多线程Active Objects设计模式
Posted zheaven
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多线程Active Objects设计模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、Active Object模式-接收异步消息的主动对象
Active是主动的意思,因此ActiveObject就是主动对象的意思。所谓主动一般指有自己特有的线程,举例来说,java.lang.Thread类的实例就是一种主动对象。
不过,在Active Object模式中出厂的主动对象可不仅仅有自己特有的线程,它同时还具备可以从外部接收和处理异步消息并根据需要返回处理结果的特征。
Active Object模式中的主动对象会通过自己特有的线程在合适的时机处理从外部接收到的异步消息。
在Active Object中,组成主动对象与许多自然人组成法人类似,即使是java语言这样没有异步消息的编程语言,也可以使用Active Object模式组成实际上能够处理异步消息的主动对象。
二、示例程序类和接口一览表
| 类名 | 说明 |
| Main.java | 测试示例程序的类 |
| MakerClientThread.java | 发出“生成字符串”请求的线程 |
| DisplayClientThread.java | 发出“显示字符串”请求的线程 |
| ActiveObject.java | 定义“主动对象”的接口(API)的接口 |
| ActiveObjectFactory.java | 创建“主动对象”的类 |
| Proxy.java | 将方法调用转换为MethodRequest对象的类(实现了ActiveObject的接口) |
| SchedulerThread.java | 调用execute方法处理 MethodRequest对象的类 |
| ActivationQueue.java | 按顺序保存MethodRequest对象的类 |
| MethodRequest.java | 表示请求的抽象类 |
| MakeStringRequest.java | makeString方法(生成字符串)对应的类,MethodRequest类的子类 |
| DisplayStringRequest.java | displayString方法(显示字符串)对应的类,MethodRequest类的子类 |
| Result.java | 表示执行结果的抽象类 |
| FutureResult.java | 在Future模式中表示执行结果的类 |
| RealResult.java | 表示实际的执行结果的类 |
| Servant.java | 执行实际处理的类(实现了ActiveObject接口) |
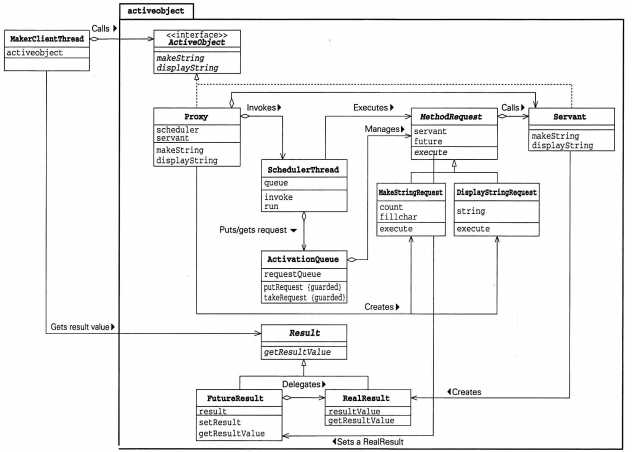
三、示例程序的类图
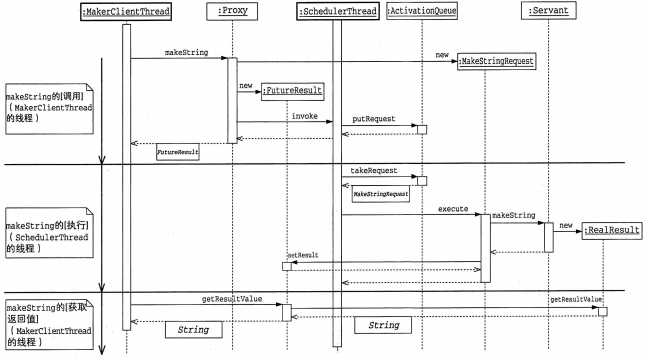
四、示例程序时序图
五、代码演示
ActiveObject接口
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; /** * 接受异步消息的主动对象,类似 System.gc(); */ public interface ActiveObject { Result makeString(int count, char fillChar); void displayString(String text); }
Servant
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; class Servant implements ActiveObject { @Override public void displayString(String text) { try { System.out.println("Display:" + text); Thread.sleep(10); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override public Result makeString(int count, char fillChar) { char[] buf = new char[count]; for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) { buf[i] = fillChar; try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (Exception e) { } } return new RealResult(new String(buf)); } }
ActivationQueue
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; import java.util.LinkedList; public class ActivationQueue { private final static int MAX_METHOD_REQUEST_QUEUE_SIZE = 100; private final LinkedList<MethodRequest> methodQueue; public ActivationQueue() { this.methodQueue = new LinkedList<>(); } public synchronized void put(MethodRequest request) { while (methodQueue.size() >= MAX_METHOD_REQUEST_QUEUE_SIZE) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } this.methodQueue.addLast(request); this.notifyAll(); } public synchronized MethodRequest take() { while (methodQueue.isEmpty()) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } MethodRequest methodrequest = methodQueue.removeFirst(); this.notifyAll(); return methodrequest; } }
MethodRequest
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; /** * 对应ActiveObjects的每一个方法,将每个方法转换成一个对象 */ public abstract class MethodRequest { protected final Servant servant; protected final FutureResult futureresult; public MethodRequest(Servant servant, FutureResult futureresult) { this.servant = servant; this.futureresult = futureresult; } public abstract void execute(); }
MakeStringRequest
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; /** * {@link ActiveObject#makeString(int, char)} */ public class MakeStringRequest extends MethodRequest { private final int count; private final char fillChar; public MakeStringRequest(Servant servant, FutureResult futureresult, int count, char fillChar) { super(servant, futureresult); this.count = count; this.fillChar = fillChar; } @Override public void execute() { Result result = servant.makeString(count, fillChar); futureresult.setResult(result); } }
DisplayStringRequest
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public class DisplayStringRequest extends MethodRequest { private final String text; public DisplayStringRequest(Servant servant, final String text) { super(servant, null); this.text = text; } @Override public void execute() { this.servant.displayString(text); } }
Result接口
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public interface Result { Object getResultValue(); }
