用TetGen对圆柱组合体进行网格剖分
Posted jessica216
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了用TetGen对圆柱组合体进行网格剖分相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
TetGen 是一款网格剖分的软件,可以生成高质量的非结构四面体网格。他可以编译生成可执行文件后作为一个独立的软件通过命令行调用,或者嵌入其他程序之中。它支持的输入文件格式有很多,如 .poly ,.smesh ,.node 文件,我习惯采用的是 .poly 文件作为输入文件。tetgen使用手册里只给出了立方体.poly文件的示例,如果想生成一个圆柱体,或者多个圆柱组合体的 .poly 文件就没有参考的例子了,只好自己动手丰衣足食。
圆柱体构造的主要思想在于用多边形逼近圆,所以文中的python代码也适合用于生成多边形网格。
生成一个单独的圆柱体:
#generate only one cylinder import os import sys import time import math def main(argv): cputime_start = time.clock() cylinder_r = float(argv[1]) #the radius of the cylinder cylinder_h = float(argv[2]) #the height of the cylinder print ‘=================================================‘ #print ‘* The box mesh generation *‘ print ‘-------------------------------------------------‘ print ‘The radius of the cylinder is %0.3f‘ % cylinder_r print ‘The height of the cylinder is %0.3f‘ % cylinder_h boxname = ‘cylinder‘ + ‘-‘ + str(cylinder_r) + ‘-‘ + str(cylinder_h) + ‘.poly‘ boxf = open(boxname,‘w‘) theta = math.pi/64 #use a polygon to approximat a circle nodenum = 256 nodenum_half = 128 #save the information of nodes node = [[0 for col in range(4)] for row in range(nodenum)] for i in range(0,nodenum): node[i] = [i+1,0,0,0] for i in range(0, nodenum_half): node[i][1:] = [cylinder_r * math.cos(i * theta), cylinder_r * math.sin(i * theta), 0] for i in range(nodenum_half, nodenum): node[i][1:] = [cylinder_r * math.cos(i * theta), cylinder_r * math.sin(i * theta), cylinder_h] #save the information of facets facenum = nodenum_half + 2 # sides & top facet & bottom facet faceAll = [[0 for col in range(6)] for row in range(facenum-2)] for i in range(0, facenum-3): faceAll[i] = [4, i+1, i+2, i+2+nodenum_half, i+1+nodenum_half, 4] faceAll[facenum-3] = [4, facenum-2, 1, nodenum_half + 1, nodenum, 4] face = [[0 for col in range(5)] for row in range(facenum-2)] faceMark = [[0 for col in range(3)] for row in range(facenum-2)] for i in range(0,facenum-2): face[i] = faceAll[i][0:5] faceMark[i] = [1,0,faceAll[i][-1]] meshsize = [0.1] # the size of mesh numVolumMark = 1 # one region SolventMark = 1 # the region mark is 1 region = [[0 for col in range(6)] for row in range(numVolumMark)] for i in range(0,len(region)): region[i] = [i+1,0,0,0,0,0] region[0][1] = (node[0][1] + node[nodenum_half/2+nodenum_half][1])/2 region[0][2] = (node[0][2] + node[nodenum_half/2+nodenum_half][2])/2 region[0][3] = (node[0][3] + node[nodenum_half/2+nodenum_half][3])/2 