栈的链表实现
Posted wjundong
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了栈的链表实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
栈的链表实现
链栈结构如下图所示:len用来存储栈中元素个数
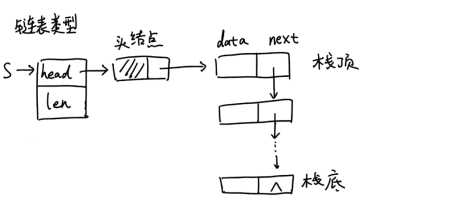
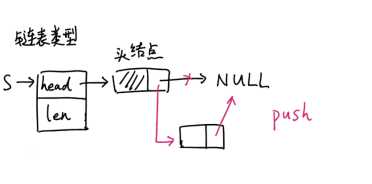
图示:当链表为空时,即栈为空栈时插入情况
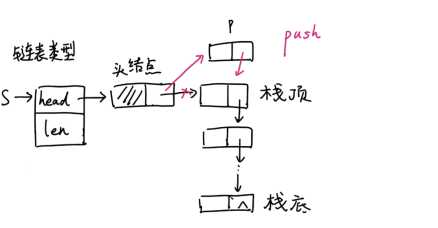
图示:非空时插入
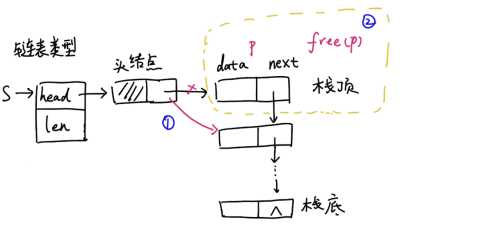
图示:弹出栈顶
示例代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int Status;
typedef int SElemType;
typedef struct SLNode{
SElemType data;
struct SLNode * next;
}SLNode;
typedef struct
{
SLNode * head; /* 指向链表头结点 */
int len; /* 栈元素的长度 */
}*SLinkList,SList;
/* 构造一个空战 */
Status InitStack(SLinkList *S)
{
*S = (SLinkList)malloc(sizeof(SList)); /* 创建一个链表 */
if(!S)
return ERROR;
(*S)->head = (SLNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLNode)); /* 创建头结点 */
if(!(*S)->head) {
free(*S);
return ERROR;
}
(*S)->len = 0; /* 栈元素长度初始化为0 */
(*S)->head->next = NULL; /* 初始为空链表 */
return OK;
}
/* 销毁栈S,S不再存在 */
Status DestoryStack(SLinkList *S)
{
if(!(*S) || !(*S)->head)
return ERROR;
SLNode * p, * q;
p = (*S)->head->next; /* 指向第一个结点 */
while(p) { /* 该结点存在 */
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
free((*S)->head);
free((*S));
*S = NULL; /* 销毁S指针本身 */
return OK;
}
/* 把栈S置为空栈 */
Status ClearStack(SLinkList S)
{
if(!S || !S->head)
return ERROR;
SLNode * p, * q;
p = S->head->next; /* 指向第一个结点 */
while(p) { /* 该结点存在 */
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
S->head->next = NULL;
/* 这里要注意,S->head->next指向的那片内存已经free掉了
* 但是S->head->next 还是指向哪里,需要将其指向空 */
return OK;
}
/* 如果栈为空则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
Status StackEmpty(SLinkList S)
{
if(!S || !S->head)
return ERROR;
if(!(S->head->next)) /* 如果第一个元素为空 */
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/* 返回栈的长度 */
int StackLength(SLinkList S)
{
if(!S || !S->head)
return ERROR;
return S->len;
}
/* 插入元素e为新的栈顶 */
Status Push(SLinkList S, SElemType e)
{
if(!S || !S->head)
return ERROR;
SLNode *p;
p = (SLNode *)malloc(sizeof(SLNode)); /* 新建一个结点 */
if(!p)
return ERROR;
p->data = e;
p->next = S->head->next;
S->head->next = p;
S->len++; /* 栈元素计数器加1 */
return OK;
}
/* 若栈不空,则弹出栈顶元素,用e保存返回值 */
Status Pop(SLinkList S,SElemType *e)
{
if(!S || !S->head || !S->head->next)
return ERROR;
SLNode * p = S->head->next; /* 指向第一个结点,备份起来 */
S->head->next = p->next; /* 将S->head->next 指向第二个结点 */
*e = p->data;
free(p);
S->len--; /* 栈元素计数器减1 */
return OK;
}
/* 若栈不为空,则用e返回S的栈顶元素,并返回OK,否则返回ERROR */
Status GetTop(SLinkList S, SElemType *e)
{
if(!S || !S->head || !S->head->next)
return ERROR;
*e = S->head->next->data; /* 取出第一个结点的数据 */
return OK;
}
/* 从栈顶往下打印栈中的数据 */
void printSList(SLinkList S)
{
if(!(S) || !(S)->head)
return ;
SLNode * p = S->head->next; /* 指向第一个结点 */
while(p) {
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("
");
}
int main()
{
SLinkList pS;
SElemType e;
// 初始化栈
InitStack(&pS);
// push 测试
for(int i=1;i<=110;i++) {
Push(pS,i);
}
// 获取栈长度测试
printf("len %d
",StackLength(pS));
// 弹出栈顶
Pop(pS,&e);
printf("pop %d
",e);
printf("len %d
",StackLength(pS));
// 打印栈测试
printSList(pS);
// 获取栈顶测试
GetTop(pS,&e);
printf("top %d
",e);
// 销毁测试
DestoryStack(&pS);
printf("
return 0
");
}以上是关于栈的链表实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章