Tensor--tensorflow的数据类型
Posted zdm-code
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Tensor--tensorflow的数据类型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在tensorflow2.0版本之前,1.x版本的tensorflow的基本数据类型有计算图(Computation Graph)和张量(Tensor)两种,但tensorflow2.0之后的版本取消了Graph和Session的概念。今天简单记录一下Tensor的相关内容。
从Tensorflow的命名就不难看出,Tensor(张量)在整个tensorflow的框架体系中都是一个重要的概念,它可以称为Tensorflow的数据模型,因为Tensor是tensorflow管理数据的形式,换句话说,在tensorflow中,所有的数据都可以借助张量的形式来表示。在张量出现之前,我们比较熟悉这样两种数据类型:list和np.array。list就不多说了,对于大量数据list的表现并不是很好,假设有一个维度[64,24,24,3]的数据,它在深度学习中其实是一个比较小的数据,但是对于list来说却是一个很庞大的数据,占用的内存空间更是无法估量。而为了解决大数据的吞吐,对于相同类型的数据载体,np.numpy有很好的表现,但是numpy是在tensorflow之前出现的一个科学计算库,对GPU并不支持,也不支持自动求导,为了更好的解决深度学习中的问题,tensorflow开始出现。
在数学中,一个0维的数据(dim=0),即1.1,2.2等等被称为一个标量(scalar),一个一维的数据(dim=1),即[1.1],[2.2,3.3,……]等被称作向量(vector),一个维度大于2的数据,如[[1,2],[3,4]]被称为矩阵(matrix),而Tensor一般是指维度大于2的向量(矩阵),但是在tensorflow中,以上所有的类型都可以被称为tensor。
创建不同类型的数据:
# int型 a = tf.constant(1) # float型 b = tf.constant(1.) # double型 c = tf.constant(2.,dtype=tf.float64) # bool型 d = tf.constant([True,False]) # string型 e = tf.constant(‘hello world‘)
得到结果如下:

常用属性如下:
# 使用numpy声明一个数据 a=np.arange(5) # 将其转化为tensor aa=tf.convert_to_tensor(a) # 强制类型转换 int——float bb=tf.cast(aa,dtype=tf.float32) # .numpy()将tensor返回numpy显示数据 print(aa.numpy())
得到![]()
如何创建一个tensor:
# 通过numpy创建数据转换 a = tf.convert_to_tensor(np.ones([2,3])) # list转换 b = tf.convert_to_tensor([1,2]) # 初始化全为0的tensor(tf.ones()用法同tf.zeros()) c = tf.zeros([2,2]) # 以指定tensor的shape为基础创建新的tensor(同tf.zeros(c.shape)) d = tf.zeros_like(c) # 填充任意元素 e = tf.fill([2,2],9) # 随机化初始化: # 正态分布,mean指定均值,stddev指定方差 f = tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=1,stddev=1) # 截断正态分布 g = tf.random.truncated_normal([2,2],mean=1,stddev=1) # 均匀分布 h = tf.random.uniform([2,2],minval=0,maxval=1)
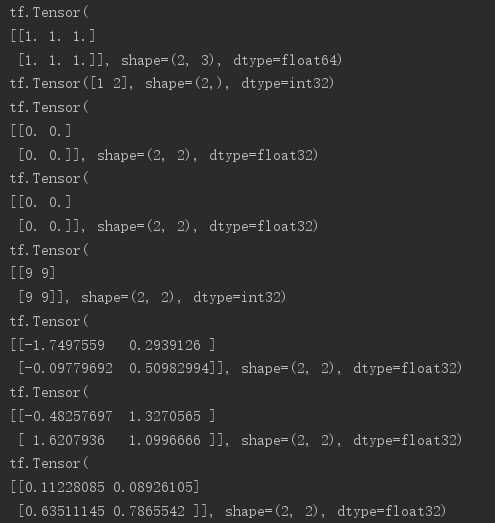
捎带提一点打乱顺序函数的用法:
# 随机打散 i = tf.range(10) i = tf.random.shuffle(i) x = tf.random.uniform([10],maxval=10,dtype=tf.int32) y = tf.random.uniform([10],maxval=10,dtype=tf.int32) print(i.numpy()) print("x:",x.numpy()) print("y:",y.numpy()) # .gather指定按照某一索引序列取值 x = tf.gather(x,i) y = tf.gather(y,i) print("x:",x.numpy()) print("y:",y.numpy())
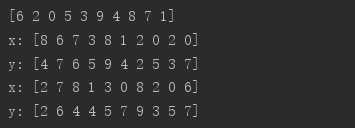
可以看到按照同一打乱序列取值后,x和y仍然是一一对应的关系
tensor中scalar最常用的部分:loss和accuracy
损失(loss)和精度(accuracy)在前面回归和mnist实战都已经提过,这里不再解释其概念,简单说明一下loss的求值方法
# 生成一组数据用来模拟四张图片的网络输出 out = tf.random.uniform([4,10]) print(out) # 模拟四张图片对应的label y = tf.range(4) print(y) # 使用one_hot对label进行编码 y = tf.one_hot(y,depth=10) print(y) # 调用keras的api来计算损失(MSE均方误差) loss = tf.keras.losses.mse(y,out) print(loss) # 求loss的均值 loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) print(loss)
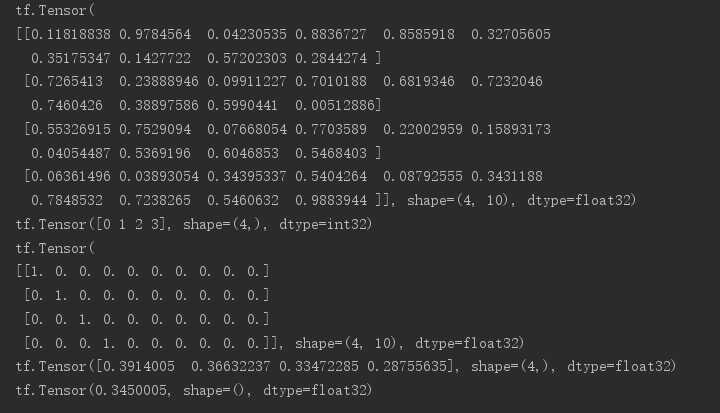
以上是关于Tensor--tensorflow的数据类型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章