链表基础算法题
Posted superjishere
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了链表基础算法题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目一

代码实现
1 package class_03; 2 3 public class Code_07_ReverseList { 4 5 public static class Node { 6 public int value; 7 public Node next; 8 9 public Node(int data) { 10 this.value = data; 11 } 12 } 13 14 public static Node reverseList(Node head) { 15 Node pre = null; 16 Node next = null; 17 while (head != null) { 18 next = head.next; 19 head.next = pre; 20 pre = head; 21 head = next; 22 } 23 return pre; 24 } 25 26 public static class DoubleNode { 27 public int value; 28 public DoubleNode last; 29 public DoubleNode next; 30 31 public DoubleNode(int data) { 32 this.value = data; 33 } 34 } 35 36 public static DoubleNode reverseList(DoubleNode head) { 37 DoubleNode pre = null; 38 DoubleNode next = null; 39 while (head != null) { 40 next = head.next; 41 head.next = pre; 42 head.last = next; 43 pre = head; 44 head = next; 45 } 46 return pre; 47 } 48 49 public static void printLinkedList(Node head) { 50 System.out.print("Linked List: "); 51 while (head != null) { 52 System.out.print(head.value + " "); 53 head = head.next; 54 } 55 System.out.println(); 56 } 57 58 public static void printDoubleLinkedList(DoubleNode head) { 59 System.out.print("Double Linked List: "); 60 DoubleNode end = null; 61 while (head != null) { 62 System.out.print(head.value + " "); 63 end = head; 64 head = head.next; 65 } 66 System.out.print("| "); 67 while (end != null) { 68 System.out.print(end.value + " "); 69 end = end.last; 70 } 71 System.out.println(); 72 } 73 74 public static void main(String[] args) { 75 Node head1 = new Node(1); 76 head1.next = new Node(2); 77 head1.next.next = new Node(3); 78 printLinkedList(head1); 79 head1 = reverseList(head1); 80 printLinkedList(head1); 81 82 DoubleNode head2 = new DoubleNode(1); 83 head2.next = new DoubleNode(2); 84 head2.next.last = head2; 85 head2.next.next = new DoubleNode(3); 86 head2.next.next.last = head2.next; 87 head2.next.next.next = new DoubleNode(4); 88 head2.next.next.next.last = head2.next.next; 89 printDoubleLinkedList(head2); 90 printDoubleLinkedList(reverseList(head2)); 91 92 } 93 94 }