region[0][4] = SolventMark region[0][5] = meshsize[0] line = ‘# Part 1 - node list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# node count, 3 dim , no attribute, no boundary marker ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum) + ‘ ‘ + ‘3‘ + ‘ ‘ + ‘0‘ + ‘ ‘ + ‘0‘ + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) for i in range(0, nodenum): line = str(node[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(node[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(node[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(node[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# Part 2 - face list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(facenum) + ‘ ‘ + ‘1‘ + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# facet count, boundary marker ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the bottom facet is 1 line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(1) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_half) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(0, nodenum_half): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line += ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of sides is 4 for i in range(0,facenum-2): line = str(faceMark[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(face[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][4]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the top facet is 2 line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(2) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_half) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(0, nodenum_half): line += str(i +1+nodenum_half) + ‘ ‘ line += ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# Part 3 - hole list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘0‘ + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# Part 4 - region list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(numVolumMark) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) for i in range(0,len(region)): line = str(region[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][4]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][5]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) boxf.close() boxmeshfile = ‘cylinder_‘ + str(cylinder_r) + ‘_‘ + str(cylinder_h) + ‘-‘ + ‘refined1‘+ ‘.mesh‘ cmd = ‘./tetgen -pq1.414a0.1 >‘ + boxname os.system(cmd) cputime_end = time.clock() cputime = cputime_end - cputime_start print ‘The total CPU time is %0.3fs‘ % cputime print ‘=================================================‘ if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: main(sys.argv)
