibilityMode; _Initialized = true; }通过代码可以看出,Initialize方法从配置文件中读取表单配置信息并初始化到FormsAuthentication类的静态字段中。Cookieless指定Cookie类型, defaultUrl表示验证后重定向的默认地址,loginUrl表示找不到验证cookie重定向的登录地址,protection指定cookie的加密类型。详细说明请可以查看MSDN:https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/1d3t3c61.aspx。 在管道AuthenticateRequest步骤上,我们注册了OnEnter方法,代码如下:
private void OnEnter(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { HttpContext context = application.Context; this.OnAuthenticate(new FormsAuthenticationEventArgs(context)); CookielessHelperClass cookielessHelper = context.CookielessHelper; if (AuthenticationConfig.AccessingLoginPage(context, FormsAuthentication.LoginUrl)) { context.SetSkipAuthorizationNoDemand(true, false); cookielessHelper.RedirectWithDetectionIfRequired(null, FormsAuthentication.CookieMode); } if (!context.SkipAuthorization) { context.SetSkipAuthorizationNoDemand(AssemblyResourceLoader.IsValidWebResourceRequest(context), false); } }分析代码,首先调用了OnAuthenticate方法,OnAuthenticate通过Cookie配置信息对每次的请求作Cookie更新,例如如果设置Cookie为可调过期(Slid),那么每次请求都会对cookie的过期时间更新。然后调用了AuthenticationConfig.AccessingLoginPage方法,判断是否正在请求配置的LoginUrl,如果是则直接跳过授权步骤。如果没有跳过授权步骤,检查当前请求是否为Web资源请求,如果是则直接跳过授权步骤。在EndRequest管道步骤上,我们注册了OnLeave方法,代码如下:
private void OnLeave(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { HttpApplication application = (HttpApplication)source; HttpContext context = application.Context; //context.Response.StatusCode == 401 && buzh if ((context.Response.StatusCode == 0x191) && !context.Response.SuppressFormsAuthenticationRedirect) { //当前请求的原始地址 string rawUrl = context.Request.RawUrl; if ((rawUrl.IndexOf("?" + FormsAuthentication.ReturnUrlVar + "=", StringComparison.Ordinal) == -1) && (rawUrl.IndexOf("&" + FormsAuthentication.ReturnUrlVar + "=", StringComparison.Ordinal) == -1)) { strUrl = AuthenticationConfig.GetCompleteLoginUrl(context, FormsAuthentication.LoginUrl); CookielessHelperClass cookielessHelper = context.CookielessHelper; if (strUrl.IndexOf(‘?‘) >= 0) { strUrl = FormsAuthentication.RemoveQueryStringVariableFromUrl(strUrl, FormsAuthentication.ReturnUrlVar); str3 = strUrl + "&" + FormsAuthentication.ReturnUrlVar + "=" + HttpUtility.UrlEncode(rawUrl, context.Request.ContentEncoding); } else { str3 = strUrl + "?" + FormsAuthentication.ReturnUrlVar + "=" + HttpUtility.UrlEncode(rawUrl, context.Request.ContentEncoding); } int index = rawUrl.IndexOf(‘?‘); if ((index >= 0) && (index < (rawUrl.Length - 1))) { str3 = str3 + "&" + rawUrl.Substring(index + 1); } cookielessHelper.SetCookieValue(‘F‘, null); cookielessHelper.RedirectWithDetectionIfRequired(str3, FormsAuthentication.CookieMode); context.Response.Redirect(str3, false); } } }先列举一个场景,例如我们在taobao首页查看到某个商品,点击“购买”,但我们还没有登录。这个时候taobao会跳转到登录界面,登录成功后直接跳转到你的购买界面。OnLeave所做的正是这样的工作,首先校验返回状态status是否为0x191(401,权限验证失败),如果是则获取登录界面地址,并且在后面加上ReturnUrl=请求地址。例如我请求地址是http://buy.heavi.com,但请求状态返回了401,这则时候OnLeave拼凑登录地址:http://login.heavi.com? ReturnUrl=http://buy.heavi.com。最后直接通过context.Response.Redirect(str3, false)重定向到登录界面。当登录成功后,在重定向到http://buy.heavi.com界面。
5. DefaultAuthenticationModule
所在管道步骤:AuthenticateRequest。DefaultAuthenticationModule的Init把OnEnter方法注册到AuthenticateRequest管道步骤上。OnEnter代码如下:
