分割数据集label转换为目标检测boundingbox
Posted smartweed
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了分割数据集label转换为目标检测boundingbox相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实现功能
将分割的label图转换为目标检测boundingbox标注文件(VOC格式)。
注:
1.分割样本里一张图片只有同一类别的多个目标。
2.转换为boundingbox标注通过连通域实现,所以重叠的目标处理不了,会标为1个。
数据集格式
其中,语义分割数据集格式如下:
原图片在JPEGImages文件夹中,命名格式为ImageID.jpg

Label图在labelimage文件夹中,命名格式为ImageID_classname.png

生成的boundingbox标注命名格式为ImageID.xml
XML标注格式
<annotation>
<folder>road_dataset</folder> #文件名
<filename>3425.jpg</filename> #原图片名
<path>D:
oad_datasetJPEGImages3425.jpg</path> #原图片地址
<source>
<database>Unknown</database>
</source>
<size> #图片尺寸
<width>512</width>
<height>512</height>
<depth>3</depth>
</size>
<segmented>0</segmented> #是否用于分割,0为否
<object> #目标
<name>butt</name> #类别名称
<pose>Unspecified</pose> #拍摄角度
<truncated>0</truncated> #是否被截断
<difficult>0</difficult> #是否为困难样本
<bndbox> #boundingbox坐标(左下、右上)
<xmin>327</xmin>
<ymin>38</ymin>
<xmax>394</xmax>
<ymax>69</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
<object> #多个目标
<name>Cigarette butts</name>
<pose>Unspecified</pose>
<truncated>0</truncated>
<difficult>0</difficult>
<bndbox>
<xmin>139</xmin>
<ymin>279</ymin>
<xmax>214</xmax>
<ymax>318</ymax>
</bndbox>
</object>
</annotation>
其中<pose> <truncated> <difficult> 全是默认值。
得到label图中的连通域
使用skimage的morphology, measure通过连通域得到每一副一幅图片上的目标数量和boundingbox。
import os import numpy as np from itertools import groupby from skimage import morphology,measure from PIL import Image from scipy import misc # 因为一张图片里只有一种类别的目标,所以label图标记只有黑白两色 rgbmask = np.array([[0,0,0],[255,255,255]],dtype=np.uint8) # 从label图得到 boundingbox 和图上连通域数量 object_num def getboundingbox(image): # mask.shape = [image.shape[0], image.shape[1], classnum] mask = np.zeros((image.shape[0], image.shape[1]), dtype=np.uint8) mask[np.where(np.all(image == rgbmask[1],axis=-1))[:2]] = 1 # 删掉小于10像素的目标 mask_without_small = morphology.remove_small_objects(mask,min_size=10,connectivity=2) # 连通域标记 label_image = measure.label(mask_without_small) #统计object个数 object_num = len(measure.regionprops(label_image)) boundingbox = list() for region in measure.regionprops(label_image): # 循环得到每一个连通域bbox boundingbox.append(region.bbox) return object_num, boundingbox
在label图片上显示boundingbox,查看结果:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.patches as patch # 输出成图片查看得到boundingbox效果 imagedir = r‘D: est_datasetlabelimage‘ if ~os.path.exists(r‘D: est_dataset est_getbbox‘): os.mkdir(r‘D: est_dataset est_getbbox‘) for root, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(imagedir)): for fname in sorted(fnames): imagepath = os.path.join(root, fname) image = misc.imread(imagepath) objectnum, bbox = getboundingbox(image) ImageID = fname.split(‘.‘)[0] fig,ax = plt.subplots(1) ax.imshow(image) for box in bbox: rect = patch.Rectangle((box[1], box[0]), box[3]-box[1], box[2]-box[0],edgecolor = ‘r‘, linewidth = 1,fill = False) ax.add_patch(rect) plt.savefig(‘D:/test_dataset/test_getbbox/‘+ImageID+‘.png‘)
输出图像为:
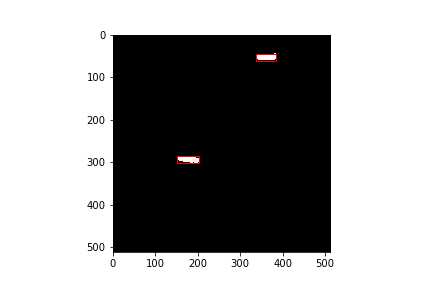
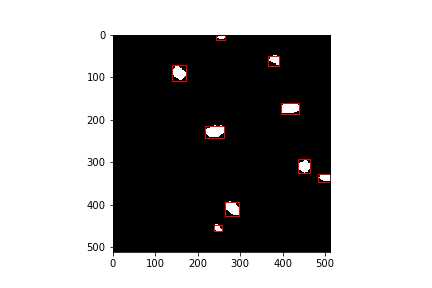
生成XML标注文件
createXMLlabel: 根据标注信息生成XML标注文件