题目二

思路
有点类似归并排序外排的方式, 从小的开始比对,如果都相等就打印。
代码实现
1 package class_03; 2 3 public class Code_10_PrintCommonPart { 4 5 public static class Node { 6 public int value; 7 public Node next; 8 public Node(int data) { 9 this.value = data; 10 } 11 } 12 13 public static void printCommonPart(Node head1, Node head2) { 14 System.out.print("Common Part: "); 15 while (head1 != null && head2 != null) { 16 if (head1.value < head2.value) { 17 head1 = head1.next; 18 } else if (head1.value > head2.value) { 19 head2 = head2.next; 20 } else { 21 System.out.print(head1.value + " "); 22 head1 = head1.next; 23 head2 = head2.next; 24 } 25 } 26 System.out.println(); 27 } 28 29 public static void printLinkedList(Node node) { 30 System.out.print("Linked List: "); 31 while (node != null) { 32 System.out.print(node.value + " "); 33 node = node.next; 34 } 35 System.out.println(); 36 } 37 38 public static void main(String[] args) { 39 Node node1 = new Node(2); 40 node1.next = new Node(3); 41 node1.next.next = new Node(5); 42 node1.next.next.next = new Node(6); 43 44 Node node2 = new Node(1); 45 node2.next = new Node(2); 46 node2.next.next = new Node(5); 47 node2.next.next.next = new Node(7); 48 node2.next.next.next.next = new Node(8); 49 50 printLinkedList(node1); 51 printLinkedList(node2); 52 printCommonPart(node1, node2); 53 54 } 55 56 }
题目三

链表问题在笔试和面试上的要求不一样,笔试中一般都考虑最快的方式,不用考虑空间,面试中除了考虑时间复杂度外还要考虑空间复杂度。
思路
①准备一个栈,遍历的过程中,把所有的节点压入栈中,第二次遍历,每遍历到一个数,就从栈中弹出一个数,每一步比对值都相等,就是回文结构;有任何一个不相等就不是回文结构。
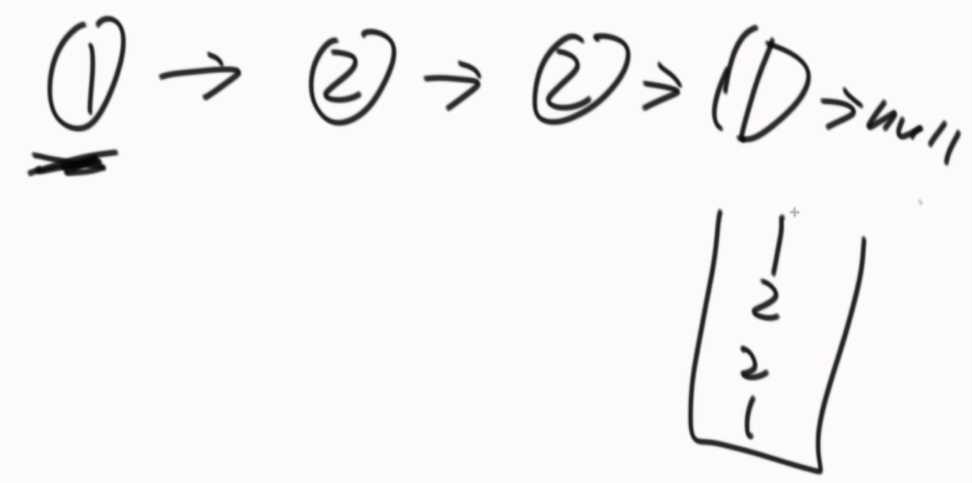
②准备一个栈,一个慢指针,一个快指针,第一次遍历的过程中,快指针一次走2个节点,慢指针一次走一个节点,当快指针到达最后一个节点时,把慢指针所指向的节点之后的节点依次压入栈中,第二次遍历,每遍历到一个数,就从栈中弹出一个数,直到把栈中的数都比对完,每一步比对值都相等,就是回文结构;有任何一个不相等就不是回文结构。相当于把右边的一半折过去,比对是否相等。
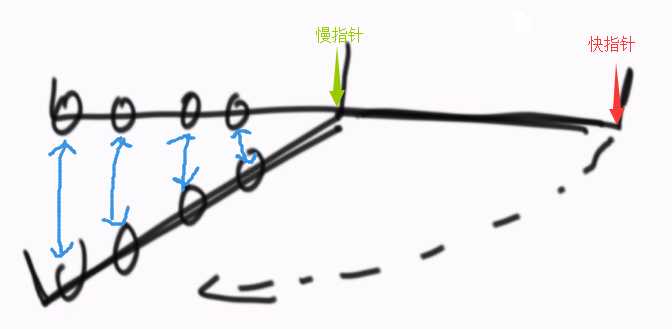
③在②的基础上改进,不准备辅助数组,还是一个慢指针一个快指针,快指针到终点,慢指针在中点时,将右半边的链表逆序。
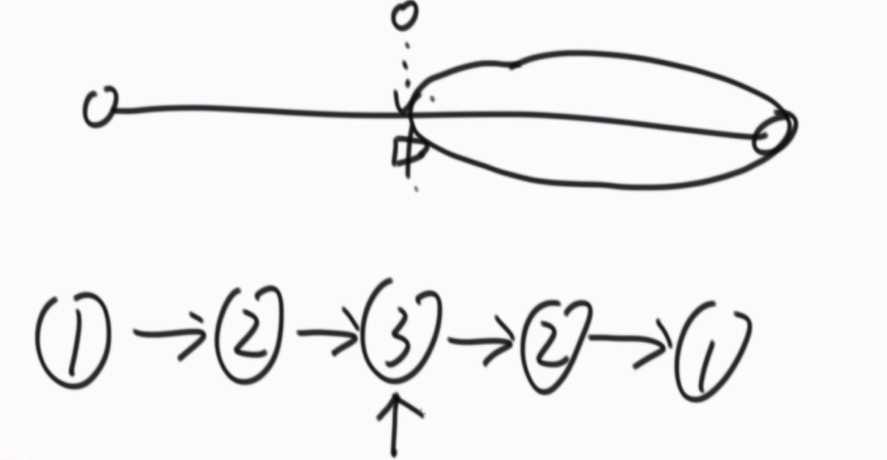
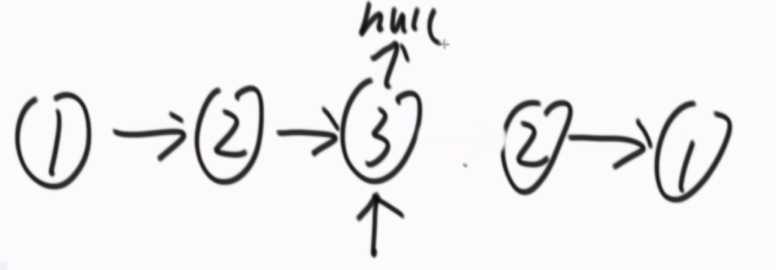 ??
??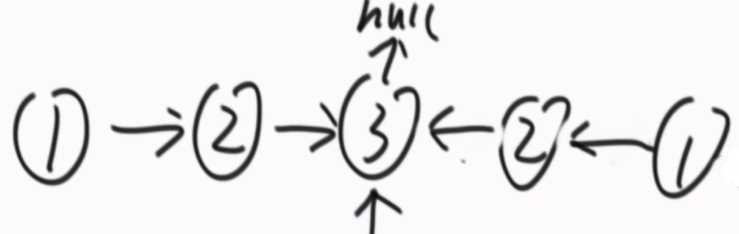 ??
