LRU算法与增强
Posted gggong
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LRU算法与增强相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
概要
本文的想法来自于本人学习mysql时的一个知识点:MySQL Innodb引擎中对缓冲区的处理。虽然没有仔细研究其源码实现,但其设计仍然启发了我。
本文针对LRU存在的问题,思考一种增强算法来避免或降低缓存污染,主要办法是对原始LRU空间划分出young与old两段区域 ,通过命中数(或block时间)来控制,并用一个0.37的百分比系数规定old的大小。
内容分以下几小节,实现代码为Java:
1.LRU基本概念
2.LRU存在问题与LRUG设计
3.LRUG详细说明
4.完整示例代码
1.LRU基本概念
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据。常用于一些缓冲区置换,页面置换等处理。
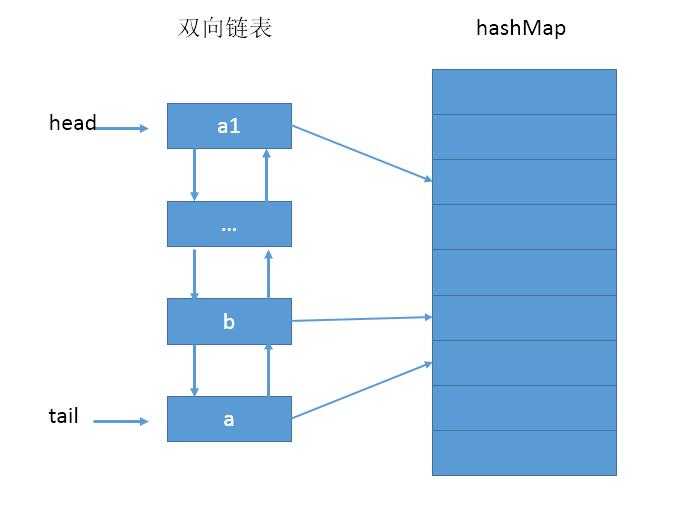
一个典型的双向链表+HashMap的LRU如下:
2.LRU存在问题与LRUG设计
LRU的问题是无法回避突发性的热噪数据,造成缓存数据的污染。对此有些LRU的变种,如LRU-K、2Q、MQ等,通过维护两个或多个队列来控制缓存数据的更新淘汰。我把本文讨论的算法叫LRUG,仅是我写代码时随便想的一个名字。
LRUG使用HashMap和双向链表,没有其他的维护队列,而是在双向链表上划分young,old区域,young段在old段之前,有新数据时不会马上插入到young段,而是先放入old段,若该数据持续命中,次数超过一定数量(也可以是锁定一段时间)后再进行插入首部的动作。两段以37%为界,即满载后old段的大小最多占总容量的37%。(图1)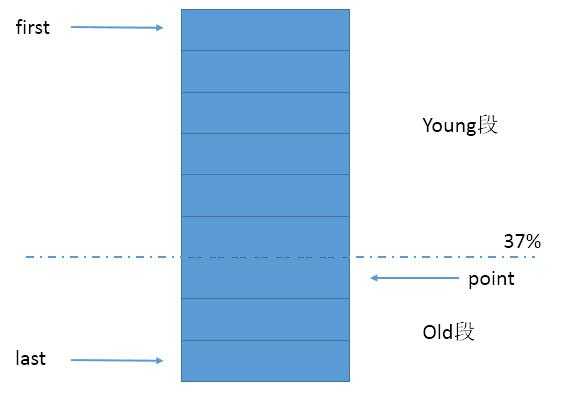
(图1)
3.LRUG详细说明
3.1首先给出双向链表的节点结构,其中hitNum是命中次数:
private static class Node<K,V>{
int hitNum;
K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> prev;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(K key,V value){
this.key=key;
this.value=value;
hitNum=0;
}
}
3.2在加载阶段,数据以先后顺序加入链表,半满载时,young段已满,新数据以插入方式加入到old段,如图2所示。注意半满载时,也可能有madeYoung操作,把old区的数据提到young头。
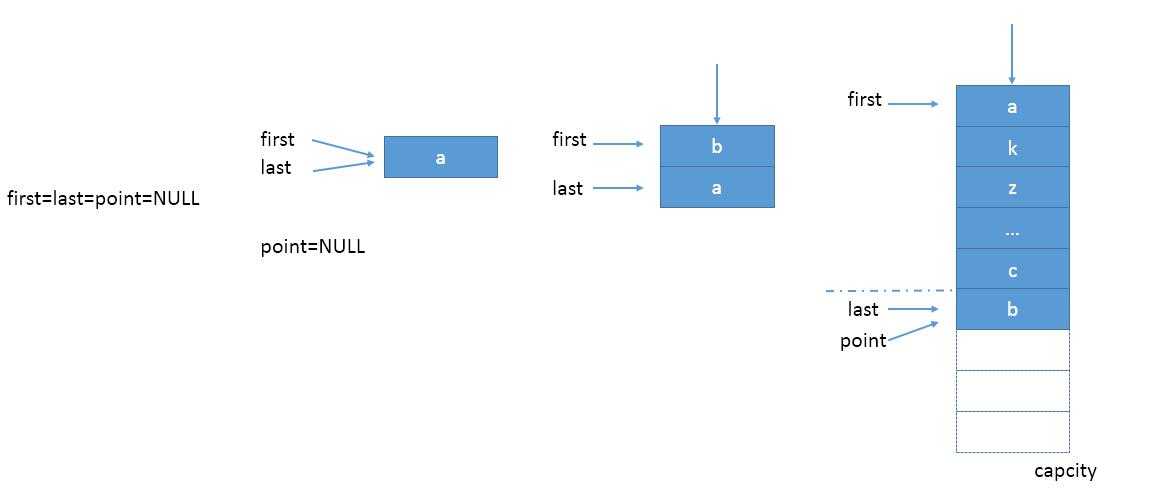
(图2)
public void put(K key,V value){
