ansible安装及模块的管理
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ansible安装及模块的管理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简介1、ansible安装部署过程特别简单,学习曲线很平坦;
2、不需要单独安装客户端,知识利用现有的SSHD服务(协议)即可。
3、基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
ansible 特点
1、部署简单,只需在主控端部署Ansible环境,被控端无需做任何操作;
2、默认使用SSH协议对设备进行管理;
3、有大量常规运维操作模块,可实现日常绝大部分操作;
4、配置简单、功能强大、扩展性强;
5、支持API及自定义模块,可通过Python轻松扩展;
6、通过Playbooks来定制强大的配置、状态管理;
7、轻量级,无需在客户端安装agent,更新时,只需在操作机上进行一次更新即可;
8、提供一个功能强大、操作性强的Web管理界面和REST API接口——AWX平台。
架构图
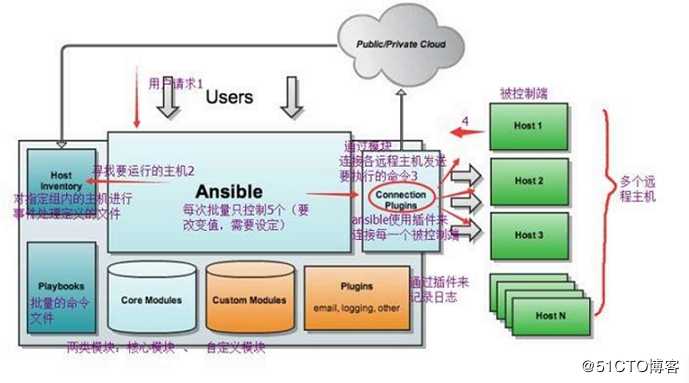
Ansible:Ansible核心程序。
HostInventory:记录由Ansible管理的主机信息,包括端口、密码、ip等。
Playbooks:“剧本”YAML格式文件,多个任务定义在一个文件中,定义主机需要调用哪些模块来完成的功能。
CoreModules:核心模块,主要操作是通过调用核心模块来完成管理任务。
CustomModules:自定义模块,完成核心模块无法完成的功能,支持多种语言。
ConnectionPlugins:连接插件,Ansible和Host通信使用ansible 任务执行模式
Ansible 系统由控制主机对被管节点的操作方式可分为两类,即adhoc和playbook:
ad-hoc模式(点对点模式)
使用单个模块,支持批量执行单条命令。ad-hoc 命令是一种可以快速输入的命令,而且不需要保存起来的命令。就相当于bash中的一句话shell。
playbook模式(剧本模式)
是Ansible主要管理方式,也是Ansible功能强大的关键所在。playbook通过多个task集合完成一类功能,如Web服务的安装部署、数据库服务器的批量备份等。可以简单地把playbook理解为通过组合多条ad-hoc操作的配置文件。
ansible 执行流程
简单理解就是Ansible在运行时, 首先读取ansible.cfg中的配置, 根据规则获取Inventory中的管理主机列表, 并行的在这些主机中执行配置的任务, 最后等待执行返回的结果。
实操
环境
管理端:CentOS 7-2 192.168.18.147
被管理端1:CentOS 7-3 192.168.18.128
被管理端2:CentOS 7-4 192.168.18.148管理端:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# yum install epel-release -y
[root@localhost ~]# yum install ansible -y
[root@localhost ~]# ansible --version
ansible 2.9.2
[root@localhost ~]# yum install tree -y
[root@localhost ~]# tree /etc/ansible/
/etc/ansible/
├── ansible.cfg #配置文件
├── hosts
└── roles
1 directory, 2 files
`配置主机清单`
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/ansible/hosts
#在24行下插入以下内容
[webserver]
192.168.18.128
[mysql]
192.168.18.148
`生成密钥对`
[root@localhost ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa): #直接回车
Created directory ‘/root/.ssh‘.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): #输入密码:abc123
Enter same passphrase again: #再次输入密码:abc123
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:5RvIVqbI9hscNK1Y4YivNnnUEgQeNfNm/WJcBXr8jWc root@localhost.localdomain
The key‘s randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| oo= . ... |
| . + * + o . |
| o o O B + |
| o @ @ + . o |
| O S * . o E|
| = = o + o |
| = . + . |
| . o o |
| . |
+----[SHA256]-----+
`密钥对位置`
[root@localhost ~]# ls -la
总用量 56
......
