Linux虚拟化 xen的工具栈介绍
Posted xiaoshiwang
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux虚拟化 xen的工具栈介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
试验环境centos6.10
xen的工具栈介绍:
查看xl目录的帮助:xl help
查看xen下安装了哪些虚拟机:xl list
# xl list Domain-0
Name ID Mem VCPUs State Time(s)
Domain-0 0 1024 2 r----- 53.1ID:从0开始的编号,即使中间删除了某个虚拟机,编号不会重用,继续往下发。
Mem:分配给虚拟机多少内存
VCPUS:分配给虚拟机几个CPU核心
State:虚拟机的状态
- r:正常运行中
- b:阻塞
- p:暂停
- s:停止
- c:崩溃了
- d:正在关机的过程中
Time:此虚拟机运行了多久了。
创建虚拟机domU
首先要指定domu的模式(pv,hvm,pv on hvm)
创建pv模式的domu
1,指定kernel,kernel文件放到哪里?可以在dom0中,也可以在domu中
2,initrd或initramfs
3,domu内核模块
4,根文件系统
5,swap设备
将上述内容定义在domu的配置文件
注意:xm和xl命令启动domu的配置文件略有区别。
创建domu的配置文件的具体写法,可以参考man xl.cfg
name:域名称,必须唯一,必须有
builder:指明虚拟机的类型。generic表示pv;hvm表示hvm
vcpus:虚拟机使用cpu核心的数量
maxvcpus:最大的cpu核心使用数量,要大于vcpus。当vcpus数量不够用时,就会增加到maxvcpus
cpus:指明vcpu可以运行在哪些物理cpu核心
- all:所有
- "0-3,5,^1":运行在0,2,3,5物理cpu上
memory=MBYTES:虚拟机使用的内存大小
maxmem=MBYTES:最大内存大小(原理同maxvcpus)
on-poweroff=ACTION:指明当用户输入了关机命令后,虚拟机应该怎么响应。不指定的话,就是关闭虚拟机。
ACTION:destroy(关机),restart(重启),preserve等
on-reboot=ACTION:指明当用户输入了关机命令后,虚拟机应该怎么响应。不指定的话,就是重启虚拟机。
on-crash=ACTION:指明当虚拟机崩溃时,应该怎么响应
uuid:domu的唯一标识
disk=[ "DISK_SPEC_STRING", "DISK_SPEC_STRING", ...]:指明磁盘设备列表。
有2种方式指定磁盘。一个是使用磁盘映像文件;另一个是dom0在物理磁盘上划分一个分区给domu使用,这种方式性能好,但不利于xen的整体迁移。
常用选项:[<target>, [<format>, [<vdev>, [<access>]]]],
target:磁盘映像文件
format:磁盘的种类,可以使用
qemu-img命令查看,支持的种类有:raw cow qcow vdi vmdk cloop dmg bochs vpc vvfat qcow2 qed vhdx parallels nbd blkdebug null host_cdrom host_floppy host_device file glustervdev:在domu种的设备文件类型,支持hd[x], xvd[x], sd[x] 等
access:访问权限
ro,r(specifies read-only)rw,w(specifies read/write)disk=[ "/images/xen/linux.img,raw,xvda,rw"]
用
qemu-img创建磁盘映像:qemu-img create [-f fmt] [-o options] filename [size]用-o?,查看都有什么options
# qemu-img create -f raw -o? /images/xen/busybox.img Supported options: size Virtual disk size preallocation Preallocation mode (allowed values: off, falloc, full)下面的命令创建了一个大小为2G的,格式为raw的磁盘映像文件,但实际是0字节。
# qemu-img create -f raw -o size=2G /images/xen/busybox.img # qemu-img create -f raw /images/xen/busybox.img 2G Formatting '/images/xen/busybox.img', fmt=raw size=2147483648 # ll -h -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2.0G Feb 1 11:51 busybox.img # du -sh busybox.img 0 busybox.img
vif=[ "NET_SPEC_STRING", "NET_SPEC_STRING", ...]:指明网络接口列表。
vfb=[ "VFB_SPEC_STRING", "VFB_SPEC_STRING", ...]:指明virtual frame buffer列表
pci=[ "PCI_SPEC_STRING", "PCI_SPEC_STRING", ...]:pci插槽的设备列表。
kernel="PATHNAME":内核文件路径,此路径为dom0中的路径
ramdisk="PATHNAME":为kernel指定内核提供的ramdisk文件路径
root="STRING":指明根文件系统。
extra="STRING":额外传递给内核引导时使用的参数。
pv模式下的专用的bootloader="PROGRAM":如果domu使用自己的kernel和ramdisk,此时需要一个dom0中的应用程序来实现其bootloader功能。
要么使用kernel和ramdisk的组合,要么使用bootloader。
下面创建一个虚拟机:
1,创建一个磁盘映像
# qemu-img create -f raw -o size=2G /images/xen/busybox.img
# qemu-img create -f raw /images/xen/busybox.img 2G
Formatting '/images/xen/busybox.img', fmt=raw size=2147483648
# ll -h
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 2.0G Feb 1 11:51 busybox.img
# du -sh busybox.img
0 busybox.img2,给磁盘分区创建ext4文件系统
不给此磁盘映像分区了,就按一个分区使用。分区命令(fdisk)
# mkfs -t ext2 busybox.img
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
busybox.img is not a block special device.
