缓存中间件概述
Posted aidata
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了缓存中间件概述相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、缓存
是什么
在计算中,缓存是一个高速存储层,其中存储了数据子集,且通常是短暂性存储,这样日后再次请求此数据时,速度要比访问数据的主存储位置快。通过缓存,可以高效地重用之前的检索或计算的数据。
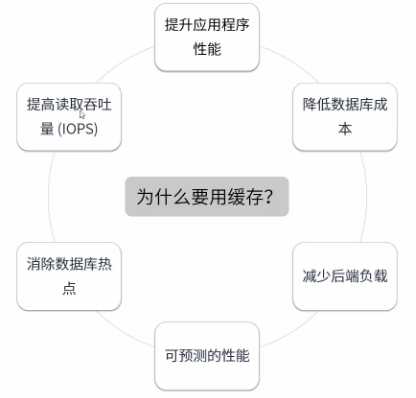
为什么用缓存
二、自研Java内存缓存
在Java应用中,对于访问频率高,更新少的数据,通常的方案是将这类数据加入缓存中。相对从数据库中读取来说,读缓存效率会有很大提升。
在集群环境下,常用的分布式缓存有Redis、Memcached等。但在某些业务场景下可能不需要去搭建一套复制的分布式缓存系统,在单机环境下,通常是会希望使用内部的缓存(LocalCache)。
基于JSR107规范自研
http://jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=107
1. 目标
为应用程序提供缓存Java对象的功能。
定义了一套通用的缓存概念和工具。
最小化开发人员使用缓存的学习成本。
最大化应用程序在使用不同缓存实现之间的可移植性。
支持进程内和分布式的缓存实现。2. 核心概念
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期,即Expiry Duration。
一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
基于ConcurrentHashMap实现数据缓存
import java.lang.ref.SoftReference; import java.util.*; import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; // 用map实现一个简单的缓存功能 public class MapCacheDemo { // 我使用了 ConcurrentHashMap,线程安全的要求。 //我使用SoftReference <Object> 作为映射值,因为软引用可以保证在抛出OutOfMemory之前,如果缺少内存,将删除引用的对象。 //在构造函数中,我创建了一个守护程序线程,每5秒扫描一次并清理过期的对象。 private static final int CLEAN_UP_PERIOD_IN_SEC = 5; private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, SoftReference<CacheObject>> cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public MapCacheDemo() { Thread cleanerThread = new Thread(() -> { // 5秒扫描并清理,lambda表达式 while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { try { Thread.sleep(CLEAN_UP_PERIOD_IN_SEC * 1000); cache.entrySet().removeIf(entry -> Optional.ofNullable(entry.getValue()).map(SoftReference::get).map(CacheObject::isExpired).orElse(false)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } }); cleanerThread.setDaemon(true); cleanerThread.start(); } public void add(String key, Object value, long periodInMillis) { if (key == null) { return; } if (value == null) { cache.remove(key); } else { long expiryTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + periodInMillis; cache.put(key, new SoftReference<>(new CacheObject(value, expiryTime))); } } public void remove(String key) { cache.remove(key); } public Object get(String key) { return Optional.ofNullable(cache.get(key)).map(SoftReference::get).filter(cacheObject -> !cacheObject.isExpired()).map(CacheObject::getValue).orElse(null); } public void clear() { cache.clear(); } public long size() { return cache.entrySet().stream().filter(entry -> Optional.ofNullable(entry.getValue()).map(SoftReference::get).map(cacheObject -> !cacheObject.isExpired()).orElse(false)).count(); } // 缓存对象value private static class CacheObject { private Object value; private long expiryTime; private CacheObject(Object value, long expiryTime) { this.value = value; this.expiryTime = expiryTime; } boolean isExpired() { return System.currentTimeMillis() > expiryTime; } public Object getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(Object value) { this.value = value; } } }
测试
public class MapCacheDemoTests { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MapCacheDemo mapCacheDemo = new MapCacheDemo(); mapCacheDemo.add("uid_10001", "{1}", 5 * 1000); mapCacheDemo.add("uid_10002", "{2}", 5 * 1000); mapCacheDemo.add("uid_10003", "{3}", 5 * 1000); System.out.println("从缓存中取出值:" + mapCacheDemo.get("uid_10001")); Thread.sleep(5000L); System.out.println("5秒钟过后"); System.out.println("从缓存中取出值:" + mapCacheDemo.get("uid_10001")); // 5秒后数据自动清除了~ } }
加了自动清除功能的map
不推荐
三、谷歌guava提供的缓存
Guava Cache是google guava中的一个内存缓存模块,用于将数据缓存到JVM内存中。实际项开发中经常将一些公关或者常用的数据缓存起来方便快速访问。


maven添加依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.study.cache</groupId> <artifactId>java-demo</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>javax.cache</groupId> <artifactId>cache-api</artifactId> <version>1.1.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>27.0.1-jre</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
主代码
import com.google.common.cache.*; import com.study.cache.java.pojo.User; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; // https://github.com/google/guava public class GuavaCacheDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException { //缓存接口这里是LoadingCache,LoadingCache在缓存项不存在时可以自动加载缓存 LoadingCache<String, User> userCache //CacheBuilder的构造函数是私有的,只能通过其静态方法newBuilder()来获得CacheBuilder的实例 = CacheBuilder.newBuilder() //设置并发级别为8,并发级别是指可以同时写缓存的线程数 .concurrencyLevel(8) //设置写缓存后8秒钟过期 .expireAfterWrite(8, TimeUnit.SECONDS) //设置写缓存后1秒钟刷新 .refreshAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) //设置缓存容器的初始容量为10 .initialCapacity(10) //设置缓存最大容量为100,超过100之后就会按照LRU最近虽少使用算法来移除缓存项 .maximumSize(100) //设置要统计缓存的命中率 .recordStats() //设置缓存的移除通知 .removalListener(new RemovalListener<Object, Object>() { @Override public void onRemoval(RemovalNotification<Object, Object> notification) { System.out.println(notification.getKey() + " 被移除了,原因: " + notification.getCause()); } }) //build方法中可以指定CacheLoader,在缓存不存在时通过CacheLoader的实现自动加载缓存 .build( new CacheLoader<String, User>() { @Override public User load(String key) throws Exception { System.out.println("缓存没有时,从数据库加载" + key); // TODO jdbc的代码~~忽略掉 return new User("tony" + key, key); } } ); // 第一次读取 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { User user = userCache.get("uid" + i); System.out.println(user); } // 第二次读取 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { User user = userCache.get("uid" + i); System.out.println(user); } System.out.println("cache stats:"); //最后打印缓存的命中率等 情况 System.out.println(userCache.stats().toString()); } }
pojo
import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private String userName; private String userId; public User(String userName, String userId) { this.userName = userName; this.userId = userId; } public String getUserId() { return userId; } public void setUserId(String userId) { this.userId = userId; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } @Override public String toString() { return userId + " --- " + userName; } }
以上是关于缓存中间件概述的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章