单元测试
Posted zhanghan123
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了单元测试相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 为什么做单测单测的好处不得不写单测的原因难处难于坚持,在快速迭代开发过程中,可供写单测的时间过少 扩展TDD(Test Drive Develop):测试驱动开发,是一种非常高效的开发方式 2. 测试框架2.1 概述2.2 junit4.12Junit测试是程序员测试,即所谓白盒测试,因为程序员知道被测试的软件如何(How)完成功能和完成什么样(What)的功能。Junit是一套框架,继承TestCase类,就可以用Junit进行自动测试了。 示例代码: @Before: 执行单测之前的初始化操作。 @After:单测完成后收尾工作。 @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
}
assume: 用于判断测试用例的入参是否有业务含义的工具,如果入参不符合预期时会抛出 assumptionViolatedException、assumeTrue/assumeFalse、 assumeNotNull、 assumeThat、 assumeNoException @RunWith(Theories.class)
public class AssumeTest
{
@DataPoints
public static String[] names = {"LiLei", "HanMeiMei"};
@DataPoints
public static int[] ages = {10, -2, 12};
@Theory
public void printAge(String name, int age)
{
Assume.assumeTrue(age > 0);
System.out.println(String.format("%s‘s Name is %s.", name, age));
}
}
assert :用于常用的测试结果验证 AssertTrue、AssertFalse:结果的true、false。 AssertThat:使用Matcher做自定义的校验。 AssertEquals、AssertNotEquals:判断两个对象是否相等。 AssertNull、AssertNotNull:判断对象是否为空。 AssertSame:判断两个对象是否为同一个,不同于equals这里是使用“==”判断。 AssertArrayEquals:判断两个数组是否相等。 @Test
public void sum() throws Exception {
assertEquals(mCalculator.sum(3, 4), 7);
}
verify : 主要用于验证方法是否执行 @Test
public void testVerify() {
List mockedList = mock(List.class);
mockedList.add("one");
mockedList.clear();
mockedList.add("3");
// verification
verify(mockedList).add("one");
verify(mockedList).clear();
}
其他高级用法: @Test(timeout = 1000): 限时操作,若超过制定时间,强制停止 @Test(expected = ArithmeticException.class): 预测抛出指定异常 2.3 mockito1.9.5创建mock对象不能对final,Anonymous ,primitive类进行mock。 when… thenRetrun; when… thenThrow doNothing().doRetrun(); doNothing.doThrow() anyInt、anyString、anyMap…..(参数匹配器) @Test
public void argumentMatcherTest2(){
Map
2.4 robolectric3.1.21.测试跳转 /**
* Activity跳转测试
*/
@Test
public void testStartActivity() {
//按钮点击后跳转到下一个Activity
forwardBtn.performClick();
Intent expectedIntent = new Intent(sampleActivity, LoginActivity.class);
Intent actualIntent = ShadowApplication.getInstance().getNextStartedActivity();
assertEquals(expectedIntent.getComponent(), actualIntent.getComponent());
}
2.模拟activity sampleActivity = Robolectric.setupActivity(SampleActivity.class);