Node<K,V> node=caches.get(key);
if(node==null){
if(caches.size()>=capcity){
caches.remove(last.key);
removeLast();
}
node=new Node(key,value);
if(caches.size()>=pointBorder){
madeOld(node);
}else{
madeYoung(node);
}
}else {
node.value=value;
if(++node.hitNum>BLOCK_HIT_NUM){
madeYoung(node);
}
}
caches.put(key,node);
}
3.3当数据命中时,如果位于young区,命中数+1后进行常规的madeYoung操作,把该项提到链表首部。如图3
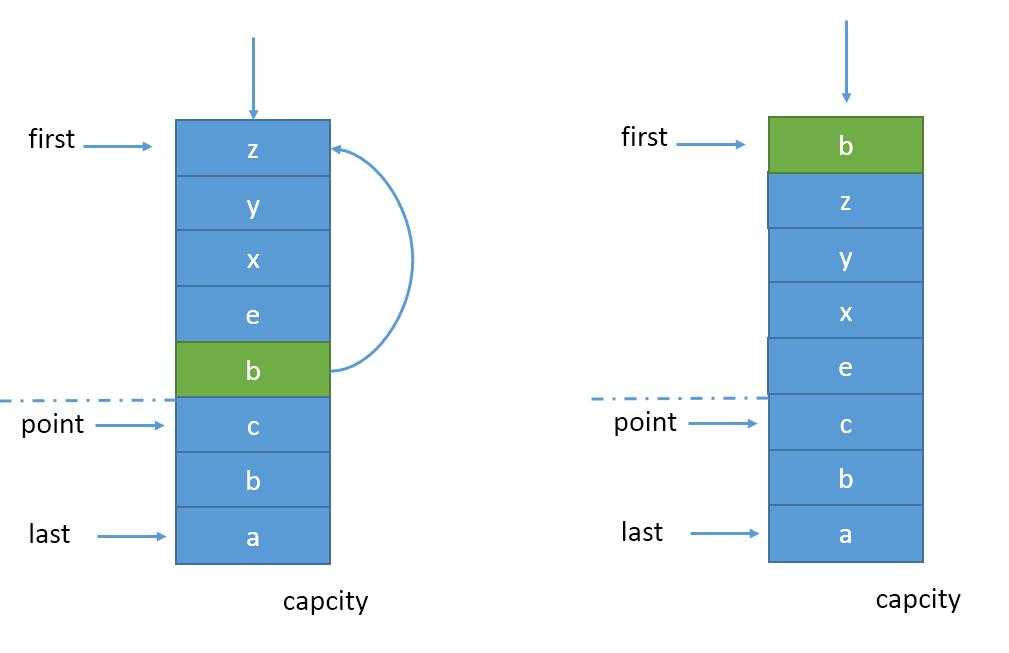
(图3)
如果命中项位于old区,对命中数+1后与BLOCK_HIT_NUM设置的值做判断,超过设定值说明该项数据可能不是突发数据,进行madeYoung操作提到链表首部,否则不做处理。
特别的,如果命中项正好是point,则point应该往后退一项,指向原point的下一项,此时young区膨胀了一项,而old区缩小了一项。极端情况下,ponit项持续被命中并进行madeYoung,point不断后退直到尾巴,此时young区占有100%容量,而old区为0,设置point指向last,意味着新数据项加入时,淘汰掉young区的末尾,而新数据项放在末尾成为old区。如图4
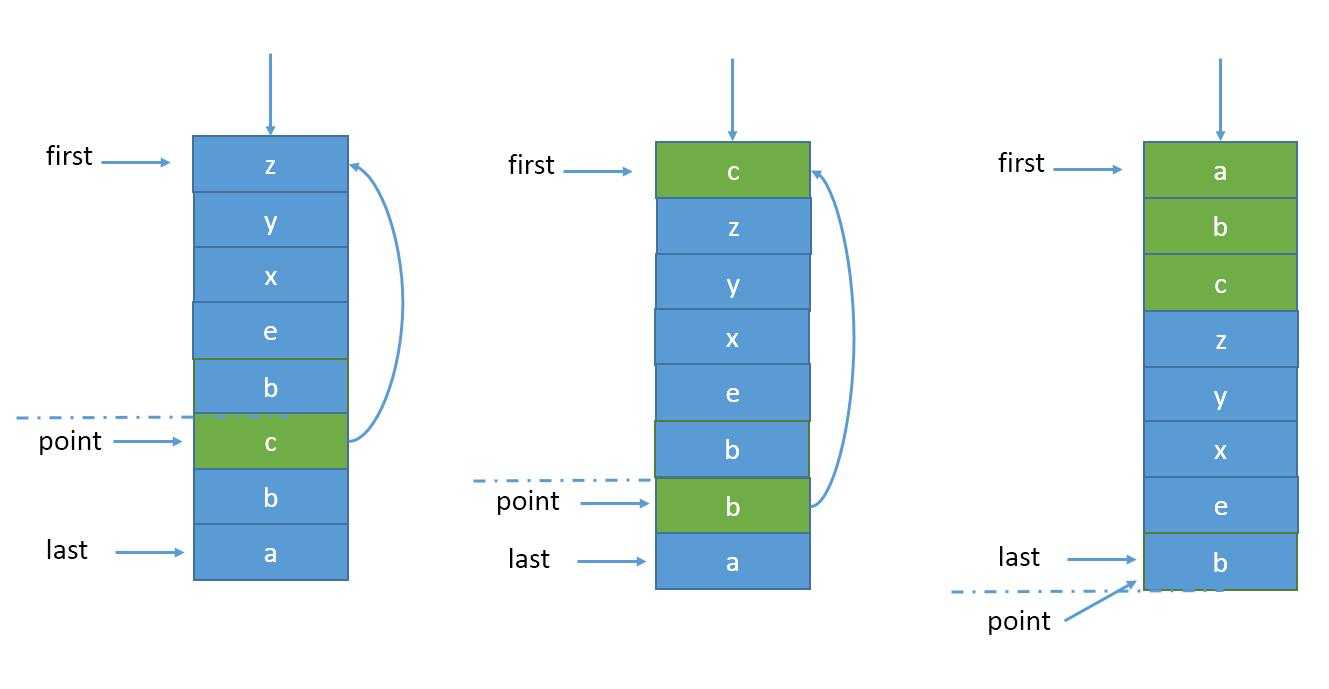
(图4)
public void madeYoung(Node node){
if(first==node){
return;
}
if(node==point){
point=node.next;
if(point==null) {
point=last;
}
}
if(node.next!=null){
node.next.prev=node.prev;
}
if(node.prev!=null){
node.prev.next=node.next;
}
if(node==last){
last=node.prev;
}
if(first==null||last==null){
first=last=node;
point=null;
return;
}
node.next=first;
first.prev=node;
first=node;
}
public void madeOld(Node node){
if(point.prev!=null){
point.prev.next=node;
node.prev=point.prev;
}
if(point.next!=null){
node.next=point.next;
point.next.prev=node;
}
