数据结构与算法实例(复数实现)
Posted miaowulj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构与算法实例(复数实现)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
数据结构与算法实例分析——复数实现
数据结构与算法要求:
学会分析研究计算机加工处理的对象的特征,以便为应用涉及的对象选择适当的逻辑结构,存储结构以及相应的算法,并初步掌握算法的时间分析以及空间分析技术
数据结构:是相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合。在任何问题中,数据元素都不是孤立存在的,而是在他们之间存在着某种关系,这种数据元素相互之间的关系称为结构。根据数据元素之间的不同特性,通常有下列四种基本结构
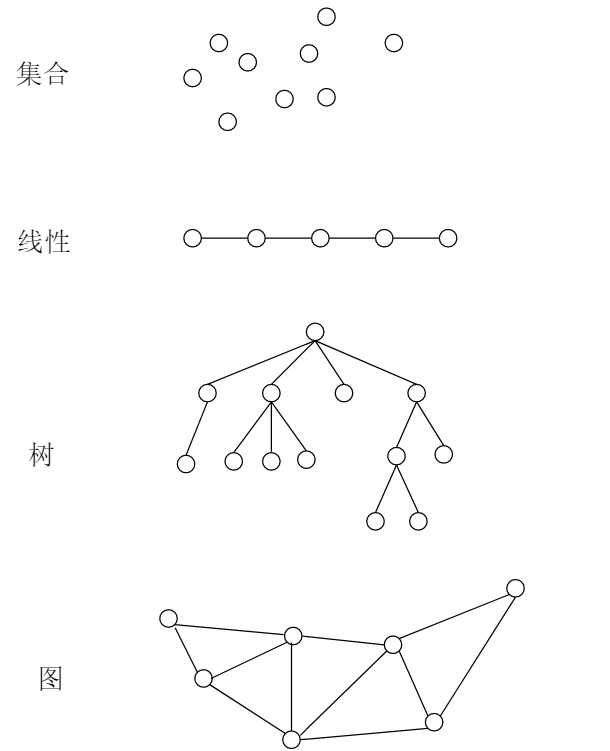
①集合——结构中的数据元素之间除了"同属于一个聚合"的关系外,别无其他关系②线性结构——结构中的数据元素之间存在一个对一个的关系;③树形结构——结构中的数据元素之间存在一个对多个的关系;④图状结构或网状结构——结构中的数据元素之间存在多个对多个的关系
算法和算法分析:
算法是对特定问题求解步骤的一种描述,它是指令的有限序列,其中每一条指令表示一个或多个操作;此外,一个算法还具有下列5个重要特性:
★ 有穷性:一个算法必须总是(对任何合法的输入值)在执行有穷步之后结束,且每一步都可在有穷时间内完成
★ 确定性:算法中每一条指令必须有确切的含义并且在任何条件下,算法只有唯一的一条执行路径,即对于相同的输入只能得出相同的输出。
★ 可行性:一个算法是能行的,即算法中描述的操作都是可以通过已经实现的基本运算执行有限次来实现的。
★ 输入:一个算法有零个或多个的输入,这些输入取自于某个特定的对象的集合
★ 输出:一个算法有一个或多个的输出,这些输出是同输入有着某些特定关系的量
复数四则运算
一.复数基本操作
1.复数的四则运算操作:(z1=a(实部)+b(虚部)i,z2=c+di)
z1+z2=(a+c)+(c+d)i;
z1-z2=(a-c)+(c-d)i;
z1*z2=(ac-bd)+(ad+bc)i;
z1/z2=(ac+bd)/(c2+d2)+(bc-ad)/(c2+d2)i;
2.复数的基本操作
建造空间:struct complex_t complex_init();
释放已经开辟内存空间:void complex_free(struct complex_t z);
访问指定内存空间(实部):double complex_get_real(struct complex_t z);
访问指定内存空间(虚部):double complex_get_imag(struct complex_t z);
修改指定内存参数(实部):void complex_set_real(struct complex_t z,double real);
修改指定内存参数(虚部):void complex_set_imag(struct complex_t z,double imag);
复数相加操作:void complex_additive(struct complex_t z1,struct complex_t z2,struct complex_t z3);
复数相减操作:void complex_subtract(struct complex_t z1,struct complex_t z2,struct complex_t z3);
复数相乘操作:void complex_multiply(struct complex_t z1,struct complex_t z2,struct complex_t z3);
复数相除操作:void complex_devide(struct complex_t z1,struct complex_t z2,struct complex_t z3);
二.复数的存储结构
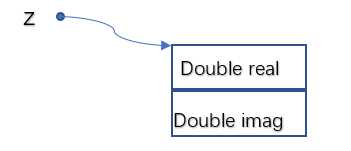
1.结构A:
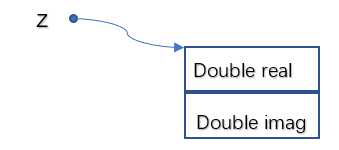
定义结构体分别存放复数的实部和虚部
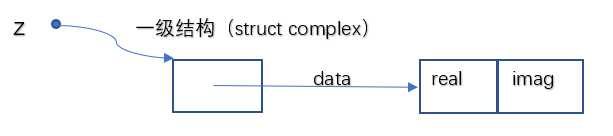
2.结构B:
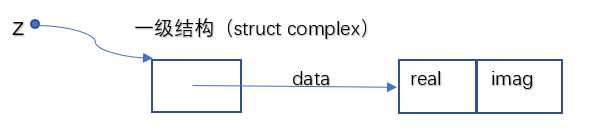
定义数组,将实部和虚部分别存放到数组中。将数组的首地址存放到一级结构(结构体)中,方便调用
3.结构C:
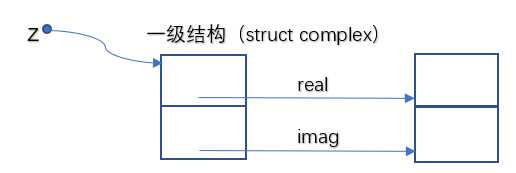
定义结构体作为一级结构,分别存放实部和虚部地址
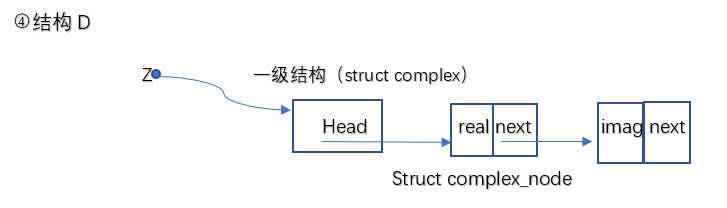
4.结构D:
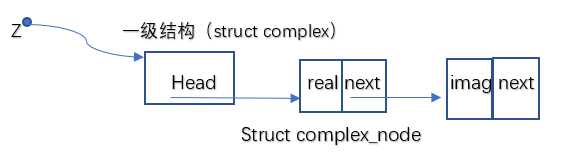
使用链表存放数据,一级结构Head存放实部节点的地址,虚部结构地址存放到实部节点的next中。
complex_t.h
#ifndef __COMPLEX_T_H__
#define __COMPLEX_T_H__
struct complex_t;
struct complex_t *complex_init();
void complex_free(struct complex_t *z);
double complex_get_real(struct complex_t *z);
double complex_get_imag(struct complex_t *z);
void complex_set_real(struct complex_t *z,double real);
void complex_set_imag(struct complex_t *z,double imag);
void complex_addition(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2);
void complex_subtract(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2);
void complex_multiply(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2);
void complex_devide(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2);
#endifmain.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "complex_t.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
//定义三个存储结构,分别存放两个算式的实部虚部以及结果的实部和虚部
//定义三个结构体指针变量,指向结构体(一级结构)
struct complex_t *z1=NULL;
struct complex_t *z2=NULL;
struct complex_t *z3=NULL;
z1=complex_init();
//根据定义的结构,将3.32存储到指定结构的实部