/**
* Toast的测试
*/
@Test
public void testToast() {
//点击按钮,出现吐司
toastBtn.performClick();
assertEquals(ShadowToast.getTextOfLatestToast(), "we love UT");
}
/**
* Dialog的测试
*/
@Test
public void testDialog() {
//点击按钮,出现对话框
dialogBtn.performClick();
AlertDialog latestAlertDialog = ShadowAlertDialog.getLatestAlertDialog();
assertNotNull(latestAlertDialog);
}
/**
* 测试控件状态
*/
@Test
public void testViewState() {
CheckBox checkBox = (CheckBox) sampleActivity.findViewById(R.id.checkbox);
Button inverseBtn = (Button) sampleActivity.findViewById(R.id.btn_inverse);
assertTrue(inverseBtn.isEnabled());
checkBox.setChecked(true);
//点击按钮,CheckBox反选
inverseBtn.performClick();
assertTrue(!checkBox.isChecked());
inverseBtn.performClick();
assertTrue(checkBox.isChecked());
}
/**
* 资源文件访问测试
*/
@Test
public void testResources() {
Application application = RuntimeEnvironment.application;
String appName = application.getString(R.string.app_name);
String activityTitle = application.getString(R.string.title_activity_simple);
assertEquals("LoveUT", appName);
assertEquals("SimpleActivity", activityTitle);
}
/**
* 测试广播
*/
@Test
public void testBoradcast() {
ShadowApplication shadowApplication = ShadowApplication.getInstance();
String action = "com.geniusmart.loveut.login";
Intent intent = new Intent(action);
intent.putExtra("EXTRA_USERNAME", "geniusmart");
//测试是否注册广播接收者
assertTrue(shadowApplication.hasReceiverForIntent(intent));
//以下测试广播接受者的处理逻辑是否正确
MyReceiver myReceiver = new MyReceiver();
myReceiver.onReceive(RuntimeEnvironment.application, intent);
SharedPreferences preferences = RuntimeEnvironment.application.getSharedPreferences("account", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
assertEquals("geniusmart", preferences.getString("USERNAME", ""));
}
/**
* 测试Fragment
*/
@Test
public void testFragment() {
SampleFragment sampleFragment = new SampleFragment();
//此api可以主动添加Fragment到Activity中,因此会触发Fragment的onCreateView()
SupportFragmentTestUtil.startFragment(sampleFragment);
assertNotNull(sampleFragment.getView());
}
4.登录场景测试
@Test
public void loginSuccess() {
emailView.setText("zhangzhan35@gmail.com");
passwordView.setText("123");
button.performClick();