drwx------. 2 root root 38 1月 22 17:34 .ssh
......此处省略多行
[root@localhost ~]# cd .ssh/
[root@localhost .ssh]# ls
id_rsa(私钥) id_rsa.pub(公钥)
`把密钥推给被管理端1`
[root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.18.128
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host ‘192.168.18.128 (192.168.18.128)‘ can‘t be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:mTT+FEtzAu4X3D5srZlz93S3gye8MzbqVZFDzfJd4Gk.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:fa:5a:88:23:49:60:9b:b8:7e:4b:14:4b:3f:cd:96:a0.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes #确认链接
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.18.128‘s password: #输入相对应被管理端的root密码
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh ‘root@192.168.18.128‘"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
`把密钥推给被管理端2`
[root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.18.148
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host ‘192.168.18.148 (192.168.18.148)‘ can‘t be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:mTT+FEtzAu4X3D5srZlz93S3gye8MzbqVZFDzfJd4Gk.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:fa:5a:88:23:49:60:9b:b8:7e:4b:14:4b:3f:cd:96:a0.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes #确认链接
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.18.148‘s password: #输入相对应被管理端的root密码
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh ‘root@192.168.18.148‘"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.验证密钥是否推送成功:
被管理端1:192.168.18.128
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# cd .ssh/
[root@localhost .ssh]# ls
authorized_keys
#此时密钥推送成功被管理端2:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0
[root@localhost ~]# cd .ssh/
[root@localhost .ssh]# ls
authorized_keys
#此时密钥推送成功Ansible模块管理
1、command模块
`使用IP地址查看被管理端1的时间`
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible 192.168.18.128 -m command -a ‘date‘
Enter passphrase for key ‘/root/.ssh/id_rsa‘: #输入密钥密码abc123
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2020年 02月 02日 星期日 15:53:20 CST
`使用别名查看被管理端2的时间`
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible mysql -m command -a ‘date‘
Enter passphrase for key ‘/root/.ssh/id_rsa‘: #输入密钥密码abc123
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2020年 02月 02日 星期日 15:55:13 CST
`为避免总是输入密码的麻烦,我们可以执行免交互代理`
[root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-agent bash
[root@localhost .ssh]# ssh-add
Enter passphrase for /root/.ssh/id_rsa: #输入密钥密码abc123
Identity added: /root/.ssh/id_rsa (/root/.ssh/id_rsa)
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible webserver -m command -a ‘date‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2020年 02月 02日 星期日 16:01:40 CST
#此时可以免交互直接显示时间
`所有hosts主机执行date命令`
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible all -a ‘date‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2020年 02月 02日 星期日 16:21:08 CST
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2020年 02月 02日 星期日 16:21:08 CST2、cron模块【两种状态(state):present表示添加(可以省略),absent表示移除】
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible mysql -m cron -a ‘minute="*/1" job="/usr/bin/echo hello" name="test hello"‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": [
"test hello"
]
}
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible mysql -a ‘crontab -l‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
#Ansible: test hello
*/1 * * * * /usr/bin/echo hello此时我们可以进入被管理端2进行验证:
[root@localhost .ssh]# crontab -l
#Ansible: test hello
*/1 * * * * /usr/bin/echo hello
您在 /var/spool/mail/root 中有新邮件
[root@localhost .ssh]# vim /var/spool/mail/root
From root@localhost.localdomain Sun Feb 2 16:40:02 2020
Return-Path: <root@localhost.localdomain>
X-Original-To: root
Delivered-To: root@localhost.localdomain
Received: by localhost.localdomain (Postfix, from userid 0)
id 2255A319AE4E; Sun, 2 Feb 2020 16:40:02 +0800 (CST)
From: "(Cron Daemon)" <root@localhost.localdomain>
To: root@localhost.localdomain
Subject: Cron <root@localhost> /usr/bin/echo hello
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=UTF-8
Auto-Submitted: auto-generated
Precedence: bulk
X-Cron-Env: <XDG_SESSION_ID=19>
X-Cron-Env: <XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/0>
X-Cron-Env: <LANG=zh_CN.UTF-8>
X-Cron-Env: <SHELL=/bin/sh>
X-Cron-Env: <HOME=/root>
X-Cron-Env: <PATH=/usr/bin:/bin>
X-Cron-Env: <LOGNAME=root>
X-Cron-Env: <USER=root>
Message-Id: <20200202084002.2255A319AE4E@localhost.localdomain>
Date: Sun, 2 Feb 2020 16:40:02 +0800 (CST)
hello
#以下省略多行,每分钟生成一个此时移除计划性任务,使用absent:
[root@localhost .ssh]# ansible mysql -m cron -a ‘name="test hello" state=absent‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"envs": [],