complex_set_real(z1,3.32);
//根据定义的结构,将-5.12存储到指定结构的虚部
complex_set_imag(z1,-5.12);
//根据定义的结构,取出实部和虚部元素
printf("z1=%.2f+%.2fi
",complex_get_real(z1),complex_get_imag(z1));
z2=complex_init();
complex_set_real(z2,9.21);
complex_set_imag(z2,0.54);
printf("z2=%.2f+%.2fi
",complex_get_real(z2),complex_get_imag(z2));
z3=complex_init();
//将z1指向的实部和z2指向的复数实部相加,z1指向的复数虚部和z2指向的复数虚部相加分别存储到z3指向的实部和z3指向的虚部
complex_addition(z3,z1,z2);
printf("z1+z2=%.2f+%.2fi
",complex_get_real(z3),complex_get_imag(z3));
//将z1指向的实部和z2指向的复数实部相减,z1指向的复数虚部和z2指向的复数虚部相减分别存储到z3指向的实部和z3指向的虚部
complex_subtract(z3,z1,z2);
printf("z1_z2=%.2f+%.2fi
",complex_get_real(z3),complex_get_imag(z3));
//将z1指向的实部和z2指向的复数实部相乘,z1指向的复数虚部和z2指向的复数虚部相乘分别存储到z3指向的实部和z3指向的虚部
complex_multiply(z3,z1,z2);
printf("z1*z2=%.2f+%.2fi
",complex_get_real(z3),complex_get_imag(z3));
//将z1指向的实部和z2指向的复数实部相除,z1指向的复数虚部和z2指向的复数虚部相除分别存储到z3指向的实部和z3指向的虚部
complex_devide(z3,z1,z2);
printf("z1/z2=%.2f+%.2fi
",complex_get_real(z3),complex_get_imag(z3));
//释放内存
complex_free(z1);
complex_free(z2);
complex_free(z3);
return 0;
}complex_t.c
结构A
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "complex_t.h"
//定义结构体存放复数元素的实部和虚部
struct complex_t{
double real;//复数实部元素
double imag;//复数虚部元素
};
//初始化内存空间用来存放复数的实部和虚部,返回指向该内存的指针变量
struct complex_t *complex_init()
{
//定义结构体指针变量指向结构体
struct complex_t *z=NULL;
//使用malloc函数开辟malloc函数返回的结构体长度的空间
z=(struct complex_t *)malloc(sizeof(struct complex_t));//分配内存空间
if(z==NULL) return NULL;
//断言z不为空
assert(z!=NULL);
z->imag=0.0f;//初始化
z->real=0.0f;
return z;
}
//释放内存函数
void complex_free(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
free(z);
}
//根据传递过来的z指针变量根据已定义的存储结构取出复数的实部元素
double complex_get_real(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
return z->real;
}
//根据传递过来的z指针变量根据已定义的存储结构取出复数的虚部元素
double complex_get_imag(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
return z->imag;
}
//将数据传过来的数据放入定义结构的实部空间
void complex_set_real(struct complex_t *z,double real)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
z->real=real;
}
//将数据传过来的数据放入定义结构的虚部空间
void complex_set_imag(struct complex_t *z,double imag)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
z->imag=imag;
}
//取出z1指向已定义的存储结构中的实部和虚部相加放入z3指向的存储结构
void complex_addition(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->real;
b=z1->imag;
c=z2->real;
d=z2->imag;
z3->real=a+c;
z3->imag=b+d;
}
void complex_subtract(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->real;
b=z1->imag;
c=z2->real;
d=z2->imag;
z3->real=a-c;
z3->imag=b-d;
}
void complex_multiply(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->real;
b=z1->imag;
c=z2->real;
d=z2->imag;
z3->real=a*c+b*d;
z3->imag=b*c-a*d;
}
void complex_devide(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->real;
b=z1->imag;
c=z2->real;
d=z2->imag;
z3->real=(a*c-b*d)/(c*c+d*d);
z3->imag=(b*c+a*d)/(c*c+d*d);
}结构B
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "complex_t.h"
struct complex_t{
double *data;
};
struct complex_t *complex_init()
{
struct complex_t *z=NULL;
z=(struct complex_t *)malloc(sizeof(struct complex_t));
if(z==NULL) return NULL;
assert(z!=NULL);
z->data=NULL;
z->data=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*2);