point=node;
}
3.4需要一个清理的方法。也可以设置一些监测方法,如一段时间内的命中数(监测命中率)等,这与本篇主要内容无关就不写在这了。
public void removeLast(){
if(last!=null){
if(last==point) {
point=null;
}
last=last.prev;
if(last==null) {
first=null;
}else{
last.next=null;
}
}
}
4.示例代码
主要代码如下,时间仓促,可能一些地方会考虑不周,读者如发现,欢迎指出。
package com.company;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LRUNum<K,V> {
private HashMap<K,Node> caches;
private Node first;
private Node last;
private Node point;
private int size;
private int capcity;
private static final int BLOCK_HIT_NUM=2;
private static final float MID_POINT=0.37f;
private int pointBorder;
public LRUNum(int capcity){
this.size=0;
this.capcity=capcity;
this.caches=new HashMap<K,Node>(capcity);
this.pointBorder=this.capcity-(int)(this.capcity*this.MID_POINT);
}
public void put(K key,V value){
Node<K,V> node=caches.get(key);
if(node==null){
if(caches.size()>=capcity){
caches.remove(last.key);
removeLast();
}
node=new Node(key,value);
if(caches.size()>=pointBorder){
madeOld(node);
}else{
madeYoung(node);
}
}else {
node.value=value;
if(++node.hitNum>BLOCK_HIT_NUM){
madeYoung(node);
}
}
caches.put(key,node);
}
public V get(K key){
Node<K,V> node =caches.get(key);
if(node==null){
return null;
}
if(++node.hitNum>BLOCK_HIT_NUM){
madeYoung(node);
}
return node.value;
}
public Object remove(K key){