Proceed anyway? (y,n) y
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
131072 inodes, 524288 blocks
26214 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=536870912
16 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (16384 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 39 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.会提示【busybox.img is not a block special device.】,输入y回车。
使用df和du命令确认一下,文件系统的类型和分区的实际大小。分区大小不是0了,变成了97M了,因为在分区里安装了文件系统。
# df -T busybox.img
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/vg_c610-lv_root
ext4 6795192 2644828 3782136 42% /
[root@c610 xen]# du -sh busybox.img
97M busybox.img3,挂载此文件系统到/mnt目录。
挂载本地回环文件(ios文件,img文件等)
# mount -o loop busybox.img /mnt
[root@c610 xen]# ls /mnt/
lost+found发现有了文件lost+found,说明挂载成功。
现在就可以在此文件系统里安装操作系统了。为了简单起见,用busybox模拟操作系统。所以编译安装busybox。
到此为止我们发现,对domu的分区创建,文件系统创建等,都是在dom0里操作进行的。
为了编译,先安装开发环境:
# yum -y groupinstall "Development Tolls" "Server Platform Development"下载busybox源代码,解压缩源代码压缩包
# tar xf busybox.tar.bz2如果在操作系统上安装busybox的话,busybox使用的库是操作系统上的动态库,但我们domu上没有操作系统,所以就没有库可以供busybox使用,所以编译busybox时,就需要把所使用的库静态连接进busybox,所以先安装busybox所使用的静态库。
# yum -y install glibc-static
# yum -y install gcc配置busybox的编译选项:
# make menuconfig出现如下画面:
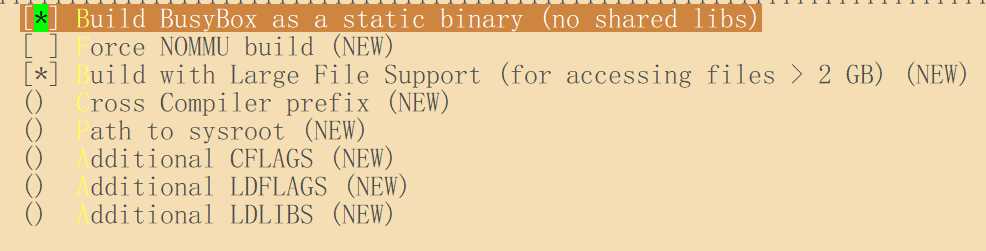
勾选:Build Busybox as a static binary (no shared libs),保存退出
编译:make
安装:make install
安装成功后,会出现[_install]目录,把此目录里的所有内容,并保持原属性,复制到挂载这domu文件系统的/mnt目录下。
# cp -a _install/* /mnt查看/mnt目录:
# ll
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Feb 1 14:17 bin
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 Feb 1 14:17 linuxrc -> bin/busybox
drwx------. 2 root root 16384 Feb 1 12:30 lost+found
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Feb 1 14:17 sbin
drwxr-xr-x. 4 root root 4096 Feb 1 14:17 usr发现已经有了几个目录,但还缺少几个目录,在/mnt下手动创建这些目录。最主要的是proc,sys,dev。
# mkdir proc sys dev etc var boot home尝试使用busybox里的sh
# chroot /mnt /bin/sh
/ # ls
bin dev home lost+found sbin usr
boot etc linuxrc proc sys var
/ #发现我们创建的目录都存在,说明一切正常。
到此为止,domu的根文件系统,我们已经准备妥当了,就差启动文件了。
前面说过,centos6不能安装在dom0上,但是可以安装在domu上,所有就直接使用原来centos上的启动文件.
