Kernel Methods for Deep Learning
Posted mtandhj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Kernel Methods for Deep Learning相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
@article{cho2009kernel,
title={Kernel Methods for Deep Learning},
author={Cho, Youngmin and Saul, Lawrence K},
pages={342--350},
year={2009}}
引
这篇文章介绍了一种新的核函数, 其启发来自于神经网络的运算.
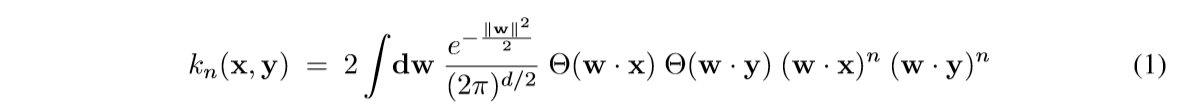
其中(Theta(z)=frac{1}{2}(1+mathrm{sign}(z))).
主要内容
主要性质, 公式(1)可以表示成:
[
k_n(mathbf{x}, mathbf{y}) = frac{1}{pi} |mathbf{x}|^n|mathbf{y}|^n J_n( heta).
ag{2}
]
其中:
[
J_n( heta) = (-1)^n (sin heta)^{2n+1} (frac{1}{sin heta} frac{partial}{partial heta})^n(frac{pi- heta}{sin heta}).
ag{3}
]
[
heta = cos^{-1} (frac{mathbf{x}cdot mathbf{y}}{|mathbf{x}| |mathbf{y}|}).
ag{4}
]
特别的:
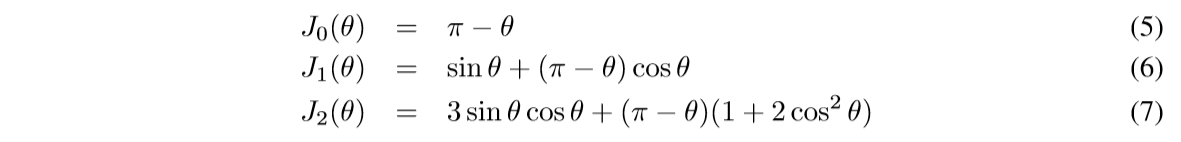
其证明如下:
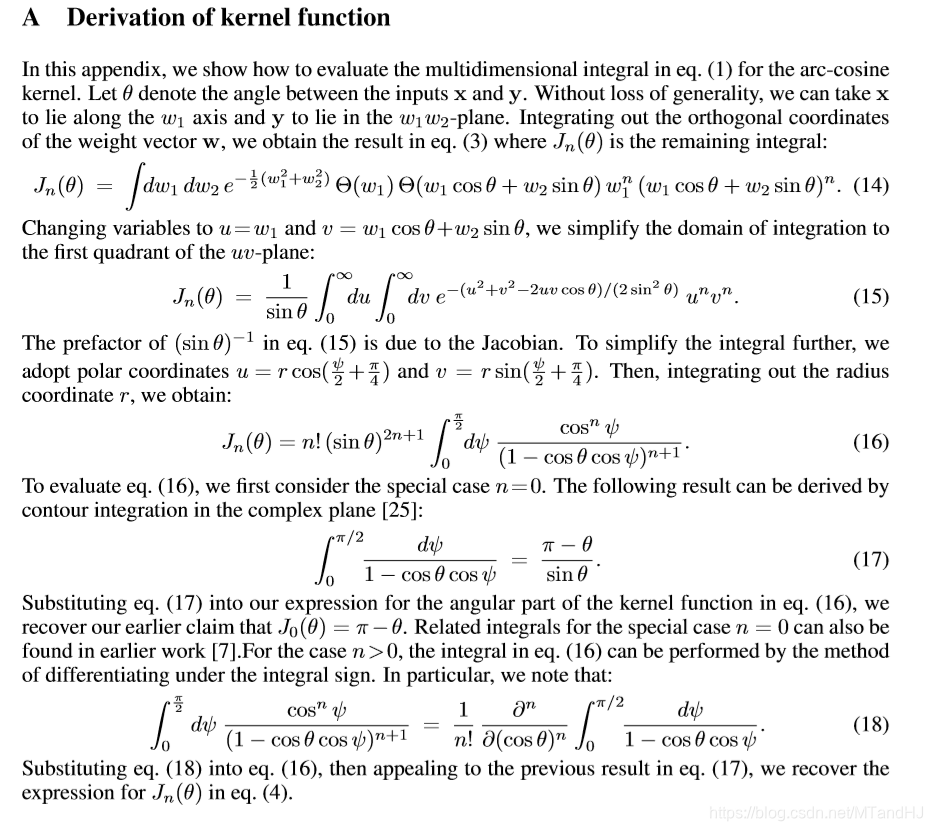
第(17)的证明我没有推, 因为 contour integration 暂时不了解.