??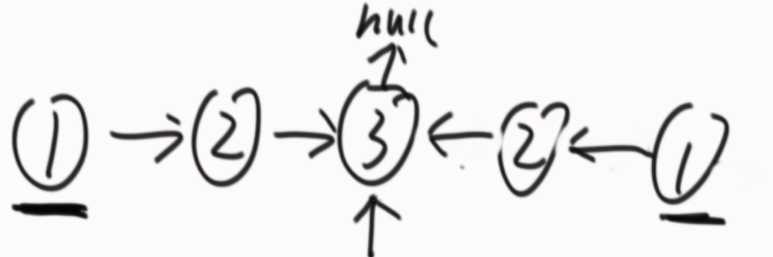
从两边开始依次往中间走,每走一个比对一次,直到两边有任何一边走到了中点的节点(怎么判断?这个节点的next为null,则代表它是那个中间的节点),如果全部相等就是回文结构,有一步不等就不是回文结构。
返回完结果后,把后半段的结构恢复成原来的样子。
注意:奇数个节点,要保证慢指针走到最中间的节点位置,偶数个节点要保证慢指针走到中间两个节点的中前面那个节点的位置。
代码实现
1 package class_03; 2 3 import java.util.Stack; 4 5 public class Code_11_IsPalindromeList { 6 7 public static class Node { 8 public int value; 9 public Node next; 10 11 public Node(int data) { 12 this.value = data; 13 } 14 } 15 16 // need n extra space 17 public static boolean isPalindrome1(Node head) { 18 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); 19 Node cur = head; 20 while (cur != null) { 21 stack.push(cur); 22 cur = cur.next; 23 } 24 while (head != null) { 25 if (head.value != stack.pop().value) { 26 return false; 27 } 28 head = head.next; 29 } 30 return true; 31 } 32 33 // need n/2 extra space 34 public static boolean isPalindrome2(Node head) { 35 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 36 return true; 37 } 38 Node right = head.next; 39 Node cur = head; 40 while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) { 41 right = right.next; 42 cur = cur.next.next; 43 } 44 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); 45 while (right != null) { 46 stack.push(right); 47 right = right.next; 48 } 49 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { 50 if (head.value != stack.pop().value) { 51 return false; 52 } 53 head = head.next; 54 } 55 return true; 56 } 57 58 // need O(1) extra space 59 public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) { 60 if (head == null || head.next == null) { 61 return true; 62 } 63 Node n1 = head; 64 Node n2 = head; 65 while (n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null) { // find mid node 66 n1 = n1.next; // n1 -> mid 67 n2 = n2.next.next; // n2 -> end 68 } 69 n2 = n1.next; // n2 -> right part first node 70 n1.next = null; // mid.next -> null 71 Node n3 = null; 72 while (n2 != null) { // right part convert 73 n3 = n2.next; // n3 -> save next node 74 n2.next = n1; // next of right node convert 75 n1 = n2; // n1 move 76 n2 = n3; // n2 move 77 } 78 n3 = n1; // n3 -> save last node 79 n2 = head;// n2 -> left first node 80 boolean res = true; 81 while (n1 != null && n2 != null) { // check palindrome 82 if (n1.value != n2.value) { 83 res = false; 84 break; 85 } 86 n1 = n1.next; // left to mid 87 n2 = n2.next; // right to mid 88 } 89 n1 = n3.next; 90 n3.next = null; 91 while (n1 != null) { // recover list 92 n2 = n1.next; 93 n1.next = n3; 94 n3 = n1; 95 n1 = n2; 96 } 97 return res; 98 } 99 100 public static void printLinkedList(Node node) { 101 System.out.print("Linked List: "); 102 while (node != null) { 103 System.out.print(node.value + " "); 104 node = node.next; 105 } 106 System.out.println(); 107 } 108 109 public static void main(String[] args) { 110 111 Node head = null; 112 printLinkedList(head); 113 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 114 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 115 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 116 printLinkedList(head); 117 System.out.println("========================="); 118 119 head = new Node(1); 120 printLinkedList(head); 121 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 122 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 123 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 124 printLinkedList(head); 125 System.out.println("========================="); 126 127 head = new Node(1); 128 head.next = new Node(2); 129 printLinkedList(head); 130 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 