BERT源码分析
Posted nxf-rabbit75
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了BERT源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、整体
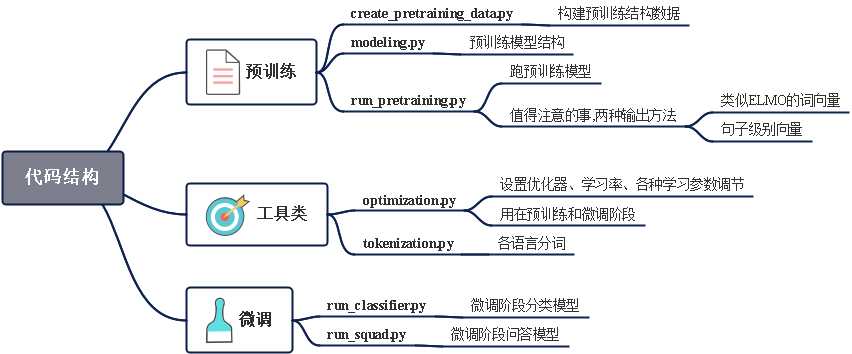
整个代码文件如下:
二、tensorflow基础
1.tf.expand_dims
作用:给定张量“ input”,此操作将在“ input”形状的尺寸索引“ axis”处插入尺寸为1的尺寸。 尺寸索引“轴”从零开始; 如果为“ axis”指定负数,则从末尾开始算起。
如果要将批次尺寸添加到单个元素,此操作很有用。 例如,如果您有一个形状为[[height,width,channels]`的图像,则可以将其与具有`expand_dims(image,0)`的1张图像一起批处理,这将使形状为[[1,height ,width,channels]。
# ‘t‘ is a tensor of shape [2]
tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t, 0)) # [1, 2]
tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t, 1)) # [2, 1]
tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t, -1)) # [2, 1]
# ‘t2‘ is a tensor of shape [2, 3, 5]
tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t2, 0)) # [1, 2, 3, 5]
tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t2, 2)) # [2, 3, 1, 5]
tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t2, 3)) # [2, 3, 5, 1]
```
This operation requires that:
`-1-input.dims() <= dim <= input.dims()`
This operation is related to `squeeze()`, which removes dimensions of
size 1.
Args:
input: A `Tensor`.
axis: 0-D (scalar). Specifies the dimension index at which to
expand the shape of `input`. Must be in the range
`[-rank(input) - 1, rank(input)]`.
name: The name of the output `Tensor`.
dim: 0-D (scalar). Equivalent to `axis`, to be deprecated.
Returns:
A `Tensor` with the same data as `input`, but its shape has an additional
dimension of size 1 added.
Raises:
ValueError: if both `dim` and `axis` are specified.
bert中源码:
# 该函数默认输入的形状为【batch_size, seq_length, input_num】 # 如果输入为2D的【batch_size, seq_length】,则扩展到【batch_size, seq_length, 1】 if input_ids.shape.ndims == 2: input_ids = tf.expand_dims(input_ids, axis=[-1])
2.tf.reshape
reshape(tensor, shape, name=None)
作用:重塑张量。给定张量,此操作将返回与形状为shape的张量具有相同值的张量。 如果“形状”的一个分量为特殊值-1,则将计算该尺寸的大小,以使总大小保持恒定。 具体来说,[-1]的“形状”会展平为一维。 “形状”的至多一个分量可以为-1。 如果“ shape”为一维或更高,则该操作将返回一个形状为“ shape”的张量,其中填充了“ tensor”的值。 在这种情况下,“形状”所隐含的元素数量必须与“张量”中的元素数量相同。
举例:
For example:
```
# tensor ‘t‘ is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
# tensor ‘t‘ has shape [9]
reshape(t, [3, 3]) ==> [[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]]
# tensor ‘t‘ is [[[1, 1], [2, 2]],
# [[3, 3], [4, 4]]]
# tensor ‘t‘ has shape [2, 2, 2]
reshape(t, [2, 4]) ==> [[1, 1, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 4, 4]]
# tensor ‘t‘ is [[[1, 1, 1],
# [2, 2, 2]],
# [[3, 3, 3],
# [4, 4, 4]],
# [[5, 5, 5],
# [6, 6, 6]]]
# tensor ‘t‘ has shape [3, 2, 3]
# pass ‘[-1]‘ to flatten ‘t‘
reshape(t, [-1]) ==> [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6]
# -1 can also be used to infer the shape
# -1 is inferred to be 9:
reshape(t, [2, -1]) ==> [[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6]]
# -1 is inferred to be 2:
reshape(t, [-1, 9]) ==> [[1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3],
[4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6]]
# -1 is inferred to be 3:
reshape(t, [ 2, -1, 3]) ==> [[[1, 1, 1],
[2, 2, 2],
[3, 3, 3]],
[[4, 4, 4],
[5, 5, 5],
[6, 6, 6]]]
# tensor ‘t‘ is [7]
# shape `[]` reshapes to a scalar
reshape(t, []) ==> 7
```
Args:
tensor: A `Tensor`.
shape: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
Defines the shape of the output tensor.
name: A name for the operation (optional).
Returns:
A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
"""
bert中源码:
# If the input is a 2D tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length], we
# reshape to [batch_size, seq_length, 1].
if input_ids.shape.ndims == 2:
input_ids = tf.expand_dims(input_ids, axis=[-1])
embedding_table = tf.get_variable(
name=word_embedding_name,
shape=[vocab_size, embedding_size],
initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range))
flat_input_ids = tf.reshape(input_ids, [-1]) #【batch_size*seq_length*input_num】
3.tf.one_hot
one_hot(indices,depth,on_value=None,off_value=None,axis=None,dtype=None,name=None)
作用:返回一个单张量的张量。
- 索引在“索引”中表示的位置取值为“ on_value”,而所有其他位置取值为“ off_value”。
- “ on_value”和“ off_value”必须具有匹配的数据类型。如果还提供了dtype,则它们必须与dtype指定的数据类型相同。
- 如果未提供`on_value`,则其默认值为‘dtype‘为‘1‘。
- 如果未提供`off_value`,则默认为‘dtype‘类型的值‘0‘。
- 如果输入“索引”是等级“ N”,则输出将具有等级“ N + 1”。新轴是在尺寸轴上创建的(默认值:新轴附加在末尾)。
- 如果`indices`是标量,则输出形状将是`depth‘长度的向量。如果`indices`是具有`features`长度的向量,则输出形状为:如果轴== -1,特征x深度,如果轴== 0,则深度x特征
- 如果`indices`是形状为[[batch,features]]的矩阵(批次),则输出
- 形状将是:如果轴== -1,则批处理x特征x深度; 如果轴== 1,则批次x深度x特征;如果轴== 0,则深度x批x特征
- 如果未提供dtype,则如果传入一个或两个,则尝试采用on_value或off_value的数据类型。
- 提供了on_value,off_value或dtype,dtype的默认值为tf.float32。
注意:如果需要输出非数字数据类型(tf.string,tf.bool等),则必须将on_value和off_value都提供给one_hot。
参考文献:
以上是关于BERT源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章