RealResult
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public class RealResult implements Result { private final Object resultValue; public RealResult(Object resultValue) { this.resultValue = resultValue; } @Override public Object getResultValue() { return this.resultValue; } }
FutureResult
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public class FutureResult implements Result { private Result result; private boolean ready = false; public synchronized void setResult(Result result) { this.result = result; this.ready = true; this.notifyAll(); } @Override public synchronized Object getResultValue() { while (!ready) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return this.result.getResultValue(); } }
ActiveObjectProxy
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; class ActiveObjectProxy implements ActiveObject { private final SchedulerThread schedulerThread; private final Servant servant; public ActiveObjectProxy(SchedulerThread schedulerThread, Servant servant) { this.schedulerThread = schedulerThread; this.servant = servant; } @Override public Result makeString(int count, char fillChar) { FutureResult future = new FutureResult(); schedulerThread.invoke(new MakeStringRequest(servant, future, count, fillChar)); return future; } @Override public void displayString(String text) { schedulerThread.invoke(new DisplayStringRequest(servant, text)); } }
ActiveObjectFactory
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public final class ActiveObjectFactory { private ActiveObjectFactory() { } public static ActiveObject createActiveObject() { Servant servant = new Servant(); ActivationQueue queue = new ActivationQueue(); SchedulerThread schedulerThread = new SchedulerThread(queue); ActiveObjectProxy proxy = new ActiveObjectProxy(schedulerThread, servant); schedulerThread.start(); return proxy; } }
SchedulerThread
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public class SchedulerThread extends Thread { private final ActivationQueue activationQueue; public SchedulerThread(ActivationQueue activationQueue) { this.activationQueue = activationQueue; } public void invoke(MethodRequest request) { this.activationQueue.put(request); } @Override public void run() { while (true) { this.activationQueue.take().execute(); } } }
MakerClientThread
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public class MakerClientThread extends Thread { private final ActiveObject activeObject; private final char fillChar; public MakerClientThread(ActiveObject activeObject, String name) { super(name); this.activeObject = activeObject; this.fillChar = name.charAt(0); } @Override public void run() { try { for (int i = 0; true; i++) { Result result = activeObject.makeString(i + 1, fillChar); Thread.sleep(20); String value = (String)result.getResultValue(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": value=" + value); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
DisplayClientThread
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public class DisplayClientThread extends Thread { private final ActiveObject activeObject; public DisplayClientThread(String name, ActiveObject activeObject) { super(name); this.activeObject = activeObject; } @Override public void run() { try { for(int i = 0; true; i++) { String text = Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + i; activeObject.displayString(text); Thread.sleep(200); } } catch (Exception e) { } } }
main
package com.dwz.concurrency2.chapter19; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ActiveObject activeObject = ActiveObjectFactory.createActiveObject(); new MakerClientThread(activeObject, "Alex").start(); new MakerClientThread(activeObject, "Bobby").start(); new DisplayClientThread("Chris", activeObject).start(); } }
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/smartdt/article/details/79363022
https://blog.csdn.net/cuichaox/article/details/1414305
以上是关于多线程Active Objects设计模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
多线程设计模式:第六篇 - ThreadLocal和Active Object模式
Java多线程编程模式实战指南一:Active Object模式(下)
C++11多线程运行报错:terminate called without an active exception(没有join或detach子线程)
C++11多线程运行报错:terminate called without an active exception(没有join或detach子线程)