if(z->data==NULL){
free(z);
return NULL;
}
assert(z!=NULL);
z->data[1]=0.0f;
z->data[2]=0.0f;
return z;
}
void complex_free(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
assert(z->data!=NULL);
free(z->data);
free(z);
}
double complex_get_real(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
assert(z->data!=NULL);
return z->data[1];
}
double complex_get_imag(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
assert(z->data!=NULL);
return z->data[2];
}
void complex_set_real(struct complex_t *z,double real)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
assert(z->data!=NULL);
z->data[1]=real;
}
void complex_set_imag(struct complex_t *z,double imag)
{
assert(z!=NULL);
assert(z->data!=NULL);
z->data[2]=imag;
}
void complex_addition(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->data[1];
b=z1->data[2];
c=z2->data[1];
d=z2->data[2];
z3->data[1]=a+c;
z3->data[2]=b+d;
}
void complex_subtract(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->data[1];
b=z1->data[2];
c=z2->data[1];
d=z2->data[2];
z3->data[1]=a-c;
z3->data[2]=b-d;
}
void complex_multiply(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->data[1];
b=z1->data[2];
c=z2->data[1];
d=z2->data[2];
z3->data[1]=a*c+b*d;
z3->data[2]=b*c-a*d;
}
void complex_devide(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->data[1];
b=z1->data[2];
c=z2->data[1];
d=z2->data[2];
z3->data[1]=(a*c-b*d)/(c*c+d*d);
z3->data[2]=(b*c+a*d)/(c*c+d*d);
}结构C:

#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "complex_t.h"
struct complex_t{
double *real;
double *imag;
};
struct complex_t *complex_init()
{
struct complex_t *z=NULL;
z=(struct complex_t *)malloc(sizeof(struct complex_t));
if(z==NULL) return NULL;
assert(z!=NULL);
z->real=NULL;
z->real=(double *)malloc(sizeof(double));
if(z->real==NULL) {
free(z);
return NULL;
}
assert(z->real!=NULL);
z->imag=NULL;
z->imag=(double *)malloc(sizeof(double));
if(z->imag==NULL){
free(z);
return NULL;
}
*(z->real)=0.0f;
*(z->imag)=0.0f;
return z;
}
void complex_free(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z->real!=NULL);
assert(z->imag!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
free(z);
free(z->real);
free(z->imag);
}
double complex_get_real(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z->real!=NULL);
assert(z->imag!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
return *(z->real);
}
double complex_get_imag(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z->real!=NULL);
assert(z->imag!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
return *(z->imag);
}
void complex_set_real(struct complex_t *z,double real)
{
assert(z->real!=NULL);
assert(z->imag!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
*(z->real)=real;
}
void complex_set_imag(struct complex_t *z,double imag)
{
assert(z->real!=NULL);
assert(z->imag!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
*(z->imag)=imag;
}
void complex_addition(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=*(z1->real);
b=*(z1->imag);
c=*(z2->real);
d=*(z2->imag);
*(z3->real)=a+c;
*(z3->imag)=b+d;
}
void complex_subtract(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=*(z1->real);
b=*(z1->imag);
c=*(z2->real);
d=*(z2->imag);