131 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 132 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 133 printLinkedList(head); 134 System.out.println("========================="); 135 136 head = new Node(1); 137 head.next = new Node(1); 138 printLinkedList(head); 139 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 140 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 141 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 142 printLinkedList(head); 143 System.out.println("========================="); 144 145 head = new Node(1); 146 head.next = new Node(2); 147 head.next.next = new Node(3); 148 printLinkedList(head); 149 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 150 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 151 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 152 printLinkedList(head); 153 System.out.println("========================="); 154 155 head = new Node(1); 156 head.next = new Node(2); 157 head.next.next = new Node(1); 158 printLinkedList(head); 159 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 160 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 161 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 162 printLinkedList(head); 163 System.out.println("========================="); 164 165 head = new Node(1); 166 head.next = new Node(2); 167 head.next.next = new Node(3); 168 head.next.next.next = new Node(1); 169 printLinkedList(head); 170 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 171 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 172 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 173 printLinkedList(head); 174 System.out.println("========================="); 175 176 head = new Node(1); 177 head.next = new Node(2); 178 head.next.next = new Node(2); 179 head.next.next.next = new Node(1); 180 printLinkedList(head); 181 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 182 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 183 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 184 printLinkedList(head); 185 System.out.println("========================="); 186 187 head = new Node(1); 188 head.next = new Node(2); 189 head.next.next = new Node(3); 190 head.next.next.next = new Node(2); 191 head.next.next.next.next = new Node(1); 192 printLinkedList(head); 193 System.out.print(isPalindrome1(head) + " | "); 194 System.out.print(isPalindrome2(head) + " | "); 195 System.out.println(isPalindrome3(head) + " | "); 196 printLinkedList(head); 197 System.out.println("========================="); 198 199 } 200 201 }
题目四

思路
笔试:将链表中的数依次放入数组中,用荷兰国旗问题的方法来解决,之后再把数组中各个元素重新链接,恢复成链表结构。
进阶:荷兰国旗问题的方法保证不了稳定性,且因为需要一个辅助数组,额外空间复杂度得O(n)。
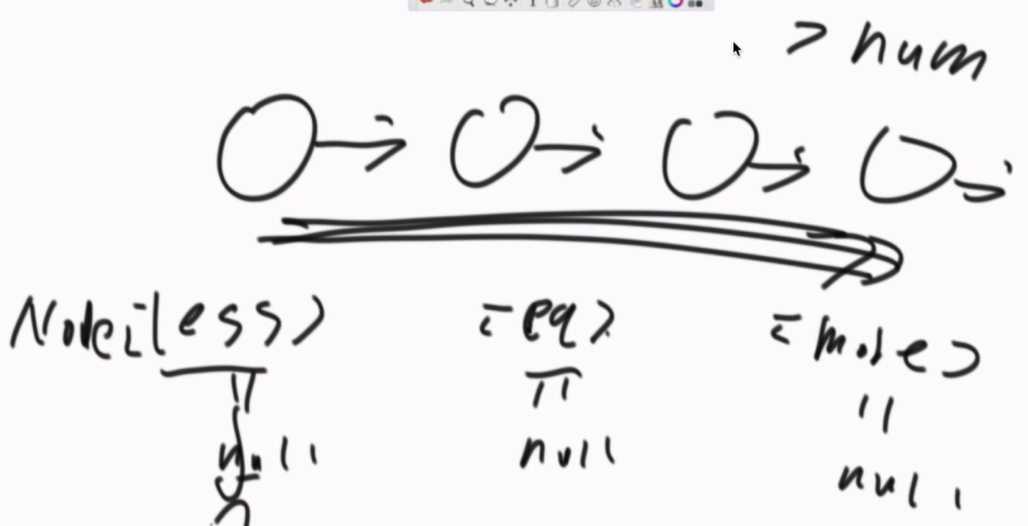
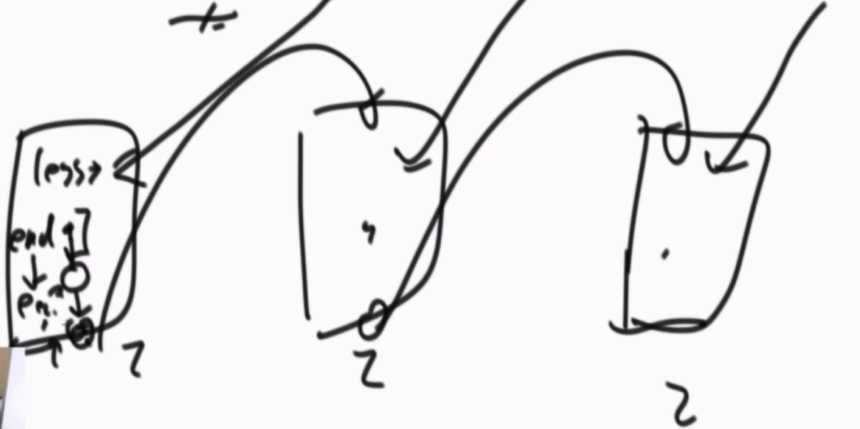
引入6个变量,less,equal,more都是节点类型,初始都为null。它们三个“类型”每个“类型”还各需要一个变量来链接对应“类型”的链表,less-end、equal-end、more-end。
相当于把一个大的链表拆成3种小链表,再把三种小链表合成一个大链表。
先遍历一下链表,找到第一个小于num的节点,让less和less-end等于该节点;找到第一个大于num的节点,让more和more-end等于该节点;找到第一个等于num的节点,让equal和equal-end等于该节点;
再遍历一次链表,找到小于num的节点,先判断是不是less,如果是不用管,如果不是,将这个节点挂在less-end的next上;equal和more也一样。直到整个链表遍历完成。
最后将三个链表整合为一个链表。less-end和equal相连,equal-end和more相连。其中,还要考虑某种链表没有节点的情况。
代码实现