ShadowApplication application = ShadowApplication.getInstance();
assertThat("Next activity has started", application.getNextStartedActivity(), is(notNullValue()));
}
@Test
public void loginWithEmptyUsernameAndPassword() {
button.performClick();
ShadowApplication application = ShadowApplication.getInstance();
assertThat("Next activity should not started", application.getNextStartedActivity(), is(nullValue()));
assertThat("Show error for Email field ", emailView.getError(), is(notNullValue()));
assertThat("Show error for Password field ", passwordView.getError(), is(notNullValue()));
assertEquals(emailView.getError().toString(), RuntimeEnvironment.application.getString(R.string.error_field_required));
}
@Test
public void loginFailure() {
emailView.setText("invalid@email");
passwordView.setText("invalidpassword");
button.performClick();
ShadowApplication application = ShadowApplication.getInstance();
assertThat("Next activity should not started", application.getNextStartedActivity(), is(nullValue()));
assertThat("Show error for Email field ", emailView.getError(), is(notNullValue()));
assertThat("Show error for Password field ", passwordView.getError(), is(notNullValue()));
}
更多场景还需探索。。。 与espresso的对比Google 官方提供的一个易于测试 Android UI 的开源框架 , 于2013年10月推出它的 released 版本 , 目前最新版本已更新到2.x . 并且在AndroidStudio 2.2 预览版中已经默认集成该测试库 。 ViewMatchers - 在当前View层级去匹配指定的View . ViewActions - 执行Views的某些行为,如点击事件 . ViewAssertions - 检查Views的某些状态,如是否显示 . @RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class)
public class LoginUITest {
@Rule
public ActivityTestRule rule=new ActivityTestRule(LogingActivity.class,true);
@Test
public void login(){
//login
onView(withId(R.id.userName)).perform(typeText("Jack"),closeSoftKeyboard());
onView(withId(R.id.password)).perform(typeText("1234"),closeSoftKeyboard());
onView(withText("登录")).perform(click());
//verify
onView(withId(R.id.content)).check(matches(isDisplayed()));
}
}
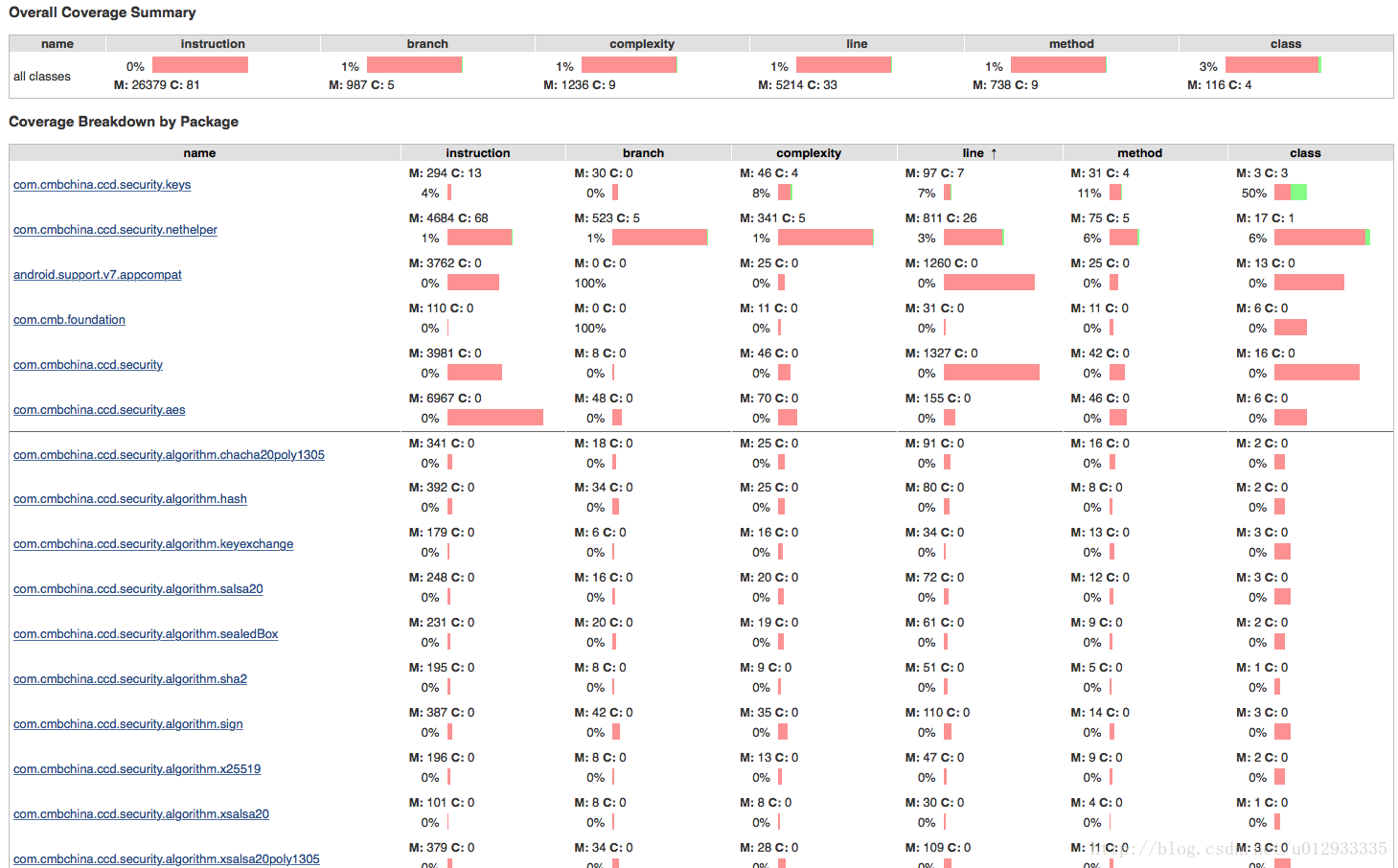
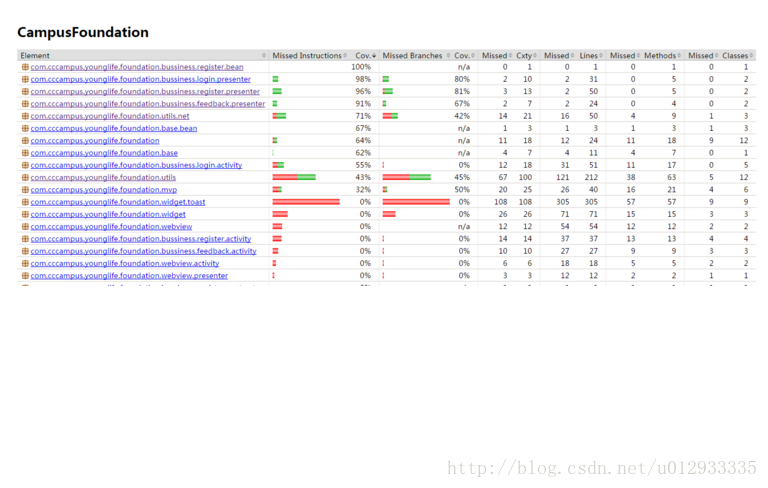
espresso更偏向于自动化测试,集成后执行单元测试需要跑在Android手机上,其有个高级功能,根据你的点击轨迹,自动生成自动测试代码。 3. 覆盖率行覆盖率:度量被测程序的每行代码是否被执行,判断标准行中是否至少有一个指令被执行。 类覆盖率:度量计算class类文件是否被执行。 分支覆盖率:度量if和switch语句的分支覆盖情况,计算一个方法里面的 总分支数,确定执行和不执行的 分支数量。 方法覆盖率:度量被测程序的方法执行情况,是否执行取决于方法中是否有至少一个指令被执行。 指令覆盖:计数单元是单个java二进制代码指令,指令覆盖率提供了代码是否被执行的信息,度量完全 独立源码格式。 圈复杂度:在(线性)组合中,计算在一个方法里面所有可能路径的最小数目,缺失的复杂度同样表示测试案例没有完全覆盖到这个模块。 集成配置: apply plugin: ‘jacoco‘
