FileCoin Lotus复制证明 PoRep 源码梳理
Posted nirao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了FileCoin Lotus复制证明 PoRep 源码梳理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
流程图
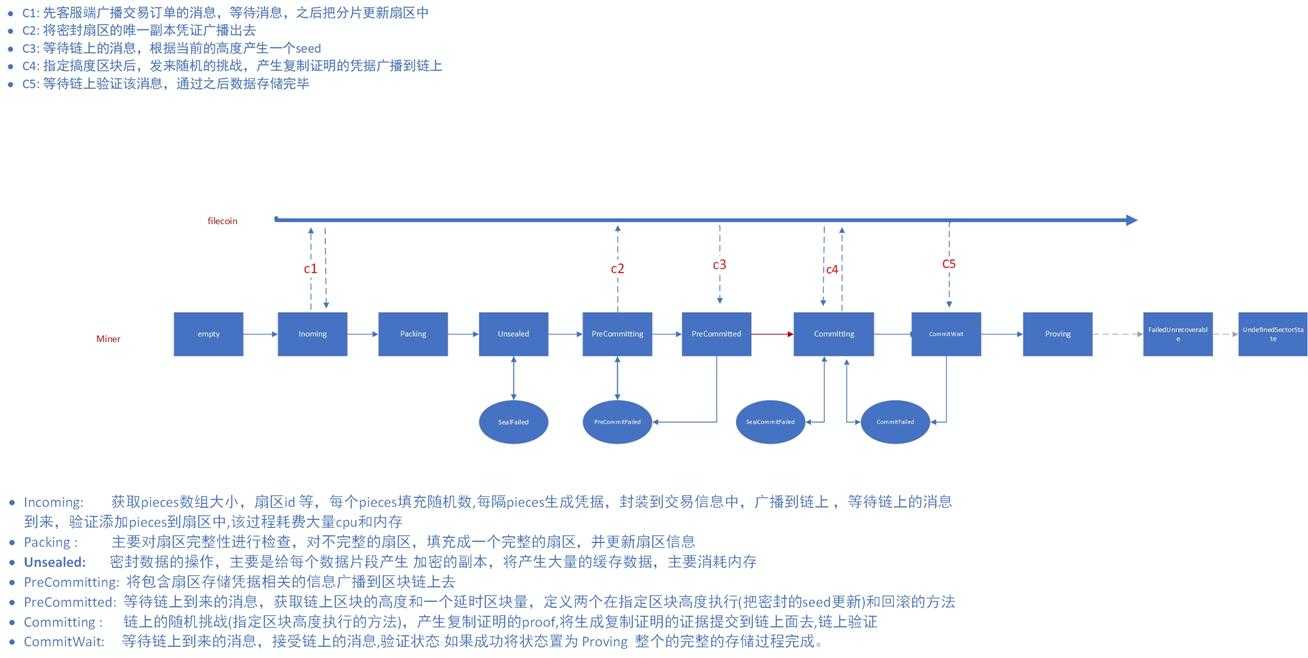
Incoming
lotus-miner-storage,首先调用 PledgeSector 通过类似微服务的方式调用
在 cmd/lotus-storage-miner/sectors.go 发出生成扇区的命令,通过微服务的方式调用
var pledgeSectorCmd = &cli.Command{
Name: "pledge-sector",
Usage: "store random data in a sector",
Action: func(cctx *cli.Context) error {
// 获取miner网关地址
nodeApi, closer, err := lcli.GetStorageMinerAPI(cctx)
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer closer()
ctx := lcli.ReqContext(cctx)
return nodeApi.PledgeSector(ctx)
},
}在 storage/garbage.go 生成新的扇区,获取分片数组大小,扇区id,该过程关键在调用内部方法 m.pledgeSector产生数据,填满扇区数据。
func (m *Miner) PledgeSector() error {
go func() {
ctx := context.TODO() // we can't use the context from command which invokes
// this, as we run everything here async, and it's cancelled when the
// command exits
// 一共多少个分片,是否跟生成默克尔书的分块对应?
size := sectorbuilder.UserBytesForSectorSize(m.sb.SectorSize())
// 扇区id
sid, err := m.sb.AcquireSectorId()
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("%+v", err)
return
}
// 产生分片数组,该方法中会将生成的签名信息提交到链上,重点方法
pieces, err := m.pledgeSector(ctx, sid, []uint64{}, size)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("%+v", err)
return
}
// 产生新的扇区
if err := m.newSector(context.TODO(), sid, pieces[0].DealID, pieces[0].ppi()); err != nil {
log.Errorf("%+v", err)
return
}
}()
return nil
}在重点查看m.pledgeSector,该方法主要作用是为每隔扇区生成一个凭据,并把每隔凭据封装成一个交易信息,提交到链上,并解析出链上的提交信息进行判断交易id是否一致,存储数据;返回信息为分片信息数组
func (m *Miner) pledgeSector(ctx context.Context, sectorID uint64, existingPieceSizes []uint64, sizes ...uint64) ([]Piece, error) {
...