1 package class_03; 2 3 public class Code_12_SmallerEqualBigger { 4 5 public static class Node { 6 public int value; 7 public Node next; 8 9 public Node(int data) { 10 this.value = data; 11 } 12 } 13 14 public static Node listPartition1(Node head, int pivot) { 15 if (head == null) { 16 return head; 17 } 18 Node cur = head; 19 int i = 0; 20 while (cur != null) { 21 i++; 22 cur = cur.next; 23 } 24 Node[] nodeArr = new Node[i]; 25 i = 0; 26 cur = head; 27 for (i = 0; i != nodeArr.length; i++) { 28 nodeArr[i] = cur; 29 cur = cur.next; 30 } 31 arrPartition(nodeArr, pivot); 32 for (i = 1; i != nodeArr.length; i++) { 33 nodeArr[i - 1].next = nodeArr[i]; 34 } 35 nodeArr[i - 1].next = null; 36 return nodeArr[0]; 37 } 38 39 public static void arrPartition(Node[] nodeArr, int pivot) { 40 int small = -1; 41 int big = nodeArr.length; 42 int index = 0; 43 while (index != big) { 44 if (nodeArr[index].value < pivot) { 45 swap(nodeArr, ++small, index++); 46 } else if (nodeArr[index].value == pivot) { 47 index++; 48 } else { 49 swap(nodeArr, --big, index); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 54 public static void swap(Node[] nodeArr, int a, int b) { 55 Node tmp = nodeArr[a]; 56 nodeArr[a] = nodeArr[b]; 57 nodeArr[b] = tmp; 58 } 59 60 public static Node listPartition2(Node head, int pivot) { 61 Node sH = null; // small head 62 Node sT = null; // small tail 63 Node eH = null; // equal head 64 Node eT = null; // equal tail 65 Node bH = null; // big head 66 Node bT = null; // big tail 67 Node next = null; // save next node 68 // every node distributed to three lists 69 while (head != null) { 70 next = head.next; 71 head.next = null; 72 if (head.value < pivot) { 73 if (sH == null) { 74 sH = head; 75 sT = head; 76 } else { 77 sT.next = head; 78 sT = head; 79 } 80 } else if (head.value == pivot) { 81 if (eH == null) { 82 eH = head; 83 eT = head; 84 } else { 85 eT.next = head; 86 eT = head; 87 } 88 } else { 89 if (bH == null) { 90 bH = head; 91 bT = head; 92 } else { 93 bT.next = head; 94 bT = head; 95 } 96 } 97 head = next; 98 } 99 // small and equal reconnect 100 if (sT != null) { 101 sT.next = eH; 102 eT = eT == null ? sT : eT; 103 } 104 // all reconnect 105 if (eT != null) { 106 eT.next = bH; 107 } 108 return sH != null ? sH : eH != null ? eH : bH; 109 } 110 111 public static void printLinkedList(Node node) { 112 System.out.print("Linked List: "); 113 while (node != null) { 114 System.out.print(node.value + " "); 115 node = node.next; 116 } 117 System.out.println(); 118 } 119 120 public static void main(String[] args) { 121 Node head1 = new Node(7); 122 head1.next = new Node(9); 123 head1.next.next = new Node(1); 124 head1.next.next.next = new Node(8); 125 head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 126 head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(2); 127 head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 128 printLinkedList(head1); 129 // head1 = listPartition1(head1, 4); 130 head1 = listPartition2(head1, 5); 131 printLinkedList(head1); 132 133 } 134 135 }
题目五


简而言之就是,一个节点不光有next指针,还有一个random指针,可能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向null。
不要动原结构,返回一个与原结构一样的副本,也是node类型。
思路
方法一:利用哈希表
哈希表:
 插入,查询的时间复杂度都是O(1),与数据量没关系。空间复杂度O(n)
插入,查询的时间复杂度都是O(1),与数据量没关系。空间复杂度O(n)
第一次遍历,
准备一个哈希表,存放原结构和原结构副本的对应关系,key是原结构的某个节点,value是它的副本。
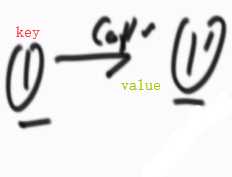
第二次遍历,
可以通过哈希表找到原结构对应的副本,但这个副本的next和random指针都是指向null。
我们可以通过①的next找到②,通过哈希表找到②的副本②‘,这时设置①的副本①’的next为②的副本②‘。
我们可以通过①的random找到③,通过哈希表找到③的副本③‘,这时设置①的副本①’的random为③的副本③‘。
·····以此类推,
直到把所有节点都遍历完毕,就完成了对原结构的深度拷贝。
方法二:不使用哈希表
第一次遍历节点,
让①的next指向①的副本①’,①的副本①’的next指向②,②的next指向②‘,②’的next指向③,③的next指向③‘,③’的next指向null。
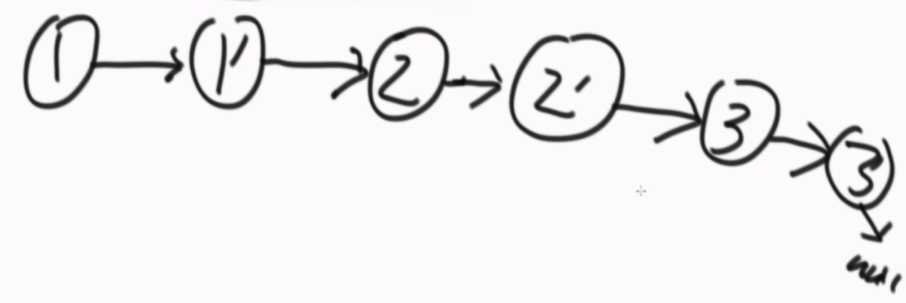
第二次遍历,
拿出①和①‘,可以通过①的random找到③,通过③的next找到③’,让①的random指针指向③‘。
同理···依次类推,把所有节点的random都设置完毕。
最后,分离next指针的指向
代码实现