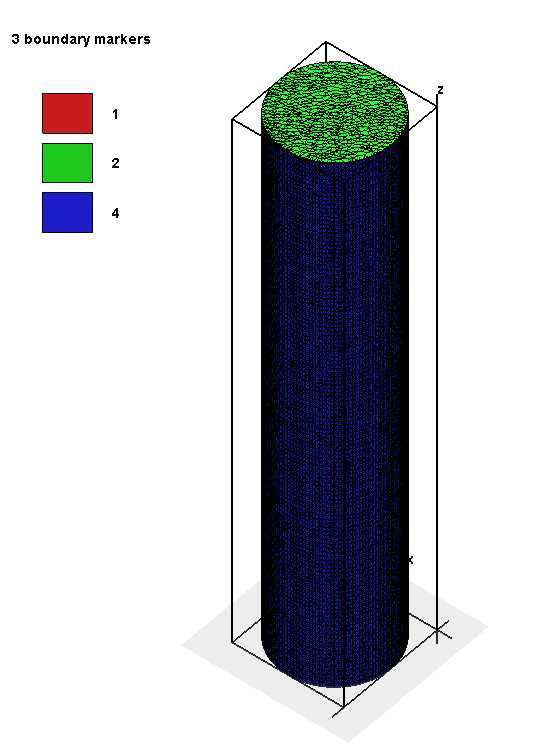
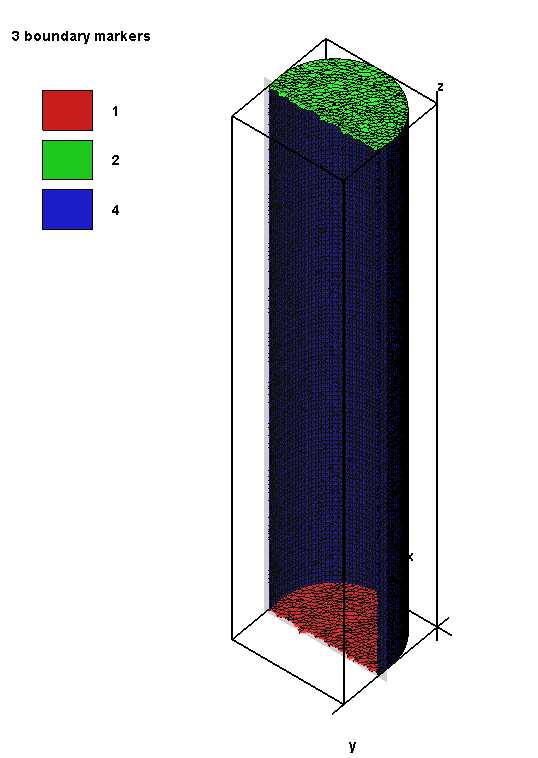
生成圆柱体的组合体:
#generate three cylinders import os import sys import time import math def main(argv): cputime_start = time.clock() #cylinder_r < bulk_r cylinder_r = float(argv[1]) #the radius of the cylinder cylinder_h = float(argv[2]) #the height of the cylinder bulk_r = float(argv[3]) #the radius of the bulk region bulk_h = float(argv[4]) #the height of the bulk region hole_flag = int(argv[5]) # 1 - there is a hole between the bulk region and the cylinder print ‘=================================================‘ #print ‘* The box mesh generation *‘ print ‘-------------------------------------------------‘ print ‘The radius of the cylinder is %0.3f‘ % cylinder_r print ‘The height of the cylinder is %0.3f‘ % cylinder_h print ‘The radius of the bulk region is %0.3f‘ % bulk_r print ‘The height of the bulk region is %0.3f‘ %bulk_h boxname = ‘cylinder‘ + ‘-‘ + str(cylinder_r) + ‘-‘ + str(cylinder_h) + ‘.poly‘ boxf = open(boxname,‘w‘) theta = math.pi/64 #use a polygon to approximat a circle nodenum_part = 128 nodenum = nodenum_part * 2 * 3 nodenum_half = nodenum_part * 3 #save the information of nodes node = [[0 for col in range(4)] for row in range(nodenum)] for i in range(0,nodenum): node[i] = [i+1,0,0,0] for i in range(0, nodenum_part): node[i][1:] = [bulk_r * math.cos(i * theta), bulk_r * math.sin(i * theta), 0] for i in range(nodenum_part, nodenum_part * 2): node[i][1:] = [bulk_r * math.cos(i * theta), bulk_r * math.sin(i * theta), bulk_h] for i in range(nodenum_part * 2, nodenum_part * 3): node[i][1:] = [cylinder_r * math.cos(i * theta), cylinder_r * math.sin(i * theta), bulk_h] for i in range(nodenum_part * 3, nodenum_part * 4): node[i][1:] = [cylinder_r * math.cos(i * theta), cylinder_r * math.sin(i * theta), cylinder_h + bulk_h] for i in range(nodenum_part * 4, nodenum_part * 5): node[i][1:] = [bulk_r * math.cos(i * theta), bulk_r * math.sin(i * theta), cylinder_h + bulk_h] for i in range(nodenum_part * 5, nodenum_part * 6): node[i][1:] = [bulk_r * math.cos(i * theta), bulk_r * math.sin(i * theta), cylinder_h + bulk_h + bulk_h] #save the information of facets if(hole_flag): facenum = nodenum_half + 4 # sides & top facet & bottom facet & interfaces between two regions else: facenum = nodenum_half + 6 faceAll = [[0 for col in