*(z3->real)=a-c;
*(z3->imag)=b-d;
}
void complex_multiply(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=*(z1->real);
b=*(z1->imag);
c=*(z2->real);
d=*(z2->imag);
*(z3->real)=a*c+b*d;
*(z3->imag)=b*c-a*d;
}
void complex_devide(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=*(z1->real);
b=*(z1->imag);
c=*(z2->real);
d=*(z2->imag);
*(z3->real)=(a*c-b*d)/(c*c+d*d);
*(z3->imag)=(b*c+a*d)/(c*c+d*d);
}结构D:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include "complex_t.h"
struct complex_node{
double data;
struct complex_node *next;
};
struct complex_t{
struct complex_node *head;
};
struct complex_t *complex_init()
{
struct complex_t *z=NULL;
z=(struct complex_t *)malloc(sizeof(struct complex_t));
if(z==NULL) return NULL;
assert(z!=NULL);
z->head=NULL;
z->head=(struct complex_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct complex_node));
if(z->head==NULL){
free(z);
return NULL;
}
assert(z->head!=NULL);
z->head->data=0.0f;
z->head->next=NULL;
z->head->next=(struct complex_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct complex_node));
if(z->head->next==NULL){
free(z->head);
free(z);
return NULL;
}
assert(z->head->next!=NULL);
z->head->next->data=0.0f;
z->head->next->next=NULL;
return z;
}
void complex_free(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z->head->next!=NULL);
assert(z->head!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
free(z->head->next);
free(z->head);
free(z);
}
double complex_get_real(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z->head->next!=NULL);
assert(z->head!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
return z->head->data;
}
double complex_get_imag(struct complex_t *z)
{
assert(z->head->next!=NULL);
assert(z->head!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
return z->head->next->data;
}
void complex_set_real(struct complex_t *z,double real)
{
assert(z->head->next!=NULL);
assert(z->head!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
z->head->data=real;
}
void complex_set_imag(struct complex_t *z,double imag)
{
assert(z->head->next!=NULL);
assert(z->head!=NULL);
assert(z!=NULL);
z->head->next->data=imag;
}
void complex_addition(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->head->data;
b=z1->head->next->data;
c=z2->head->data;
d=z2->head->next->data;
z3->head->data=a+c;
z3->head->next->data=b+d;
}
void complex_subtract(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->head->data;
b=z1->head->next->data;
c=z2->head->data;
d=z2->head->next->data;
z3->head->data=a-c;
z3->head->next->data=b-d;
}
void complex_multiply(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->head->data;
b=z1->head->next->data;
c=z2->head->data;
d=z2->head->next->data;
z3->head->data=a*c+b*d;
z3->head->next->data=b*c-a*d;
}
void complex_devide(struct complex_t *z3,struct complex_t *z1,struct complex_t *z2)
{
assert(z1!=NULL);
assert(z2!=NULL);
assert(z3!=NULL);
double a,b,c,d;
a=z1->head->data;
b=z1->head->next->data;
c=z2->head->data;
d=z2->head->next->data;
z3->head->data=(a*c-b*d)/(c*c+d*d);
z3->head->next->data=(b*c+a*d)/(c*c+d*d);
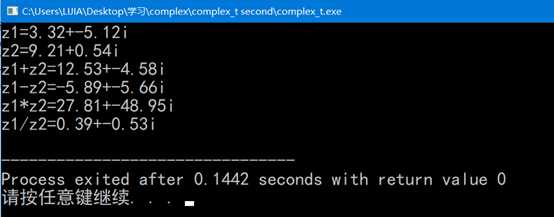
}三.编译结果
以上是关于数据结构与算法实例(复数实现)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章