1 package class_03; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 5 public class Code_13_CopyListWithRandom { 6 7 public static class Node { 8 public int value; 9 public Node next; 10 public Node rand; 11 12 public Node(int data) { 13 this.value = data; 14 } 15 } 16 17 public static Node copyListWithRand1(Node head) { 18 HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); 19 Node cur = head; 20 while (cur != null) { 21 map.put(cur, new Node(cur.value)); 22 cur = cur.next; 23 } 24 cur = head; 25 while (cur != null) { 26 map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); 27 map.get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand); 28 cur = cur.next; 29 } 30 return map.get(head); 31 } 32 33 public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head) { 34 if (head == null) { 35 return null; 36 } 37 Node cur = head; 38 Node next = null; 39 // copy node and link to every node 40 while (cur != null) { 41 next = cur.next; 42 cur.next = new Node(cur.value); 43 cur.next.next = next; 44 cur = next; 45 } 46 cur = head; 47 Node curCopy = null; 48 // set copy node rand 49 while (cur != null) { 50 next = cur.next.next; 51 curCopy = cur.next; 52 curCopy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null; 53 cur = next; 54 } 55 Node res = head.next; 56 cur = head; 57 // split 58 while (cur != null) { 59 next = cur.next.next; 60 curCopy = cur.next; 61 cur.next = next; 62 curCopy.next = next != null ? next.next : null; 63 cur = next; 64 } 65 return res; 66 } 67 68 public static void printRandLinkedList(Node head) { 69 Node cur = head; 70 System.out.print("order: "); 71 while (cur != null) { 72 System.out.print(cur.value + " "); 73 cur = cur.next; 74 } 75 System.out.println(); 76 cur = head; 77 System.out.print("rand: "); 78 while (cur != null) { 79 System.out.print(cur.rand == null ? "- " : cur.rand.value + " "); 80 cur = cur.next; 81 } 82 System.out.println(); 83 } 84 85 public static void main(String[] args) { 86 Node head = null; 87 Node res1 = null; 88 Node res2 = null; 89 printRandLinkedList(head); 90 res1 = copyListWithRand1(head); 91 printRandLinkedList(res1); 92 res2 = copyListWithRand2(head); 93 printRandLinkedList(res2); 94 printRandLinkedList(head); 95 System.out.println("========================="); 96 97 head = new Node(1); 98 head.next = new Node(2); 99 head.next.next = new Node(3); 100 head.next.next.next = new Node(4); 101 head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 102 head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); 103 104 head.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 1 -> 6 105 head.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next.next; // 2 -> 6 106 head.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next.next; // 3 -> 5 107 head.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next; // 4 -> 3 108 head.next.next.next.next.rand = null; // 5 -> null 109 head.next.next.next.next.next.rand = head.next.next.next; // 6 -> 4 110 111 printRandLinkedList(head); 112 res1 = copyListWithRand1(head); 113 printRandLinkedList(res1); 114 res2 = copyListWithRand2(head); 115 printRandLinkedList(res2); 116 printRandLinkedList(head); 117 System.out.println("========================="); 118 119 } 120 121 }
题目六(难)

思路
怎么判断一个单链表有环还是无环?
进阶:如果有环,返回第一个入环的节点,如果无环,返回null。
答:
方法一:用哈希表。
hashMap结构,有key和对应的value,能获取哈希表中是否有这个key,也可以设置或查询某个key的value。
hashSet结构,不用管key的value,只要能获取哈希表中是否有这个key即可。
从head开始遍历链表,放入哈希表中,当发现某个节点在哈希表中已经记录过时,则表明该链表是有环的,且该节点是第一个入环的节点。当遍历到最后,最后一个节点next指针指向null,表示无环。
方法二:不用哈希表。
准备两个指针,一个快指针一个慢指针,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步。
如果快指针在走的过程中遇到null了,直接返回无环。
如果有环,快指针一定会和慢指针在环上相遇。
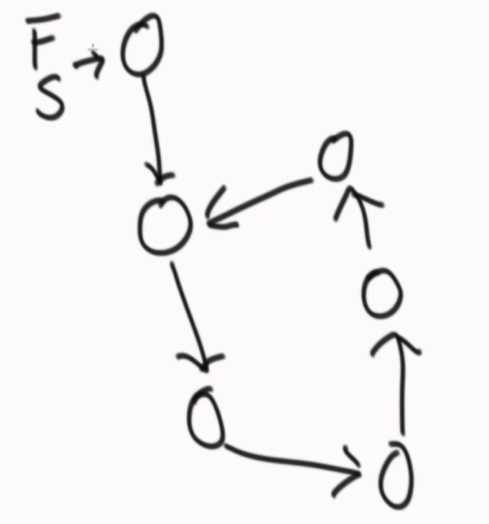 ??
?? 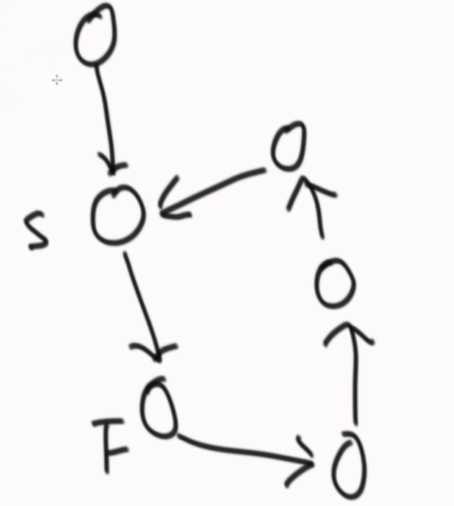 ??
??  ??