"jobs": []
}
`此时再回到被管理端2中会发现计划任务消失`
[root@localhost ~]# crontab -l3、user模块【user模块是请求的是useradd, userdel, usermod三个指令】
`创建用户test01`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m user -a ‘name=test01‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1001,
"home": "/home/test01",
"name": "test01",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 1001
}
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1001,
"home": "/home/test01",
"name": "test01",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 1001
}
`此时回到被管理端1中验证添加用户`
[root@localhost ~]# id test01
uid=1001(test01) gid=1001(test01) 组=1001(test01)
`此时回到被管理端2中验证添加用户`
[root@localhost ~]# id test01
uid=1001(test01) gid=1001(test01) 组=1001(test01)
#此时两台被管理端test01用户均添加成功
`删除webserver端中的test01用户`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m user -a ‘name=test01 state=absent‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "test01",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
`此时回到被管理端1:webserver中验证用户情况`
[root@localhost ~]# id test01
id: test01: no such user
#此时显示找不到,说明已被删除group模块【group模块请求的是groupadd, groupdel, groupmod 三个指令】
`创建mysql组`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m group -a ‘name=mysql gid=306 system=yes‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 306,
"name": "mysql",
"state": "present",
"system": true
}
`远程查看被管理端2:mysql中是否有mysql组`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a ‘tail /etc/group‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
postfix:x:89:
stapusr:x:156:
stapsys:x:157:
stapdev:x:158:
tcpdump:x:72:
zhou:x:1000:
dhcpd:x:177:
named:x:25:
test01:x:1001:
mysql:x:306: #此时有mysql组,同时gid号为306
`创建新用户test02并添加到mysql组`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m user -a ‘name=test02 uid=306 group=mysql system=yes‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 306,
"home": "/home/test02",
"name": "test02",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": true,
"uid": 306
}
`远程查看被管理端2:mysql中是否在mysql组是否有新创建的用户test02`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a ‘id test02‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
uid=306(test02) gid=306(mysql) 组=306(mysql)copy模块
`远程把被管理端2:mysql中的etc目录下fstab自动挂载文件,复制到opt目录下并且取名为fstab.bk,属组为root,权限为644`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m copy -a ‘src=/etc/fstab dest=/opt/fstab.bk owner=root mode=644‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "100f3bbf6644926857bbec2a40ab2f70bf1c060b",
"dest": "/opt/fstab.bk",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "f57167de0e8f6f2963771a72af8a2840",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 595,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1580693038.81-171191249824445/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
`远程查看被管理端2:mysql的opt目录下是否在mysql组是否有fstab.bk文件`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a ‘ls -l /opt‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
总用量 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 595 2月 3 09:24 fstab.bk
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
`指定内容this is test,重定向生成新文件test.txt在opt目录下`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m copy -a ‘content="this is test" dest=/opt/test.txt‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"checksum": "b6794b2000d94d348203d0279c2e7322b922cb16",
"dest": "/opt/test.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "8c6d115258631625b625486f81b09532",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 12,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1580693472.89-123279558248268/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
`远程查看被管理端2:mysql的opt目录下的test.txt文件中内容是否为this is test`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -a ‘cat /opt/test.txt‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
this is testfile模块
`路径opt下的文件test.txt,用户为test02,组指定为mysql,权限为666`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a ‘path=/opt/test.txt owner=test02 group=mysql mode=666‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"gid": 306,
"group": "mysql",
"mode": "0666",
"owner": "test02",
"path": "/opt/test.txt",
"secontext": "system_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 12,
"state": "file",
"uid": 306
}
`此时回到被管理端2:mysql中opt目录下的test.txt文件的详细情况`
[root@localhost ~]# cd /opt/
[root@localhost opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 595 2月 3 09:24 fstab.bk
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
-rw-rw-rw-. 1 test02 mysql 12 2月 3 09:31 test.txt