细心的读者可能会发现, 最后的结果是(frac{partial^n}{partial(cos heta)^n}), 注意对于一个函数(f(cos heta)), 我们可以令(g( heta) = f(cos heta))则:
[
frac{partial f}{partial cos heta} = frac{partial{g}}{partial heta} frac{partial heta}{partial cos heta},
]
又
[
mathrm{d}cos heta =-sin heta mathrm{d} heta.
]
便得结论.
与深度学习的联系
如果我们把注意力集中在某一层, 假设输入为(mathbf{x}), 输出为:
[
mathbf{f}(mathbf{x}) = g(Wmathbf{x}) in mathbb{R}^m,
]
其中(g(z) = Theta(z) z^n)是激活函数, 不同的n有如下的表现:
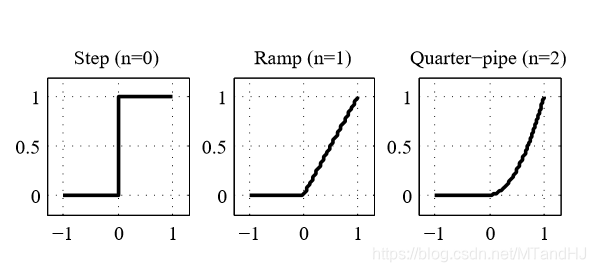
(n=1)便是我们熟悉的ReLU.
考虑俩个输入(mathbf{x},mathbf{y})所对应的输出(mathbf{f}(mathbf{x}),mathbf{f}(mathbf{y}))的内积:
[
mathbf{f}(mathbf{x}) cdot mathbf{f}(mathbf{y}) = sum_{i=1}^m Theta(mathbf{w}_i cdot mathbf{x}) Theta(mathbf{w}_i cdot mathbf{y}) (mathbf{w}_i cdot mathbf{x})^n (mathbf{w}_i cdot mathbf{y})^n
]
如果每个权重(W_{ij})都服从标准正态分布, 则:
[
lim_{m
ightarrow infty} frac{2}{m} mathbf{f} (mathbf{x}) cdot mathbf{f}(mathbf{x}) = k_n(mathbf{x}, mathbf{y}).
]
实验
实验失败了, 代码如下.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import NuSVC"""
Arc_cosine kernel
"""
class Arc_cosine:
def __init__(self, n=1):
self.n = n
self.own_kernel = self.kernels(n)
def kernel0(self, x, y):
norm_x = np.linalg.norm(x)
norm_y = np.linalg.norm(y)
cos_value = x @ y / (norm_x *
norm_y)
angle = np.arccos(cos_value)
return 1 - angle / np.pi
def kernel1(self, x, y):
norm_x = np.linalg.norm(x)
norm_y = np.linalg.norm(y)
cos_value = x @ y / (norm_x *
norm_y)
angle = np.arccos(cos_value)
sin_value = np.sin(angle)
return (norm_x * norm_y) ** self.n * (sin_value + (np.pi - angle) *
cos_value) / np.pi
def kernel2(self, x, y):
norm_x = np.linalg.norm(x)
norm_y = np.linalg.norm(y)
cos_value = x @ y / (norm_x *
norm_y)
angle = np.arccos(cos_value)
sin_value = np.sin(angle)
return (norm_x * norm_y) ** self.n * 3 * sin_value * cos_value + (np.pi - angle) * (1 + 2 * cos_value ** 2)
def kernels(self, n):
if n is 0:
return self.kernel0
elif n is 1:
return self.kernel1
elif n is 2:
return self.kernel2
else:
raise ValueError("No such kernel, n should be "
"0, 1 or 2")
def kernel(self, X, Y):
m = X.shape[0]
n = Y.shape[0]
C = np.zeros((m, n))
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