private void OnEnter(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { if (context.Response.StatusCode > 200) { if (context.Response.StatusCode == 0x191) { this.WriteErrorMessage(context); } application.CompleteRequest(); } else { if (context.User == null) { this.OnAuthenticate(new DefaultAuthenticationEventArgs(context)); if (context.Response.StatusCode > 200) { if (context.Response.StatusCode == 0x191) { this.WriteErrorMessage(context); } application.CompleteRequest(); return; } } if (context.User == null) { context.SetPrincipalNoDemand(new GenericPrincipal(new GenericIdentity(string.Empty, string.Empty), new string[0]), false); } Thread.CurrentPrincipal = context.User; } }代码也比较简单,判断Response中的Status状态是等于401,是则写日志,直接结束本次请求。不是则设置当前线程的CurrentPrincipal为当前请求的用户。
6. RoleManagerModule
所在管道步骤:AuthenticateRequest、EndRequest。RoleManagerModule的Init方法把OnEnter方法注册到AuthenticateRequest管道步骤上,把OnLeave方法注册到EndRequest。OnEnter方法代码如下:
private void OnEnter(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { if (Roles.CacheRolesInCookie) { if (context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated && (!Roles.CookieRequireSSL || context.Request.IsSecureConnection)) { HttpCookie cookie = context.Request.Cookies[Roles.CookieName]; if (cookie != null) { string encryptedTicket = cookie.Value; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(Roles.CookiePath) && (Roles.CookiePath != "/")) { cookie.Path = Roles.CookiePath; } cookie.Domain = Roles.Domain; context.SetPrincipalNoDemand(this.CreateRolePrincipalWithAssert(context.User.Identity, encryptedTicket)); } } else { if (context.Request.Cookies[Roles.CookieName] != null) { Roles.DeleteCookie(); } if (HttpRuntime.UseIntegratedPipeline) { context.DisableNotifications(RequestNotification.EndRequest, 0); } } } if (!(context.User is RolePrincipal)) { context.SetPrincipalNoDemand(this.CreateRolePrincipalWithAssert(context.User.Identity, null)); } HttpApplication.SetCurrentPrincipalWithAssert(context.User); }如果设置了CacheRolesInCookie,并且身份已经通过认证了。接下来就从请求中获取Role的Cookie,并使用认证的身份创建角色安全体保存到上下文中;如果认证没通过,并且Cookie中有角色的Cookie,则删除角色Cookie。OnLeave代码如下:
private void OnLeave(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { if (((Roles.Enabled && Roles.CacheRolesInCookie) && !context.Response.HeadersWritten) && (((context.User != null) && (context.User is RolePrincipal)) && context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated)) { if (Roles.CookieRequireSSL && !context.Request.IsSecureConnection) { if (context.Request.Cookies[Roles.CookieName] != null) Roles.DeleteCookie(); } else { RolePrincipal user = (RolePrincipal)context.User; if (user.CachedListChanged && context.Request.Browser.Cookies) { string str = user.ToEncryptedTicket(); if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(str) || (str.Length > 0x1000)) Roles.DeleteCookie(); else { HttpCookie cookie = new HttpCookie(Roles.CookieName, str) { HttpOnly = true, Path = Roles.CookiePath, Domain = Roles.Domain }; if (Roles.CreatePersistentCookie) { cookie.Expires = user.ExpireDate; } cookie.Secure = Roles.CookieRequireSSL; context.Response.Cookies.Add(cookie); } } } } }首先判断角色是否可用、是否把角色缓存存储在Cookie、上下文身份是否是角色安全体、是否通过认证,只有满足这些条件才执行下面的流程。满足条件后,如果Cookie需要SSL认证并且不是安全连接,则删除Cookie中的角色Cookie;否则,重新生成新的Cookie并返回到Response中。
7. UrlAuthorizationModule
所在管道步骤:AuthorizeRequest。UrlAuthorizationModule的Init把OnEnter方法注册到AuthorizeRequest管道步骤上。OnEnter方法代码如下:
private void OnEnter(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { AuthorizationSection authorization = RuntimeConfig.GetConfig(context).Authorization; if (!authorization.EveryoneAllowed && !authorization.IsUserAllowed(context.User, context.Request.RequestType)) { ReportUrlAuthorizationFailure(context, this); } else { if ((context.User == null) || !context.User.Identity.IsAuthenticated) { PerfCounters.IncrementCounter(AppPerfCounter.ANONYMOUS_REQUESTS); } WebBaseEvent.RaiseSystemEvent(this, 0xfa3); } }首先从配置中获取授权节点,如果当前用户被限制,则调用ReportUrlAuthorizationFailure方法记录Url授权报告并终止本次请求;如果授权成功,执行WebSuccessAuditEvent系统事件。
8. FileAuthorizationModule
所在管道步骤:AuthorizeRequest。FileAuthorizationModule的Init把OnEnter方法注册到AuthorizeRequest管道步骤上。OnEnter代码如下:
private void OnEnter(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { if (!IsUserAllowedToFile(context, null)) { context.Response.SetStatusCode(0x191, 3); this.WriteErrorMessage(context); application.CompleteRequest(); } }代码中,调用IsUserAllowedToFile方法判断当前用户是否允许访问请求的文件。如果不允许访问,则设置返回状态为401(认证失败)并记录错误信息,结束本次请求。需要说明的是,IsUserAllowedToFile只验证Windows用户。如果是其他用户,则不需要File验证。
9. AnonymousIdentificationModule
所在管道步骤:AuthorizeRequest。AnonymousIdentificationModule的Init把OnEnter方法注册到AuthorizeRequest管道步骤上。OnEnter代码如下:
private void OnEnter(object source, EventArgs eventArgs) { if (!s_Initialized) //从配置文件中读取anonymousIdentification节点配置 Initialize(); if (s_Enabled) { isAuthenticated = context.Request.IsAuthenticated; if (isAuthenticated) flag2 = CookielessHelperClass.UseCookieless(context, false, s_CookieMode); //false表示使用cookie else flag2 = CookielessHelperClass.UseCookieless(context, true, s_CookieMode); //true表示不适用cookie //如果需要SSL,并且请求不是安全连接,并且使用cookie if ((s_RequireSSL && !context.Request.IsSecureConnection) && !flag2) { if (context.Request.Cookies[s_CookieName] != null) { //重新设置Cookie,并且设置过期时间为已过期,0x7cf表示1999年。 cookie = new HttpCookie(s_CookieName, string.Empty) { HttpOnly = true, Path = s_CookiePath, Secure = s_RequireSSL }; cookie.Expires = new DateTime(0x7cf, 10, 12); context.Response.Cookies.Add(cookie); } } //不需要SSL认证 else { if (!flag2) { cookie = context.Request.Cookies[s_CookieName]; if (cookie != null) { cookieValue = cookie.Value; cookie.Path = s_CookiePath; cookie.Domain = s_Domain; } } else { cookieValue = context.CookielessHelper.GetCookieValue(‘A‘); } decodedValue = GetDecodedValue(cookieValue); if ((decodedValue != null) && (decodedValue.AnonymousId != null)) { context.Request.AnonymousID = decodedValue.AnonymousId; } if (!isAuthenticated) { //设置AnonymousID if (context.Request.AnonymousID == null) { if (this._CreateNewIdEventHandler != null) { AnonymousIdentificationEventArgs e = new AnonymousIdentificationEventArgs(context); this._CreateNewIdEventHandler(this, e); context.Request.AnonymousID = e.AnonymousID; } flag = true; } DateTime utcNow = DateTime.UtcNow; //如果cookie设置为滑动调整,并且cookie过期时间小于cookie过期周期的一半,则需要更新cookie if (!flag && s_SlidingExpiration) { if ((decodedValue == null) || (decodedValue.ExpireDate < utcNow)) { flag = true; } else { TimeSpan span = (TimeSpan)(decodedValue.ExpireDate - utcNow); if (span.TotalSeconds < ((s_CookieTimeout * 60) / 2)) { flag = true; } } } //生成新的cookie if (flag) { DateTime dt = utcNow.AddMinutes((double)s_CookieTimeout); cookieValue = GetEncodedValue(new AnonymousIdData(context.Request.AnonymousID, dt)); if (!flag2) { cookie = new HttpCookie(s_CookieName, cookieValue) { HttpOnly = true, Expires = dt, Path = s_CookiePath, Secure = s_RequireSSL }; if (s_Domain != null) { cookie.Domain = s_Domain; } context.Response.Cookies.Add(cookie); } else { context.CookielessHelper.SetCookieValue(‘A‘, cookieValue); context.Response.Redirect(context.Request.RawUrl); } } } } }首先调用Initialize方法从配置文件中读取anonymousIdentification节点配置信息,例如我们在Web.Config中配置:
<anonymousIdentification enabled="true" cookieName="anonyIdentity" cookiePath="/Cookie/" cookieTimeout="60" cookieRequireSSL="true" cookieSlidingExpiration="true" />Initialize方法把这些配置读取到AnonymousIdentificationModule实体中。如果匿名身份需要SSL认证并且当前连接不是安全连接,则直接把Cookie设置为已过期并返回到Response中。如果不需要SSL认证,则根据配置信息以及过期周期更新匿名Cookie的AnonymousID以及过期时间,最后把更新的Cookie返回到Response.Cookie中。
10. UrlMappingsModule
所在管道步骤:BeginRequest。UrlMappingsModule的Init做了两件事,一是从配置文件中读取urlMappings 节点配置,下面就是Web.cofnig中配置实例:
<urlMappings enabled="true"> <add url="/UserInfo/Index" mappedUrl="/Home/Index" /> </urlMappings>Init的第二件事就是把OnEnter方法注册到BeginRequest管道步骤,OnEnter方法直接调用UrlMappingRewritePath方法,所以,我们可以直接分析UrlMappingRewritePath方法代码:
static void UrlMappingRewritePath(HttpContext context) { HttpRequest request = context.Request; UrlMappingsSection urlMappings = RuntimeConfig.GetAppConfig().UrlMappings; string path = request.Path; string str2 = null; string queryStringText = request.QueryStringText; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(queryStringText)) { str2 = urlMappings.HttpResolveMapping(path + "?" + queryStringText); } if (str2 == null) { str2 = urlMappings.HttpResolveMapping(path); } if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(str2)) { context.RewritePath(str2, false); } }代码比较简单,首先从配置文件中获取urlMappings节点信息,然后调用HttpResolveMapping方法,匹配请求的全路径url(包括路径和参数)是否有对应的mappedUrl。如果没有,再匹配请求的路径path是否有对应的mappedUrl。匹配成功,调用context.RewirtePath方法设置请求的路径为mappedUrl。
11. ServiceHttpModule
ServiceHttpModule没有执行任何操作。用户向后扩展
12. UrlRoutingModule
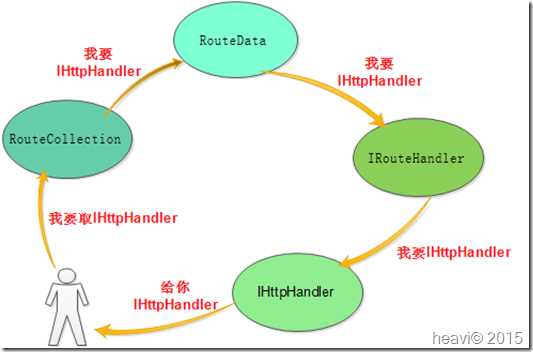
UrlRoutingModule在所有管道中起到承上启下的作用,Http请求的IHttpHandler就在是这里生成的。所在管道步骤:ResolveRequestCache。Init方法把UrlRoutingModule中的OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache方法注册到ResolveRequestCache管道步骤。
OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache方法直接调用了PostResolveRequestCache方法,PostResolveRequestCache代码如下:public virtual void PostResolveRequestCache(HttpContextBase context) { //根据上下文从路由集合中获取对应路由数据 RouteData routeData = this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context); if (routeData != null) { //获取路由处理器 IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler; if (!(routeHandler is StopRoutingHandler)) { RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(context, routeData); context.Request.RequestContext = requestContext; //获取IHttpHandler IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext); //重定向上下文中的httpHandler context.RemapHandler(httpHandler); } } }上面的代码已经是一目了然,清清楚楚的了。首先从路由集合中获取路由数据routeData,然后从routeData获取RouteHandler,接下来调用routeHandler的GetHttpHandler方法获取IHttpHandler实例。最后,调用上下文context的RemapHandler方法重定向httpHandler。下面是整个执行的流程图:
13. ScriptModule
ScriptModule没有执行任何操作。
以上是关于ASP.NET 运行时详解 揭开请求过程神秘面纱的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章