?? 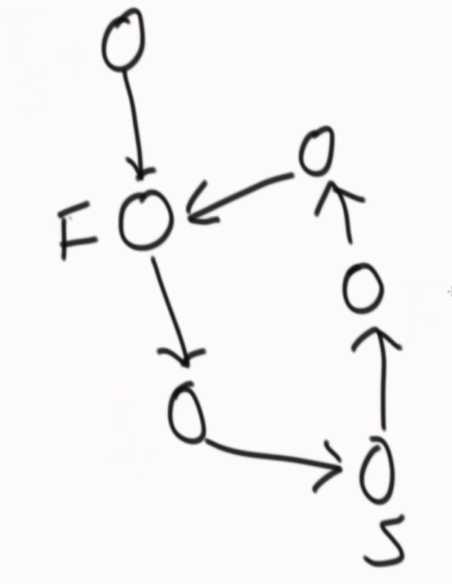 ??
?? 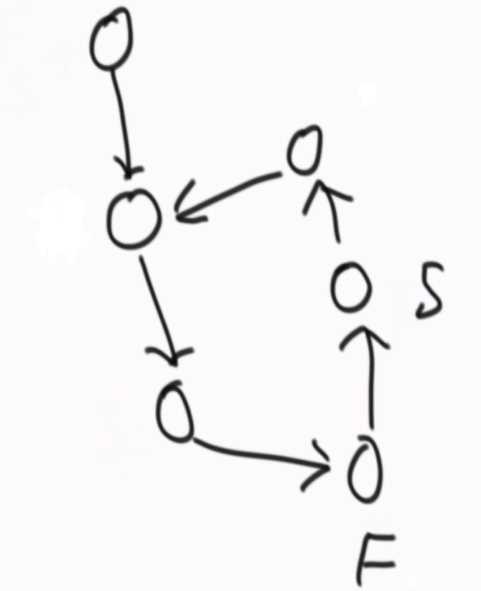 ??
?? 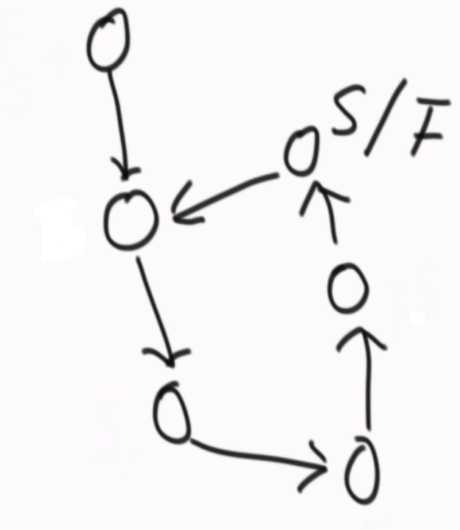
相遇的时刻,快指针回到开头,由一次走两步改为一次走一步,快指针和慢指针一定会在第一个入环节点相遇。
 ??
?? 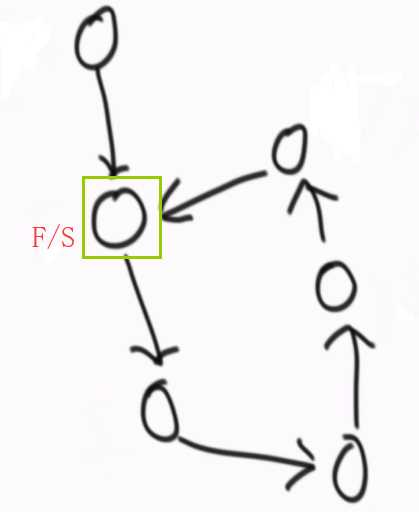
怎么判断两个无环单链表的第一个相交节点?
一个无环单链表和一个有环单链表不可能相交!要么两个都是无环,要么两个都是有环。
上一个问题我们可以得到一个链表是否有环,用loop来记录,如果为null代表无环,如果不为null则是无环,且第一个入环的节点就是loop。
方法一:用哈希表。
把链表1遍历放入哈希表中,再遍历链表2,看是否有节点出现在哈希表中过,第一个在的就是第一个相交的节点,如果到最后都没有,就是不相交的。
方法二:不用哈希表。
先遍历链表1,统计链表1的长度len1以及拿到链表1的最后一个节点end1;
再遍历链表2,统计链表2的长度len2以及拿到链表2的最后一个节点end2;
拿到四个变量后,判断end1是否和end2是同一个节点(内存地址相等),如果不等,不可能相交;如果相等,说明相交,但end不代表是第一个入环的节点。
假如len1是100,len2是80,head1先走20步,然后head1和head2一起走,最终一定会共同走到第一个相交的节点处。
怎么判断两个有环单链表的第一个相交节点?