在/boot下创建一个软连接。
# ln -sv vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64 vmlinuz
`vmlinuz' -> `vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64'
# ll -h
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 29 Feb 1 14:30 vmlinuz -> vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4.2M Jun 20 2018 vmlinuz-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64在/boot下再创建一个软连接
# ln -sv initramfs-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64.img initramfs.img
`initramfs.img' -> `initramfs-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64.img'
# ll -h
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 35 Feb 1 14:32 initramfs.img -> initramfs-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64.img
-rw-------. 1 root root 5.9M Jan 31 14:16 initrd-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64kdump.img
创建xl命令,创建domu所使用的配置文件,配置文件放在/etc/xen目录。xlexample是例子。
xl.conf文件是xl命令自己的配置文件。
# cd /etc/xen
# ll
total 24
drwx------. 2 root root 4096 Dec 12 20:07 auto
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 661 Dec 11 20:44 cpupool
drwx------. 2 root root 4096 Jan 31 14:56 scripts
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1436 Dec 11 20:44 xl.conf
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1386 Dec 11 20:44 xlexample.hvm
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1250 Dec 11 20:44 xlexample.pvlinux复制xlexample.pvlinux
# cp xlexample.pvlinux busybox.pvlinux修改busybox.pvlinux文件
因为我们使用的dom0里的内核文件,dom0里是使用SELinux功能的,我们要关闭它。
name = "busybox001.pvlinux"
kernel = "/boot/vmlinuz"
#ramdisk = "/boot/initrd.gz"
ramdisk = "/boot/initramfs.img"
extra = "selinux=0 init=/bin/sh"
memory = 256
vcpus = 2
#vif = [ '' ]
disk = [ '/images/xen/busybox.img,raw,xvda,rw' ]
root = "/dev/xvda ro"- name :domu的名字,不能和别的domu重复
- kernel:内核文件
- ramdisk:?
- extar:给内核传递的参数,这里传递的参数的目的是关闭selinux功能;init进程是/bin/sh
- memory:内存大小
- vcpus:cpu个数
- vif:网卡
- disk:文件系统
- root:系统启动是,把根文件系统挂载到哪里。ro是只读。
创建domu# xl help create
# xl help create
Usage: xl [-vfN] create <ConfigFile> [options] [vars]
Create a domain from config file <filename>.
Options:
-h Print this help.
-p Leave the domain paused after it is created.
-c Connect to the console after the domain is created.
-f FILE, --defconfig=FILE
Use the given configuration file.
-q, --quiet Quiet.
-n, --dryrun Dry run - prints the resulting configuration
(deprecated in favour of global -N option).
-d Enable debug messages.
-F Run in foreground until death of the domain.
-e Do not wait in the background for the death of the domain.
-V, --vncviewer Connect to the VNC display after the domain is created.xl [-vfN]里的v:显示详细信息;f:xl命令使用哪个配置文件,不指定的话默认使用/etc/xen/xl.conf
<ConfigFile>:创建domu所使用的配置文件
options里的-d:debug模式;-n:试验运行
# xl -v create busybox.pvlinux -n
Parsing config from busybox.pvlinux
{
"c_info": {
"type": "pv",
"name": "busybox001.pvlinux",
"uuid": "23537733-95f2-44d5-84d5-07aa76282134",
"run_hotplug_scripts": "True"
},
"b_info": {
"max_vcpus": 2,
"avail_vcpus": [
0,
1
],
"max_memkb": 262144,
"target_memkb": 262144,
"shadow_memkb": 4096,
"sched_params": {
},
"claim_mode": "True",
"kernel": "/boot/vmlinuz",
"cmdline": "root=/dev/xvda ro",
"ramdisk": "/boot/initramfs.img",
"type.pv": {
},
"arch_arm": {
}
},
"disks": [
{
"pdev_path": "/images/xen/busybox.img",
"vdev": "xvda",
"format": "raw",
"readwrite": 1
}
],
"on_reboot": "restart",
"on_soft_reset": "soft_reset"查看试验运行的结果,如果没有问题,就创建
[root@c610 xen]# xl -v create busybox.pvlinux创建成功
# xl -v create busybox.pvlinux
# xl list
Name ID Mem VCPUs State Time(s)
Domain-0 0 1024 2 r----- 748.7
busybox001.pvlinux 3 256 2 r----- 2.4c/c++ 学习互助QQ群:877684253

本人微信:xiaoshitou5854
以上是关于Linux虚拟化 xen的工具栈介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章