android {
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile(‘proguard-android.txt‘), ‘proguard-rules.pro‘
}
debug{
testCoverageEnabled true
}
}
}
jacoco {
toolVersion = "0.7.5.201505241946"
}
jacoco覆盖率报告分为两种: task jacocoTestReport(type:JacocoReport, dependsOn: "testDebugUnitTest") {
println("=========jacocoTestReport start");
group = "Reporting"
description = "Generate Jacoco coverage reports"
classDirectories = fileTree(
dir: "${project.buildDir}/intermediates/classes/debug",
excludes: [‘**/R.class‘,
‘**/R$*.class‘,
‘**/*$ViewInjector*.*‘,
‘**/BuildConfig.*‘,
‘**/Manifest*.*‘]
)
println("path==========>>" + "${project.buildDir}/intermediates/classes/debug")
def coverageSourceDirs = "${project.projectDir}/src/main/java"
println("coverageSourceDirs==========>>" + coverageSourceDirs)
additionalSourceDirs = files(coverageSourceDirs)
sourceDirectories = files(coverageSourceDirs)
executionData = fileTree(dir: project.projectDir, includes:[‘**/*.exec‘, ‘**/*.ec‘])
reports {
xml.enabled = true
html.enabled = true
}
}
task jacocoAndroidTestReport(type:JacocoReport,dependsOn:"connectedAndroidTest"){
group = "Reporting"
description = "Generate Jacoco coverage reports after running tests."
reports{
xml.enabled = true
html.enabled = true
csv.enabled = false
}
classDirectories = fileTree(
dir : "$buildDir/intermediates/classes/debug",
excludes : [
‘**/*Test.class‘,
‘**/R.class‘,
‘**/R$*.class‘,
‘**/BuildConfig.*‘,
‘**/Manifest*.*‘
]
)
def coverageSourceDirs = [‘src/main/java‘]
additionalSourceDirs = files(coverageSourceDirs)
sourceDirectories = files(coverageSourceDirs)
additionalClassDirs = files(coverageSourceDirs)
executionData = files("$buildDir/outputs/code-coverage/connected/coverage.ec")
}
结果展示总结单元测试的一些原则
|
|