range(6)] for row in range(nodenum_half)] # the boundary mark of sides of the bulk region is 3 for i in range(0, nodenum_part-1): faceAll[i] = [4, i+1, i+2, i+2+nodenum_part, i+1+nodenum_part, 3] faceAll[nodenum_part-1] = [4, nodenum_part, 1, nodenum_part + 1, nodenum_part * 2, 3] # the boundary mark of sides of the cylinder is 4 for i in range(nodenum_part, nodenum_part * 2-1): faceAll[i] = [4, i+1+nodenum_part, i+2+nodenum_part, i+2+2*nodenum_part, i+1+2*nodenum_part, 4] faceAll[nodenum_part*2-1] = [4, 3*nodenum_part, 2*nodenum_part+1, 3 * nodenum_part + 1, nodenum_part * 4, 4] # the boundary mark of sides of the bulk region is 3 for i in range(nodenum_part*2, nodenum_part * 3-1): faceAll[i] = [4, i+1+2*nodenum_part, i+2+2*nodenum_part, i+2+3*nodenum_part, i+1+3*nodenum_part, 3] faceAll[nodenum_part*3-1] = [4, 5*nodenum_part, 4*nodenum_part+1, 5 * nodenum_part + 1, nodenum_part * 6, 3] face = [[0 for col in range(5)] for row in range(nodenum_half)] faceMark = [[0 for col in range(3)] for row in range(nodenum_half)] for i in range(0,nodenum_half): face[i] = faceAll[i][0:5] faceMark[i] = [1,0,faceAll[i][-1]] meshsize = [10.0,1.0,10.0] # the size of mesh numVolumMark = 3 SolventMark = [1,1,1] # region marks of the three regions are all 1 region = [[0 for col in range(6)] for row in range(numVolumMark)] for i in range(0,len(region)): region[i] = [i+1,0,0,0,0,0] region[0][1] = (node[0][1] + node[nodenum_part/2+nodenum_part][1])/2 region[0][2] = (node[0][2] + node[nodenum_part/2+nodenum_part][2])/2 region[0][3] = (node[0][3] + node[nodenum_part/2+nodenum_part][3])/2 region[0][4] = SolventMark[0] region[0][5] = meshsize[0] region[1][1] = (node[2*nodenum_part][1] + node[nodenum_part/2+3*nodenum_part][1])/2 region[1][2] = (node[2*nodenum_part][2] + node[nodenum_part/2+3*nodenum_part][2])/2 region[1][3] = (node[2*nodenum_part][3] + node[nodenum_part/2+3*nodenum_part][3])/2 region[1][4] = SolventMark[1] region[1][5] = meshsize[1] region[2][1] = (node[4*nodenum_part][1] + node[nodenum_part/2+5*nodenum_part][1])/2 region[2][2] = (node[4*nodenum_part][2] + node[nodenum_part/2+5*nodenum_part][2])/2 region[2][3] = (node[4*nodenum_part][3] + node[nodenum_part/2+5*nodenum_part][3])/2 region[2][4] = SolventMark[2] region[2][5] = meshsize[2] line = ‘# Part 1 - node list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# node count, 3 dim , no attribute, no boundary marker ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum) + ‘ ‘ + ‘3‘ + ‘ ‘ + ‘0‘ + ‘ ‘ + ‘0‘ + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) for i in range(0, nodenum): line = str(node[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(node[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(node[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(node[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# Part 2 - face list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(facenum) + ‘ ‘ + ‘1‘ + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# facet count, boundary marker ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the bottom facet is 1 line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(1) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(0, nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line += ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of sides of the bulk region is 3 for i in range(0,nodenum_part): line = str(faceMark[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(face[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][4]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the interface is 5 line = str(2) + ‘ ‘ + str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(5) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(nodenum_part, 2*nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line +=‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(2*nodenum_part, 3*nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line +=‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(bulk_h) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the facet on the hole is 6 if(hole_flag==0): line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(6) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(2*nodenum_part, 3*nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line +=‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of sides of the cylinder is 4 for i in range(nodenum_part,2*nodenum_part): line = str(faceMark[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(face[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][4]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the interface is 5 line = str(2) + ‘ ‘ + str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(5) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(4*nodenum_part, 5*nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line +=‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(3*nodenum_part, 4*nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line +=‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(bulk_h+cylinder_h) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the facet on the hole is 6 if(hole_flag==0): line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(6) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(3*nodenum_part, 4*nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line +=‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of sides of the bulk region is 3 for i in range(2*nodenum_part,3*nodenum_part): line = str(faceMark[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(faceMark[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(face[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ + str(face[i][4]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) # the boundary mark of the top facet is 2 line = str(1) + ‘ ‘ + str(0) + ‘ ‘ + str(2) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(nodenum_part) + ‘ ‘ for i in range(5*nodenum_part, 6*nodenum_part): line += str(i+1) + ‘ ‘ line +=‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# Part 3 - hole list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘0‘ + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) line = ‘# Part 4 - region list ‘ boxf.write(line) line = str(numVolumMark) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) for i in range(0,len(region)): line = str(region[i][0]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][1]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][2]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][3]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][4]) + ‘ ‘ + str(region[i][5]) + ‘ ‘ boxf.write(line) boxf.close() #boxmeshfile = ‘box_analytic‘ + ‘-‘+ str(boxWidth) + ‘-‘+ str(boxLength) + ‘-‘ + str(boxHeight) + ‘-‘ + str(meshsize[0]) + ‘.mesh‘ boxmeshfile = ‘cylinder_reservoir_‘ + str(cylinder_r) + ‘_‘ + str(cylinder_h) + ‘-‘ + ‘refine‘+ ‘.mesh‘ cmd = ‘./tetgen2medit ‘ + boxname + ‘ ‘ + ‘-pq1.414a0.1 >‘ + boxmeshfile os.system(cmd) cputime_end = time.clock() cputime = cputime_end - cputime_start print ‘The total CPU time is %0.3fs‘ % cputime print ‘=================================================‘ if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: main(sys.argv)
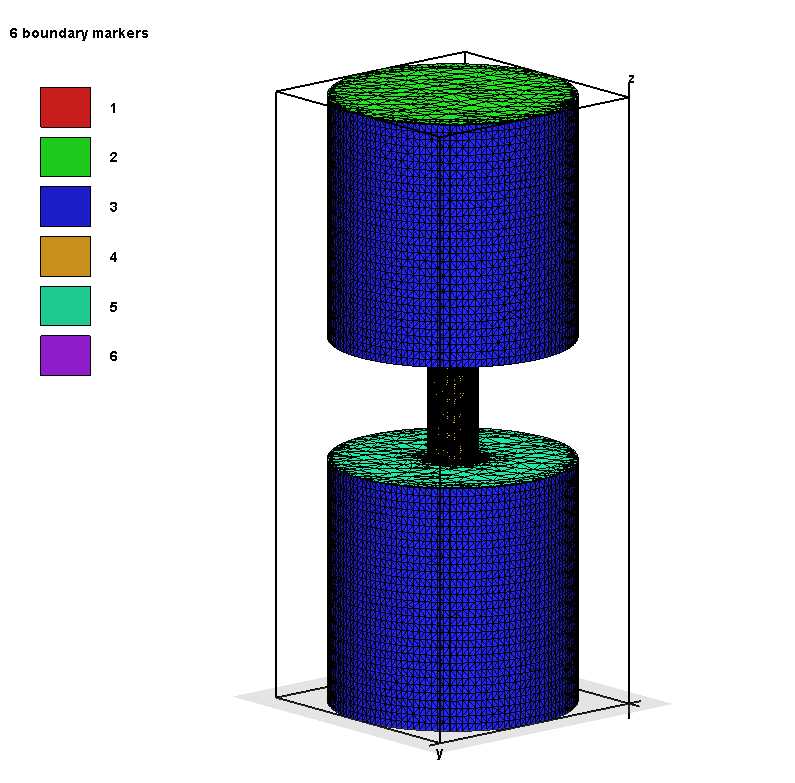
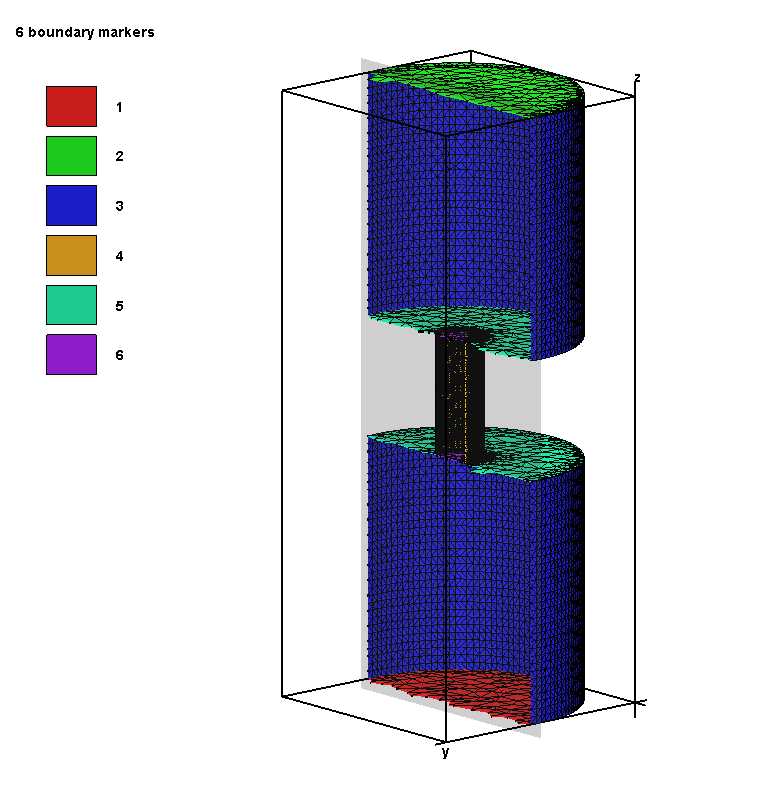
下图中中间圆柱没有上下两个面。
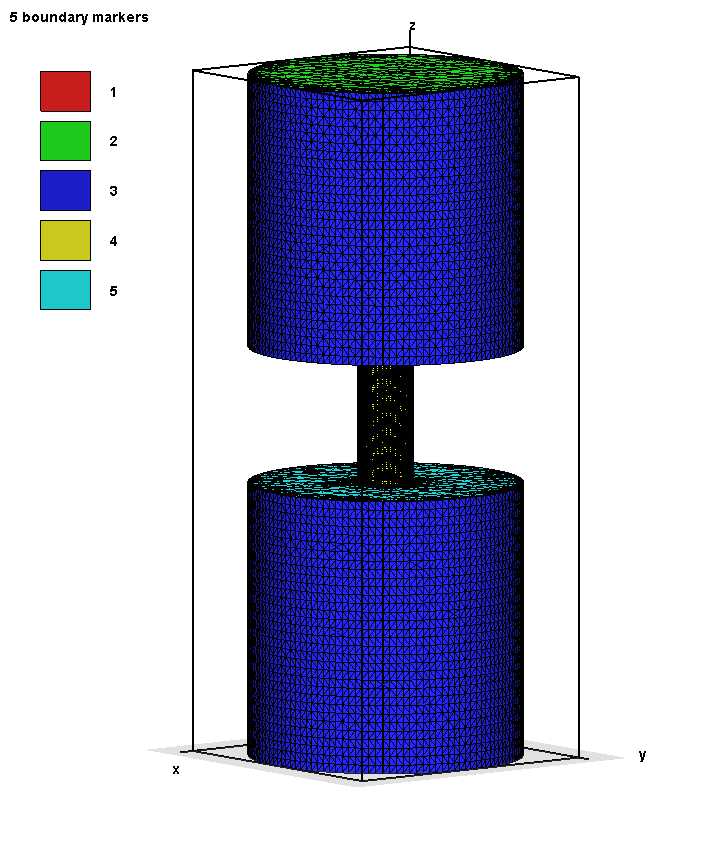
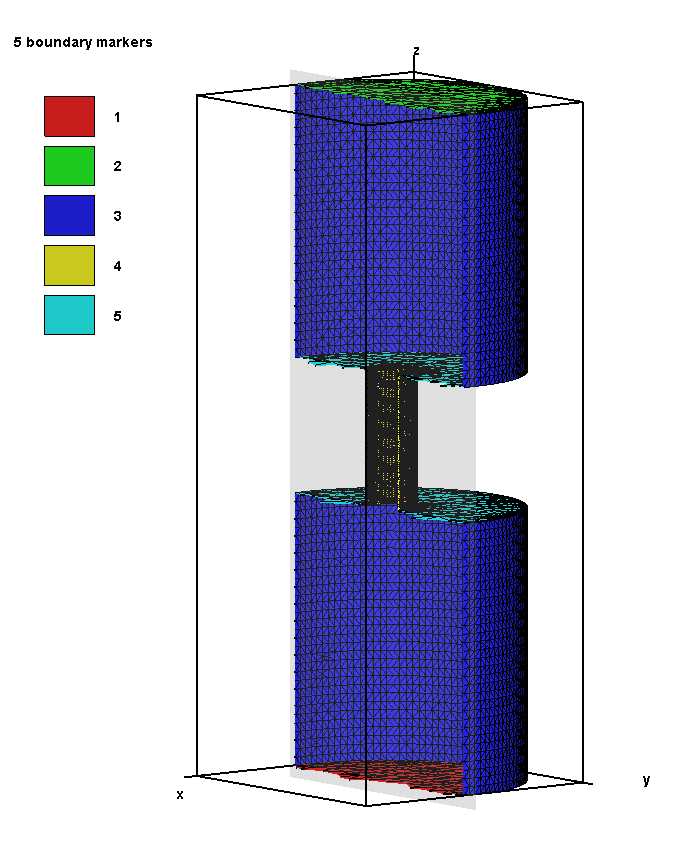
下图中中间圆柱没有两个面,标记为6。
以上是关于用TetGen对圆柱组合体进行网格剖分的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章