Node<K,V> node =caches.get(key);
if(node!=null){
if(node.prev!=null){
node.prev.next=node.next;
}
if(node.next!=null){
node.next.prev=node.prev;
}
if(node==first){
first=node.next;
}
if(node==last){
last=node.prev;
}
}
return caches.remove(key);
}
public void removeLast(){
if(last!=null){
if(last==point) {
point=null;
}
last=last.prev;
if(last==null) {
first=null;
}else{
last.next=null;
}
}
}
public void clear(){
first=null;
last=null;
point=null;
caches.clear();
}
public void madeYoung(Node node){
if(first==node){
return;
}
if(node==point){
point=node.next;
if(point==null) {
point=last;
}
}
if(node.next!=null){
node.next.prev=node.prev;
}
if(node.prev!=null){
node.prev.next=node.next;
}
if(node==last){
last=node.prev;
}
if(first==null||last==null){
first=last=node;
point=null;
return;
}
node.next=first;
first.prev=node;
first=node;
}
public void madeOld(Node node){
if(point.prev!=null){
point.prev.next=node;
node.prev=point.prev;
}
if(point.next!=null){
node.next=point.next;
point.next.prev=node;
}
point=node;
}
private static class Node<K,V>{
int hitNum;
K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> prev;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(K key,V value){
this.key=key;
this.value=value;
hitNum=0;
}
}
}
以上是关于LRU算法与增强的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章