#此时test.txt文件属主为test02,属组为mysql,权限为666
`设置/opt/test.txt.link为/opt/test.txt的链接文件`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a ‘src=/opt/test.txt path=/opt/test.txt.link state=link‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/opt/test.txt.link",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0777",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 13,
"src": "/opt/test.txt",
"state": "link",
"uid": 0
}
`此时回到被管理端2:mysql中opt目录下查看此链接文件`
[root@localhost opt]# ls -l
总用量 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 595 2月 3 09:24 fstab.bk
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 3月 26 2015 rh
-rw-rw-rw-. 1 test02 mysql 12 2月 3 09:31 test.txt
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 13 2月 3 09:59 test.txt.link -> /opt/test.txt #链接性的文件
`创建一个空文件`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a ‘path=/opt/abc.txt state=touch‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"dest": "/opt/abc.txt",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"secontext": "unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0",
"size": 0,
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
`此时回到被管理端2:mysql中opt目录下abc.txt文件的详细情况`
[root@localhost opt]# ls #此时有abc.txt文件
abc.txt fstab.bk rh test.txt test.txt.link
[root@localhost opt]# cat abc.txt #因为是空文件,所以没有内容
`删除创建的abc.txt空文件`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible mysql -m file -a ‘path=/opt/abc.txt state=absent‘
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"path": "/opt/abc.txt",
"state": "absent"
}
`此时回到被管理端2:mysql中opt目录下是否有abc.txt文件`
[root@localhost opt]# ls
fstab.bk rh test.txt test.txt.linkping模块
`测试两台被管理端是否在线`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible all -m ping
192.168.18.148 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.18.128 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}yum模块
`在被管理端1:webserver中安装httpd服务`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m yum -a ‘name=httpd‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"changes": {
"installed": [
"httpd"
]
},
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.huaweicloud.com
* extras: mirror.bit.edu.cn
* updates: mirror.bit.edu.cn
Resolving Dependencies
--> Running transaction check
---> Package httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-90.el7.centos will be installed
--> Processing Dependency: httpd-tools = 2.4.6-90.el7.centos for package: httpd-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: /etc/mime.types for package: httpd-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libaprutil-1.so.0()(64bit) for package: httpd-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64
--> Processing Dependency: libapr-1.so.0()(64bit) for package: httpd-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64
--> Running transaction check
---> Package apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-5.el7 will be installed
---> Package apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7 will be installed
---> Package httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.4.6-90.el7.centos will be installed
---> Package mailcap.noarch 0:2.1.41-2.el7 will be installed
--> Finished Dependency Resolution
Dependencies Resolved
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
httpd x86_64 2.4.6-90.el7.centos base 2.7 M
Installing for dependencies:
apr x86_64 1.4.8-5.el7 base 103 k
apr-util x86_64 1.5.2-6.el7 base 92 k
httpd-tools x86_64 2.4.6-90.el7.centos base 91 k
mailcap noarch 2.1.41-2.el7 base 31 k
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 1 Package (+4 Dependent packages)
Total download size: 3.0 M
Installed size: 10 M
Downloading packages:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 1.0 MB/s | 3.0 MB 00:03
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : apr-1.4.8-5.el7.x86_64 1/5
Installing : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 2/5
Installing : httpd-tools-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64 3/5
Installing : mailcap-2.1.41-2.el7.noarch 4/5
Installing : httpd-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64 5/5
Verifying : apr-1.4.8-5.el7.x86_64 1/5
Verifying : mailcap-2.1.41-2.el7.noarch 2/5
Verifying : httpd-tools-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64 3/5
Verifying : apr-util-1.5.2-6.el7.x86_64 4/5
Verifying : httpd-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64 5/5
Installed:
httpd.x86_64 0:2.4.6-90.el7.centos
Dependency Installed:
apr.x86_64 0:1.4.8-5.el7 apr-util.x86_64 0:1.5.2-6.el7
httpd-tools.x86_64 0:2.4.6-90.el7.centos mailcap.noarch 0:2.1.41-2.el7
Complete!