三种拓扑结构:
①两个链表各自成环,不相交。

②先相交,再共同拥有一个环。
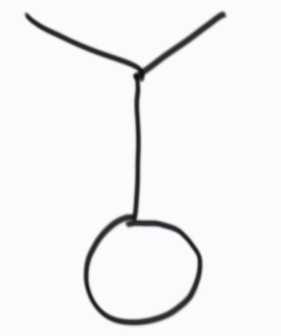

③先不相交,但共同拥有一个环。
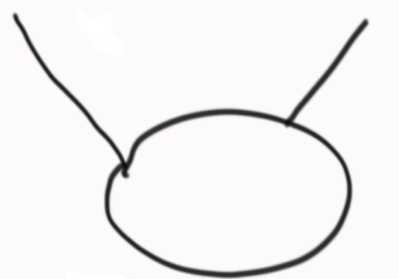
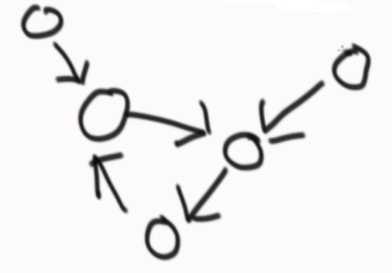
怎么区分三种拓扑结构:
如果loop1和loop2的内存地址一样,是②结构,等同于求两个无环链表相交。
如果loop1≠loop2可能是①或③的情况,让loop1继续不断通过next往下走,
如果loop1一路next之后转回自己了 ,还没遇到loop2,就是①的情况,两个链表不相交,返回null;
如果loop1一路next之后遇到loop2了,就是③的情况,两个链表相交,返回loop1或loop2中的哪一个作为第一个相交的节点都对,因为loop1是距离链表1最近的相交节点,loop2是距离链表2最近的相交节点,都叫第一个相交的节点。
代码实现
1 package class_03; 2 3 public class Code_14_FindFirstIntersectNode { 4 5 public static class Node { 6 public int value; 7 public Node next; 8 9 public Node(int data) { 10 this.value = data; 11 } 12 } 13 14 public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) { 15 if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { 16 return null; 17 } 18 Node loop1 = getLoopNode(head1); 19 Node loop2 = getLoopNode(head2); 20 if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) { 21 return noLoop(head1, head2); 22 } 23 if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) { 24 return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2); 25 } 26 return null; 27 } 28 29 public static Node getLoopNode(Node head) { 30 if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) { 31 return null; 32 } 33 Node n1 = head.next; // n1 -> slow 34 Node n2 = head.next.next; // n2 -> fast 35 while (n1 != n2) { 36 if (n2.next == null || n2.next.next == null) { 37 return null; 38 } 39 n2 = n2.next.next; 40 n1 = n1.next; 41 } 42 n2 = head; // n2 -> walk again from head 43 while (n1 != n2) { 44 n1 = n1.next; 45 n2 = n2.next; 46 } 47 return n1; 48 } 49 50 public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) { 51 if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { 52 return null; 53 } 54 Node cur1 = head1; 55 Node cur2 = head2; 56 int n = 0; 57 while (cur1.next != null) { 58 n++; 59 cur1 = cur1.next; 60 } 61 while (cur2.next != null) { 62 n--; 63 cur2 = cur2.next; 64 } 65 if (cur1 != cur2) { 66 return null; 67 } 68 cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; 69 cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; 70 n = Math.abs(n); 71 while (n != 0) { 72 n--; 73 cur1 = cur1.next; 74 } 75 while (cur1 != cur2) { 76 cur1 = cur1.next; 77 cur2 = cur2.next; 78 } 79 return cur1; 80 } 81 82 public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) { 83 Node cur1 = null; 84 Node cur2 = null; 85 if (loop1 == loop2) { 86 cur1 = head1; 87 cur2 = head2; 88 int n = 0; 89 while (cur1 != loop1) { 90 n++; 91 cur1 = cur1.next; 92 } 93 while (cur2 != loop2) { 94 n--; 95 cur2 = cur2.next; 96 } 97 cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; 98 cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; 99 n = Math.abs(n); 100 while (n != 0) { 101 n--; 102 cur1 = cur1.next; 103 } 104 while (cur1 != cur2) { 105 cur1 = cur1.next; 106 cur2 = cur2.next; 107 } 108 return cur1; 109 } else { 110 cur1 = loop1.next; 111 while (cur1 != loop1) { 112 if (cur1 == loop2) { 113 return loop1; 114 } 115 cur1 = cur1.next; 116 } 117 return null; 118 } 119 } 120 121 public static void main(String[] args) { 122 // 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->null 123 Node head1 = new Node(1); 124 head1.next = new Node(2); 125 head1.next.next = new Node(3); 126 head1.next.next.next = new Node(4); 127 head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 128 head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); 129 head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7); 130 131 // 0->9->8->6->7->null 132 Node head2 = new Node(0); 133 head2.next = new Node(9); 134 head2.next.next = new Node(8); 135 head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6 136 System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value); 137 138 // 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->4... 139 head1 = new Node(1); 140 head1.next = new Node(2); 141 head1.next.next = new Node(3); 142 head1.next.next.next = new Node(4); 143 head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); 144 head1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); 145 head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7); 146 head1.next.next.next.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next; // 7->4 147 148 // 0->9->8->2... 149 head2 = new Node(0); 150 head2.next = new Node(9); 151 head2.next.next = new Node(8); 152 head2.next.next.next = head1.next; // 8->2 153 System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value); 154 155 // 0->9->8->6->4->5->6.. 156 head2 = new Node(0); 157 head2.next = new Node(9); 158 head2.next.next = new Node(8); 159 head2.next.next.next = head1.next.next.next.next.next; // 8->6 160 System.out.println(getIntersectNode(head1, head2).value); 161 162 } 163 164 }
题目七
二分的小扩展。
以上是关于链表基础算法题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章