// 将交易信息提交到链上
params, aerr := actors.SerializeParams(&actors.PublishStorageDealsParams{
Deals: deals,
})
...
//等待链上反馈消息
r, err := m.api.StateWaitMsg(ctx, smsg.Cid())
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
...
//从链上消息中解析出DealID,看是否一致
var resp actors.PublishStorageDealResponse
if err := resp.UnmarshalCBOR(bytes.NewReader(r.Receipt.Return)); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if len(resp.DealIDs) != len(sizes) {
return nil, xerrors.New("got unexpected number of DealIDs from PublishStorageDeals")
}
....
out := make([]Piece, len(sizes))
//根据链上确认的结果,首先将piece的信息存入到sector里
for i, size := range sizes {
//填充数据
ppi, err := m.sb.AddPiece(size, sectorID, io.LimitReader(rand.New(rand.NewSource(42)), int64(size)), existingPieceSizes)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
existingPieceSizes = append(existingPieceSizes, size)
out[i] = Piece{
DealID: resp.DealIDs[i],
Size: ppi.Size,
CommP: ppi.CommP[:],
}
}
return out, nil
}扇区信息生成之后调用 /storage/secotrs.go
//扇区信息生成之后,调用该方法
func (m *Miner) onSectorIncoming(sector *SectorInfo) {
// 判断id是否存在
has, err := m.sectors.Has(sector.SectorID)
if err != nil {
return
}
if has {
log.Warnf("SealPiece called more than once for sector %d", sector.SectorID)
return
}
// 把数据写入 扇区 硬盘中
if err := m.sectors.Begin(sector.SectorID, sector); err != nil {
log.Errorf("sector tracking failed: %s", err)
return
}
go func() {
select {
case m.sectorUpdated <- sectorUpdate{ //更改状态
newState: api.Packing,
id: sector.SectorID,
}:
case <-m.stop:
log.Warn("failed to send incoming sector update, miner shutting down")
}
}()
} 以上为 Incomeing 过程,主要作用是计算piece大小,产生扇区id信息;把每个piece的大小产生凭据(包含交易信息等),提交到链上,进行验证;之后用piece数组,产生扇区信息;然后把扇区的信息写入磁盘,将状态更改 Packing状态,此过程将消耗大量的 cpu 和内存
Packing
后续的操作主要在 /storage/sector_states.go 文件中
主要是判断扇区数据是否完整,将没填满的扇区填充完整,之后将状态更改为 Unsealed状态
// 打包的状态,将没哟填满数据的扇区填满
func (m *Miner) handlePacking(ctx context.Context, sector SectorInfo) *sectorUpdate {
log.Infow("performing filling up rest of the sector...", "sector", sector.SectorID)
var allocated uint64
for _, piece := range sector.Pieces {
allocated += piece.Size
}
ubytes := sectorbuilder.UserBytesForSectorSize(m.sb.SectorSize())
if allocated > ubytes {
return sector.upd().fatal(xerrors.Errorf("too much data in sector: %d > %d", allocated, ubytes))
}
//fillers From Remaining
fillerSizes, err := fillersFromRem(ubytes - allocated)
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().fatal(err)
}
if len(fillerSizes) > 0 {
log.Warnf("Creating %d filler pieces for sector %d", len(fillerSizes), sector.SectorID)
}
//此处调用 pledgeSector将扇区填满
pieces, err := m.pledgeSector(ctx, sector.SectorID, sector.existingPieces(), fillerSizes...)
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().fatal(xerrors.Errorf("filling up the sector (%v): %w", fillerSizes, err))
}
//数据填充完毕后,扇区的状态转换到了Unsealed状态
return sector.upd().to(api.Unsealed).state(func(info *SectorInfo) {
info.Pieces = append(info.Pieces, pieces...)