C[i, j] = self.own_kernel(
X[i], Y[j]
)
return C
def __call__(self, X, Y):
return self.kernel(X, Y)
在俩个数据上进行SVM, 数据如下:
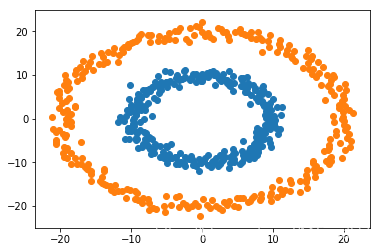
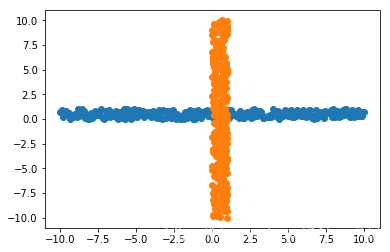
在SVM上跑:
'''
#生成圈圈数据
def generate_data(circle, r1, r2, nums=300):
variance = 1
rs1 = np.random.randn(nums) * variance + r1
rs2 = np.random.randn(nums) * variance + r2
angles = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, nums)
data1 = (rs1 * np.sin(angles) + circle[0],
rs1 * np.cos(angles) + circle[1])
data2 = (rs2 * np.sin(angles) + circle[0],
rs2 * np.cos(angles) + circle[1])
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'x':data1[0], 'y': data1[1],
'label':np.ones(nums)})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'x':data2[0], 'y': data2[1],
'label':-np.ones(nums)})
return df1, df2
'''
#生成十字数据
def generate_data(left, right, down, up,
circle=(0., 0.), nums=300):
variance = 1
y1 = np.random.rand(nums) * variance + circle[1]
x2 = np.random.rand(nums) * variance + circle[0]
x1 = np.linspace(left, right, nums)
y2 = np.linspace(down, up, nums)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(
{'x': x1,
'y': y1,
'label':np.ones_like(x1)}
)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(
{'x': x2,
'y': y2,
'label':-np.ones_like(x2)}
)
return df1, df2
def pre_test(left, right, func, nums=100):
x1, y1 = left
x2, y2 = right
x = np.linspace(x1, x2, nums)
y = np.linspace(y1, y2, nums)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y)
m, n = X.shape
Z = func(np.vstack((X.reshape(1, -1),
Y.reshape(1, -1))).T).reshape(m, n)
return X, Y, Z
df1, df2 = generate_data(-10, 10, -10, 10)
df = df1.append(df2)
classifer2 = NuSVC(kernel=Arc_cosine(n=1))
classifer2.fit(df.iloc[:, :2], df['label'])
X, Y, Z = pre_test((-10, -10), (10, 10), classifer2.predict)
plt.contourf(X, Y, Z)
plt.show()预测结果均为:
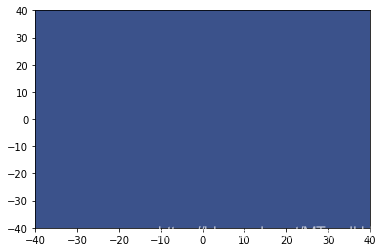
而在一般的RBF上, 结果都是很好的:

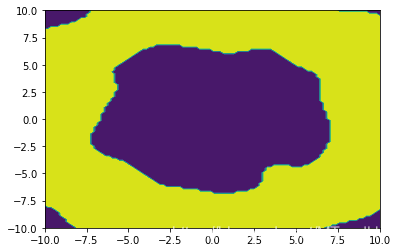
在多项式核上也ok:

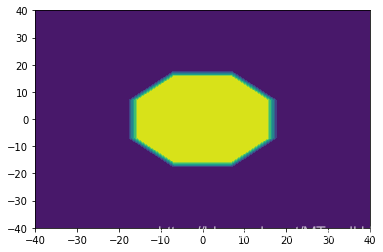
如果有人能发现代码中的错误,请务必指正.
以上是关于Kernel Methods for Deep Learning的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章