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET def createXMLlabel(savedir,objectnum, bbox, classname, foldername=‘0‘,filename=‘0‘, path=‘0‘, database=‘road‘, width=‘400‘, height=‘600‘,depth=‘3‘, segmented=‘0‘, pose="Unspecified", truncated=‘0‘, difficult=‘0‘): # 创建根节点 root = ET.Element("annotation") # 创建子节点 folder_node = ET.Element("folder") folder_node.text = foldername # 将子节点数据添加到根节点 root.append(folder_node) file_node = ET.Element("filename") file_node.text = filename root.append(file_node) path_node = ET.Element("path") path_node.text = path root.append(path_node) source_node = ET.Element("source") # 也可以使用SubElement直接添加子节点 db_node = ET.SubElement(source_node, "database") db_node.text = database root.append(source_node) size_node = ET.Element("size") width_node = ET.SubElement(size_node, "width") height_node = ET.SubElement(size_node, "height") depth_node = ET.SubElement(size_node, "depth") width_node.text = width height_node.text = height depth_node.text = depth root.append(size_node) seg_node = ET.Element("segmented") seg_node.text = segmented root.append(seg_node) for i in range(objectnum): newEle = ET.Element("object") name = ET.Element("name") name.text = classname newEle.append(name) pose_node = ET.Element("pose") pose_node.text = pose newEle.append(pose_node) trunc = ET.Element("truncated") trunc.text = truncated newEle.append(trunc) dif = ET.Element("difficult") dif.text = difficult newEle.append(dif) boundingbox = ET.Element("bndbox") xmin = ET.SubElement(boundingbox, "xmin") ymin = ET.SubElement(boundingbox, "ymin") xmax = ET.SubElement(boundingbox, "xmax") ymax = ET.SubElement(boundingbox, "ymax") xmin.text = str(bbox[i][1]) ymin.text = str(bbox[i][0]) xmax.text = str(bbox[i][3]) ymax.text = str(bbox[i][2]) newEle.append(boundingbox) root.append(newEle) ImageID = filename.split(‘.‘)[0] # 创建elementtree对象,写入文件 tree = ET.ElementTree(root) tree.write(savedir + ‘/‘+ ImageID + ".xml")
imagedir = r‘D: est_datasetlabelimage‘ saveXMLdir = r‘D: est_datasetAnnotations‘ if os.path.exists(saveXMLdir) is False: os.mkdir(saveXMLdir) for root, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(imagedir)): for fname in sorted(fnames): labelpath = os.path.join(root, fname) labelimage = misc.imread(labelpath) # 得到label图上的boundingingbox和数量 objectnum, bbox = getboundingbox(labelimage) # label图 命名格式为 ImgeID_classname.png labelfilename = labelpath.split(‘‘)[-1] ImageID = labelfilename.split(‘.‘)[0].split(‘_‘)[0] classname = labelfilename.split(‘.‘)[0].split(‘_‘)[1] origin_image_name = ImageID +‘.jpg‘ # 一些图片信息 foldername = ‘test_dataset‘ path =‘‘.join(imagedir.split(‘‘)[:-1]) + ‘JPEGImage‘+ origin_image_name database = ‘Unknown‘ width = str(labelimage.shape[0]) height = str(labelimage.shape[1]) depth = str(labelimage.shape[2]) createXMLlabel(saveXMLdir,objectnum, bbox, classname, foldername=foldername,filename=origin_image_name, path=path, database=database, width=width, height=height,depth=depth, segmented=‘0‘, pose="Unspecified", truncated=‘0‘, difficult=‘0‘)
以上是关于分割数据集label转换为目标检测boundingbox的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章