ArrayList
Posted laurarararararara
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ArrayList相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ArrayList实现类:ArrayList是List接口的实现类
基本特点:
数据插入有序
可以存储null值
数据可以重复
底层的数据结构是数组
数据插入有序
可以存储null值
数据可以重复
底层的数据结构是数组
ArrayList的继承关系:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
继承AbstractList类,实现List接口;
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E>
AbstractLiST继承AbstractCollection类,实现List接口;
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E>
AbstractCollection实现Collection接口;
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E>
Collection继承Iterable类;
public interface Iterable<T> { /** * Returns an iterator over elements of type {@code T}. * * @return an Iterator. */ Iterator<T> iterator(); }
Iterable是一个接口;
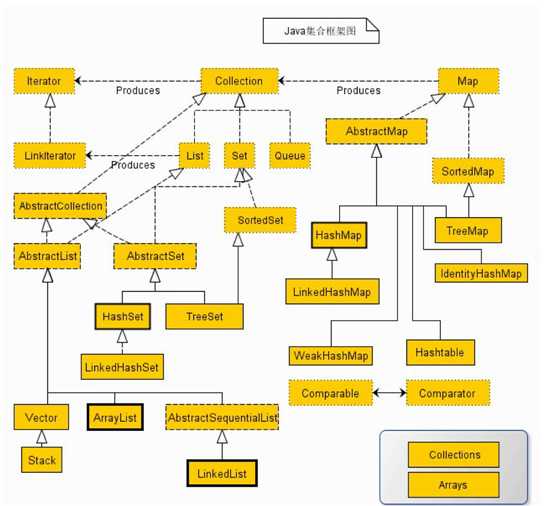
相关属性:
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;//默认容量是10 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any * empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA * will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access /** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */ private int size;
transient关键字:Java语言的关键字,变量修饰符,如果用transient声明一个实例变量,当对象存储时,它的值不需要维持。换句话来说就是,用transient关键字标记的成员变量不参与序列化过程。
作用:
Java的serialization提供了一种持久化对象实例的机制。当持久化对象时,可能有一个特殊的对象数据成员,我们不想用serialization机制来保存它。为了在一个特定对象的一个域上关闭serialization,可以在这个域前加上关键字transient。当一个对象被序列化的时候,transient型变量的值不包括在序列化的表示中,然而非transient型的变量是被包括进去的。
Java的serialization提供了一种持久化对象实例的机制。当持久化对象时,可能有一个特殊的对象数据成员,我们不想用serialization机制来保存它。为了在一个特定对象的一个域上关闭serialization,可以在这个域前加上关键字transient。当一个对象被序列化的时候,transient型变量的值不包括在序列化的表示中,然而非transient型的变量是被包括进去的。
扩容机制: 数组的扩容是按照原数组长度的1.5倍扩容
/** * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. * * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //>>1 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
得到该元素:
/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }
清空数组:clear
public void clear() { modCount++; // clear to let GC do its work垃圾回收器 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; }
删除:因为ArrayList中可以存储值为null的元素,所以需要对null进行特殊判断
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; }
fastRemove的实现:主要将index+1号以后的元素移动到index号元素
private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work }
arraycopy源码:
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
1.自定义实现ArrayList
package Lesson1; import java.util.Arrays; /** * 问题:my.size()方法不等于elementData-1 elementData.length等于构造函数初始化时,传入的capacity, * 所以mysize()方法与elementData.length无关。所以getSize()方法的返回值可以直接为size * 自定义实现ArrayList * @param <T> */ public class ArrayListMyself <T>{ private Object[] elementData;//定义了一个数组 private int size; public ArrayListMyself(int capacity){ elementData=(T[])new Object[capacity]; } public ArrayListMyself(){ this(2); } /** * 添加值为value的元素 */ public boolean add(T value) { if(full()){ Arrays.copyOf(elementData,elementData.length*2); } this.elementData[this.size++]=value; return true; } public boolean full() { return this.elementData.length==this.getSize(); } /** * * @return直接返回长度size */ public int getSize(){ return size; } /** * 获取index号元素 ,返回元素的值 */ public T get(int index) { if(index<0 || index>size){ throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("参数异常"); } for (int i=0;i<elementData.length;i++){ if(i==index){ return (T)elementData[i]; } } return null; } /** * 删除index号元素 */ public boolean remove(int index) { if(index<0 ||index>size){ return false; }else { for (int i=index;i<size-1;i++){ elementData[i]=elementData[i+1]; } size--; } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayListMyself my=new ArrayListMyself(); my.add(4); my.add(5); System.out.println(my.size);//2 System.out.println(my.elementData.length);//2 System.out.println(my.remove(1));//true System.out.println(my.getSize());//1 System.out.println(my.remove(0));//true System.out.println(my.size);//0 if (my.size!=0){ for (int i = 0; i <my.size; i++) { System.out.print(my.get(i)+" "); } }else { System.out.println("当前数组为空!"); } } }
或者可以自己写一个tooString方法,实现数组的打印:
public String tooString(){ StringBuilder s=new StringBuilder(); if(this.size==0){ return null; } else { for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) { s = s.append(get(i) + " "); } return s.toString(); } }
可以封装一个方法进行参数的检查,在添加或者删除的时候直接调用该方法:
(源码中给出了专门添加元素的方法rangeCheckForAdd)
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { if (index > size || index < 0) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }
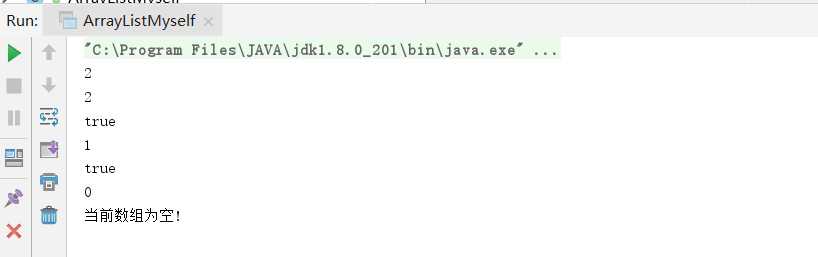
2.
以上是关于ArrayList的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章