})
}Unsealed
func (m *Miner) handleUnsealed(ctx context.Context, sector SectorInfo) *sectorUpdate {
log.Infow("performing sector replication...", "sector", sector.SectorID)
// 调用随机函数返回一个随机选票(包含区块高度,和票据)
// 随机函数在初始化矿工生成的,运用的反射,具体需要详细查看 ?
ticket, err := m.tktFn(ctx)
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().fatal(err)
}
// 开始进行密封的操作,主要根据源数据产生加密数据,产生一份副本
rspco, err := m.sb.SealPreCommit(sector.SectorID, *ticket, sector.pieceInfos())
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().to(api.SealFailed).error(xerrors.Errorf("seal pre commit failed: %w", err))
}
// 更改状态,把数据的唯一复制凭据信息,和随机数相关更新
return sector.upd().to(api.PreCommitting).state(func(info *SectorInfo) {
info.CommD = rspco.CommD[:]
info.CommR = rspco.CommR[:]
info.Ticket = SealTicket{
BlockHeight: ticket.BlockHeight,
TicketBytes: ticket.TicketBytes[:],
}
})
}/lib/sectorbuilder/sectorbuilder.go 文件中
判断在 .lotusstorage 文件下几个目录是存在 cache,staged,sealed;调用rust库的代码生成相关的凭据
func (sb *SectorBuilder) SealPreCommit(sectorID uint64, ticket SealTicket, pieces []PublicPieceInfo) (RawSealPreCommitOutput, error) {
...
// 底层是rust部分的代码生成凭据信息
rspco, err := sectorbuilder.SealPreCommit(
sb.ssize,
PoRepProofPartitions,
cacheDir,
stagedPath,
sealedPath,
sectorID,
addressToProverID(sb.Miner),
ticket.TicketBytes,
pieces,
)
log.Warn(xerrors.Errorf("[qz2.4]: time to precommit %v at :%v", sectorID, time.Since(start).Milliseconds()))
start = time.Now()
if err != nil {
return RawSealPreCommitOutput{}, xerrors.Errorf("presealing sector %d (%s): %w", sectorID, stagedPath, err)
}
// 返会相关的凭据信息
return RawSealPreCommitOutput(rspco), nil
}此过程会产生大量的缓存文件用于计算,产生加密后数据的唯一副本相关的凭据,此时并没有产生复制证明
PreCommitting
主要是讲消息广播到链上去,并把该消息cid存起来;主要是让区块到了指定的高度验证数据的有效性
func (m *Miner) handlePreCommitting(ctx context.Context, sector SectorInfo) *sectorUpdate {
// 要发到链上的消息
params := &actors.SectorPreCommitInfo{
SectorNumber: sector.SectorID,
CommR: sector.CommR,
SealEpoch: sector.Ticket.BlockHeight,
DealIDs: sector.deals(),
}
enc, aerr := actors.SerializeParams(params)
if aerr != nil {
return sector.upd().to(api.PreCommitFailed).error(xerrors.Errorf("could not serialize commit sector parameters: %w", aerr))
}
// 封装消息体
msg := &types.Message{
To: m.maddr,
From: m.worker,
Method: actors.MAMethods.PreCommitSector,
Params: enc,
Value: types.NewInt(0), // TODO: need to ensure sufficient collateral
GasLimit: types.NewInt(1000000 /* i dont know help */),
GasPrice: types.NewInt(1),
}
log.Info("submitting precommit for sector: ", sector.SectorID)
// 广播
smsg, err := m.api.MpoolPushMessage(ctx, msg)
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().to(api.PreCommitFailed).error(xerrors.Errorf("pushing message to mpool: %w", err))
}
// 将受到消息cid 保存
return sector.upd().to(api.PreCommitted).state(func(info *SectorInfo) {
mcid := smsg.Cid()
info.PreCommitMessage = &mcid
})
}PreCommitted
func (m *Miner) handlePreCommitted(ctx context.Context, sector SectorInfo) *sectorUpdate {
// 等待链上的消息
mw, err := m.api.StateWaitMsg(ctx, *sector.PreCommitMessage)
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().to(api.PreCommitFailed).error(err)
}
...
// 区块的高度+定义的延时量(8)
randHeight := mw.TipSet.Height() + build.InteractivePoRepDelay - 1 // -1 because of how the messages are applied
log.Infof("precommit for sector %d made it on chain, will start proof computation at height %d", sector.SectorID, randHeight)
updateNonce := sector.Nonce
// 一个是在区块到达一定的高度执行的方法和回滚的方法
err = m.events.ChainAt(func(ctx context.Context, ts *types.TipSet, curH uint64) error {
// 根据区块高度和ts key生成随机数
rand, err := m.api.ChainGetRandomness(ctx, ts.Key(), int64(randHeight))
if err != nil {
err = xerrors.Errorf("failed to get randomness for computing seal proof: %w", err)
m.sectorUpdated <- *sector.upd().fatal(err)
return err
}
// 更改状态
m.sectorUpdated <- *sector.upd().to(api.Committing).setNonce(updateNonce).state(func(info *SectorInfo) {
// 将密封 seed更新
info.Seed = SealSeed{
BlockHeight: randHeight,
TicketBytes: rand,
}
})
updateNonce++
return nil
}, func(ctx context.Context, ts *types.TipSet) error {
log.Warn("revert in interactive commit sector step")
// TODO: need to cancel running process and restart...