"
]
}
#安装完成后会显示过程
`此时可以返回被管理端1:webserver中查看httpd服务是否安装成功`
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -q httpd
httpd-2.4.6-90.el7.centos.x86_64 #此时服务安装完成
`可以用以下命令移除服务`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m yum -a ‘name=httpd state=absent‘service模块
`启动被管理端2中的httpd服务`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m service -a ‘enabled=true name=httpd state=started‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "httpd",
"state": "started",
......此处省略多行
`此时到被管理端1:webserver中查看httpd服务的状态`
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl status httpd.service
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 一 2020-02-03 10:24:28 CST; 2min 25s ago
#此时状态显示为running运行shell模块
`创建一个用户,为用户生成免交互密码`
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m user -a ‘name=jarry‘ #创建新用户jarry
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": true,
"group": 1001,
"home": "/home/jarry",
"name": "jarry",
"shell": "/bin/bash",
"state": "present",
"system": false,
"uid": 1001
}
[root@localhost ~]# ansible webserver -m shell -a ‘echo abc123 | passwd --stdin jarry‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
更改用户 jarry 的密码 。
passwd:所有的身份验证令牌已经成功更新。
#生成jarry用户的登录密码为abc123script模块
`首先在管理端编写脚本`
[root@localhost ~]# cd /opt/
[root@localhost opt]# vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "this is test script" > /opt/script.txt
chmod 666 /opt/script.txt
[root@localhost opt]# ls
rh test.sh
[root@localhost opt]# chmod +x test.sh #给予执行权限
`对所有被管理端执行test.sh脚本`
[root@localhost opt]# ansible all -m script -a ‘test.sh‘
192.168.18.128 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.18.128 closed.
",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.18.128 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
192.168.18.148 | CHANGED => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.18.148 closed.
",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.18.148 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
`验证两台被管理端的opt目录下是否有script.txt文件`
#被管理端1:
[root@localhost ~]# cd /opt/
[root@localhost opt]# ls
rh script.txt
[root@localhost opt]# cat script.txt
this is test script
#被管理端2:
[root@localhost opt]# ls
fstab.bk rh script.txt test.txt test.txt.link
[root@localhost opt]# cat script.txt
this is test scriptsetup模块
`列出被管理端2:mysql的所有主机信息`
[root@localhost opt]# ansible mysql -m setup
192.168.18.148 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"192.168.122.1",
"192.168.18.148"
],
"ansible_all_ipv6_addresses": [
"fe80::1cb1:b734:7f72:576f",
"fe80::578f:4368:6a2c:80d7",
"fe80::6a0c:e6a0:7978:3543"
],
"ansible_apparmor": {
"status": "disabled"
},
"ansible_architecture": "x86_64",
"ansible_bios_date": "07/29/2019",
"ansible_bios_version": "6.00",
"ansible_cmdline": {
"BOOT_IMAGE": "/vmlinuz-3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64",
"LANG": "zh_CN.UTF-8",
"crashkernel": "auto",
"quiet": true,
"rhgb": true,
"ro": true,
"root": "UUID=32c169ff-9bf7-4d89-a2f1-a99a7e59d4f2"
},
"ansible_date_time": {
"date": "2020-02-03",
"day": "03",
"epoch": "1580698171",
"hour": "10",
"iso8601": "2020-02-03T02:49:31Z",
"iso8601_basic": "20200203T104931948449",
"iso8601_basic_short": "20200203T104931",
"iso8601_micro": "2020-02-03T02:49:31.948682Z",
"minute": "49",
"month": "02",
"second": "31",
"time": "10:49:31",
"tz": "CST",
"tz_offset": "+0800",
"weekday": "星期一",
"weekday_number": "1",
"weeknumber": "05",
"year": "2020"
},
"ansible_default_ipv4": {
"address": "192.168.18.148",
"alias": "ens33",
"broadcast": "192.168.18.255",
"gateway": "192.168.18.2",
"interface": "ens33",
"macaddress": "00:0c:29:79:45:8e",
"mtu": 1500,
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"network": "192.168.18.0",
"type": "ether"
},
......
......
......以上是关于ansible安装及模块的管理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章