在开始写单测之前,已经调研了很久Android单测的框架以及demo,正好换了一个新的项目组,就从头开始将单测框架应用到开发过程中,后续也方便可以使用TDD。 调研的框架:junit,mockito, roboletric,espresso,jacoco(覆盖率报告) 具体场景:网络请求,todomvp的单测方式,UI测试等。 理想永远是美好的,撸起袖子开始干的时候,就会发现还有很多崎岖需要去踏平。 首先,我放弃了espresso(虽然是google官方出的测试框架),主要原因是espresso依赖真机或模拟器。我相信大部分应用应该都有模拟器判断,在模拟器环境下禁止启动app,为了写单测,还得改代码,很难受;另外多数开发团队应该都是持续集成,跑espresso,还需要有一台手机常年插在构建机上,很麻烦。这并不是说espresso毫无用处,espresso对于Android框架支持非常完善,基本上所有UI的测试都可以实现。另外,espresso还有一个非常强大的功能,适合测试人员手工测试:录制测试过程,自动生成测试代码。比方说:你进入app后,按照正确测试流程点击一遍后,保存下来,下一次开发人员有了些许改动,你只需要运行一次之前自动生成的测试代码,应用便会按照之前的流程进行测试,如出现异常,则测试不通过!非常强大(据团队的ios工程师说,ios也有一样的测试框架,个人觉得测试人员可以考虑一下这个)。 所以最初我采用的Android单测框架就是:junit + mockito + roboletric + jacoco。 junit和mockito就不要多讲了,都是java单元测试最基本的框架。在说roboletric之前,得先说一下powerMock,mockito无法mock static方法,而powermock则解决了这个问题。所以powermock和mockito配合使用,基本就可以覆盖绝大部分情况。不过由于powermock和mockito是两个团队实现的,经常出现版本不兼容的情况,建议直接使用powermock内部引用的mockito,这样就不会冲突了。 贴上地址: 在使用框架时,注意对应版本。页面中的第一句话: 我使用的完整配置如下: 原本使用powermock的版本是1.7.X,发现使用的过程中各种报错,还是使用了官方的1.6.6版本,不知道这两个团队什么时候兼容能做的很完善。 附上使用BaseTest: @Config(constants = BuildConfig.class , sdk = 21):原本想使用23的sdk版本,会有不兼容问题。 @PowerMockIgnore({“org.mockito.“, “org.robolectric.“, “android.“, “org.json.“, “sun.security.“, “javax.net.“}):根据我的理解:powermock类加载器忽略以上类的加载。 @PrepareForTest({CPSNetUtils.class, Common.class}):想mock static的方法,必须加上此注解。 基本配置如上,若上述配置都没问题了,就可以真正开始写单测了。目前Android端的框架使用的是google推荐的mvp框架,优缺点,网上有很多文章,就不在赘述。github地址如下: 不可否认的一点,使用mvp框架后单测实现会简单很多,极大程度减少了对view的测试。贴上一段业务测试代码: 细心的读者会发现在feedbackSuccessTest测试方法中,我开了个线程睡了半秒钟,这时候就要说到网络请求的单元测试了。网络交互是客户端最频繁的场景,而网络的不稳定,会导致客户端出现很多难以预知的情况,崩溃,闪退都有可能发生。所以对于网络请求的单测是重中之重。我使用的网络库是okhttp,而okhttp有一个很强大的功能:Interceptor。interceptor可以拦截网络请求,可以处理完后继续发送,也可以直接直接返回。废话不多说,上代码: 当然也可以模拟异常返回,404什么的都可以。另外okhttp使用的是建造者模式,客户端网络请求OkHttpClient都是一致的,故可以使用类似代码直接mock返回: 单测写完,总得看到点数据报告吧。这时候就需要覆盖率报告了。Android studio自带了jacoco 插件生成覆盖率报告。 行覆盖率:度量被测程序的每行代码是否被执行,判断标准行中是否至少有一个指令被执行。 类覆盖率:度量计算class类文件是否被执行。 分支覆盖率:度量if和switch语句的分支覆盖情况,计算一个方法里面的总分支数,确定执行和不执行的分支数量。 方法覆盖率:度量被测程序的方法执行情况,是否执行取决于方法中是否有至少一个指令被执行。 指令覆盖:计数单元是单个java二进制代码指令,指令覆盖率提供了代码是否被执行的信息,度量完全 独立源码格式。 圈复杂度:在(线性)组合中,计算在一个方法里面所有可能路径的最小数目,缺失的复杂度同样表示测试案例没有完全覆盖到这个模块。 jacoco的覆盖率报告分为两种: 方法也不尽相同。生成java层代码的任务在前面代码中已经贴出。 生成运行app期间执行的覆盖率报告代码如下: 以上代码并未测试过,点击执行测试后,会启动app,并在会生成.ec文件,通过解析.ec文件, 可以生成覆盖率报告。因为前面放弃esspreso时就说过放弃真机测试,所以此方法也未使用。 另外,中间遇到一个大坑,被坑了很久。就是jacoco和roboletric也有版本不兼容的问题。。。使用最新的jacoco的版本,发现生成的覆盖率报告始终为0 在stackoverflow中找了查了很久,最后在一个帖子里看到,在jacoco 0.7.3以上的版本使用roboletric就始终为0,尝试了多个版本,发现 0.7.1.201405082137 是OK的。千万不要随便升级版本,否则会出现异想不到的问题。。 好了,下面就看一下覆盖率报告: |