return nil
}, build.InteractivePoRepConfidence, mw.TipSet.Height()+build.InteractivePoRepDelay)
if err != nil {
log.Warn("waitForPreCommitMessage ChainAt errored: ", err)
}
return nil
}该过程主要是等待之前 生成扇区唯一副本和凭据广播到链上的消息,等待之后,根据当前的区块的高度加上一个延时变量(预估5分钟左右),生成在该区块时执行的方法,和回滚的方法。状态更改 Committing
Committing
func (m *Miner) handleCommitting(ctx context.Context, sector SectorInfo) *sectorUpdate {
...
// 产生复制证明凭据
proof, err := m.sb.SealCommit(sector.SectorID, sector.Ticket.SB(), sector.Seed.SB(), sector.pieceInfos(), sector.rspco())
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().to(api.SealCommitFailed).error(xerrors.Errorf("computing seal proof failed: %w", err))
}
...
// 把包含证明文件的消息广播
smsg, err := m.api.MpoolPushMessage(ctx, msg)
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().to(api.CommitFailed).error(xerrors.Errorf("pushing message to mpool: %w", err))
}
// 更改状态
return sector.upd().to(api.CommitWait).state(func(info *SectorInfo) {
mcid := smsg.Cid()
info.CommitMessage = &mcid
info.Proof = proof
})
}
// 这个是重点关注的方法,产生复制证明的证明凭据
func (sb *SectorBuilder) SealCommit(sectorID uint64, ticket SealTicket, seed SealSeed, pieces []PublicPieceInfo, rspco RawSealPreCommitOutput) (proof []byte, err error) {
// 产生一个工作任务
call := workerCall{
task: WorkerTask{
Type: WorkerCommit,
TaskID: atomic.AddUint64(&sb.taskCtr, 1),
SectorID: sectorID,
SealTicket: ticket,
Pieces: pieces,
SealSeed: seed,
Rspco: rspco,
},
ret: make(chan SealRes),
}
atomic.AddInt32(&sb.commitWait, 1)
select { // prefer remote
case sb.commitTasks <- call:
proof, err = sb.sealCommitRemote(call)
default:
sb.checkRateLimit()
rl := sb.rateLimit
if sb.noCommit {
rl = make(chan struct{})
}
start := time.Now()
log.Warn(xerrors.Errorf("[qz2.6]: start to commit :%v", start))
select { // use whichever is available
case sb.commitTasks <- call: // 远程work产生复制证明凭据
proof, err = sb.sealCommitRemote(call)
log.Warn(xerrors.Errorf("[qz2.7]: remote commit :%v", time.Since(start).Milliseconds()))
case rl <- struct{}{}: // 默认本地work产生复制证明的凭据,内部主要是调用 rust部分的代码
proof, err = sb.sealCommitLocal(sectorID, ticket, seed, pieces, rspco)
log.Warn(xerrors.Errorf("[qz2.8]: local commit time :%v", time.Since(start).Milliseconds()))
}
}
if err != nil {
return nil, xerrors.Errorf("commit: %w", err)
}
return proof, nil
}等待链上的消息,之后产生复制证明的凭据,并广播到链上去
CommitWait
主要是接受链上的消息,判断状态,将扇区状态更改为 proving,存储成功
func (m *Miner) handleCommitWait(ctx context.Context, sector SectorInfo) *sectorUpdate {
...
// 等待链上广播来的消息
mw, err := m.api.StateWaitMsg(ctx, *sector.CommitMessage)
if err != nil {
return sector.upd().to(api.CommitFailed).error(xerrors.Errorf("failed to wait for porep inclusion: %w", err))
}
// 判断状态
if mw.Receipt.ExitCode != 0 {
log.Errorf("UNHANDLED: submitting sector proof failed (exit=%d, msg=%s) (t:%x; s:%x(%d); p:%x)", mw.Receipt.ExitCode, sector.CommitMessage, sector.Ticket.TicketBytes, sector.Seed.TicketBytes, sector.Seed.BlockHeight, sector.Proof)
return sector.upd().fatal(xerrors.Errorf("UNHANDLED: submitting sector proof failed (exit: %d)", mw.Receipt.ExitCode))
}
// 最终产生算力,更改扇区状态
return sector.upd().to(api.Proving).state(func(info *SectorInfo) {
})
}以上是关于FileCoin Lotus复制证明 PoRep 源码梳理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章