装饰器
Posted happystudyhuan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了装饰器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、装饰器:
(1)本质:装饰器的本质是函数,其基本语法都是用关键字def去定义的。
(2)功能:装饰其他函数,即:为其他函数添加附加功能。
(3)原则:不能修改被装饰的函数的源代码,不能修改被装饰的函数的调用方式。即:装饰器对待被修饰的函数是完全透明的。
(4)简单应用:统计函数运行时间的装饰器
import time
#统计函数运行时间的装饰器
def timmer(func):
def warpper(*args,**kwargs):
strat_time = time.time()
func()
stop_time = time.time()
print("the func run time is %s" %(stop_time-strat_time))
return warpper
@timmer
def test1():
time.sleep(3)
print("in the test1")
test1()
#运行结果:
#in the test1
#the func run time is 3.000171661376953
(5)实现装饰器知识储备:
a、函数即“变量”
b、高阶函数
c、函数嵌套
d、高阶函数+嵌套函数==》装饰器
2、装饰器知识储备——函数即“变量”
定义一个函数,相当于把函数体赋值给这个函数名。
Python解释器如何回收变量:采用引用计数。当引用有没有了时(门牌号不存在),变量就被回收了。
函数的定义也有内存回收机制,与变量回收机制一样。匿名函数没有函数名,就会被回收。
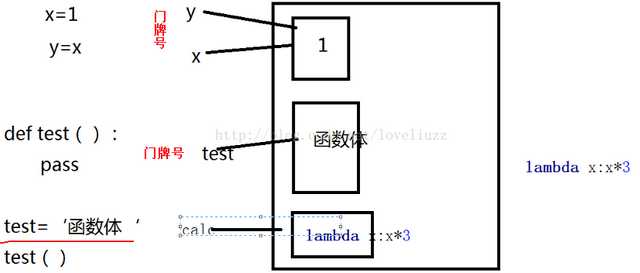
变量的使用:先定义再调用,只要在调用之前已经存在(定义)即可;函数即“变量”,函数的使用是一样的。
函数调用顺序:其他的高级语言类似,Python 不允许在函数未声明之前,对其进行引用或者调用
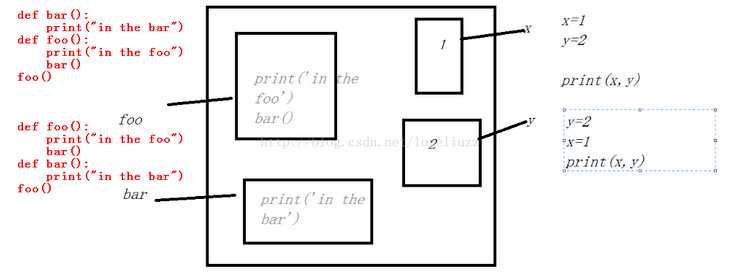
下面的两段代码运行效果一样:
def bar():
print("in the bar")
def foo():
print("in the foo")
bar()
foo()
#python为解释执行,函数foo在调用前已经声明了bar和foo,所以bar和foo无顺序之分
def foo():
print("in the foo")
bar()
def bar():
print("in the bar")
foo()
#运行结果:
#in the foo
#in the bar
#in the foo
#in the bar
注意:python为解释执行,函数foo在调用前已经声明了bar和foo,所以bar和foo无顺序之分
原理图:
3、装饰器知识储备———高阶函数
满足下列其中一种即可称之为高阶函数:
a、把一个函数名当做实参传递给另一个函数(在不修改被装饰函数的情况下为其添加附加功能)
b、返回值中包含函数名(不修改函数的调用方式)
(1)高阶函数示例:
def bar():
print("in the bar")
def test1(func):
print(func) #打印内存地址
func()
test1(bar) #门牌号func=bar
#运行结果:
#<function bar at 0x00BCDFA8>
#in the bar
2)高阶函数的妙处——把一个函数名当做实参传递给另一个函数(在不修改被装饰函数的情况下为其添加附加功能)
import time def bar(): time.sleep(3) print("in the bar") #test2在不修改被修饰函数bar的代码时添加了附加的及时功能 def test2(func): start_time = time.time() func() #run bar stop_time = time.time() print("the func run time is %s " %(stop_time-start_time)) #调用方式发生改变,不能像原来的方法去调用被修饰的函数(所以不能实现装饰器的功能) test2(bar) #bar() #运行结果: #in the bar #the func run time is 3.000171661376953
(3)高阶函数的妙处——返回值中包含函数名(不修改函数的调用方式)
import time
def bar():
time.sleep(3)
print("in the bar")
def test3(func):
print(func)
return func
bar = test3(bar)
bar() #run bar
#运行结果:
#<function bar at 0x00BADFA8>
#in the bar
4、装饰器知识储备——嵌套函数
#函数嵌套
def foo():
print("in the foo")
def bar(): #bar函数具有局部变量的特性,不能在外部调用,只能在内部调用
print("in the bar")
bar()
foo()
#运行结果:
#in the foo
#in the bar
5、装饰器应用——模拟网站登录页面,访问需要认证登录页面
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Huan
#模拟网站,访问页面和部分需要登录的页面
import time
user,passwd = "Huan","123"
def auth(func):
def wrapper(*args,**kwargs):
username = input("Username:").strip()
password = input("Password:").strip()
if username == user and password == passwd:
print("�33[32;1mUser has passed authentication!�33[0m")
res = func(*args,**kwargs)
print("-----after authentication---")
return res
else:
exit("�33[31;1mInvalid username or password!�33[0m")
return wrapper
def index():
print("welcome to index page!")
@auth
def home():
print("welcome to index home!")
return "from home"
@auth
def bbs():
print("welcome to index bbs!")
#函数调用
index()
print(home())
bbs()
#运行结果:
#welcome to index page!
#Username:liu
#Password:liu123
#User has passed authentication!
#welcome to home page!
#-----after authentication---
#from home
#Username:liu
#Password:liu123
#User has passed authentication!
#welcome to bbs page!
#-----after authentication---
6、装饰器带参数
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:Huan
#模拟网站,访问页面和部分需要登录的页面,多种认证方式
import time
user,passwd = "Huan","123"
def auth(auth_type):
print("auth func:",auth_type)
def outer_wrapper(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("wrapper func args:",*args, **kwargs)
if auth_type == "local":
username = input("Username:").strip()
password = input("Password:").strip()
if username == user and password == passwd:
print("�33[32;1mUser has passed authentication!�33[0m")
#被装饰的函数中有返回值,装饰器中传入的参数函数要有返回值
res = func(*args, **kwargs) #from home
print("-----after authentication---")
return res
else:
exit("�33[31;1mInvalid username or password!�33[0m")
elif auth_type == "ldap":
print("ldap....")
return wrapper
return outer_wrapper
def index():
print("welcome to index page!")
@auth(auth_type="local") #利用本地登录 home = wrapper()
def home():
print("welcome to home page!")
return "from home"
@auth(auth_type="ldap") #利用远程的ldap登录
def bbs():
print("welcome to bbs page!")
#函数调用
index()
print(home()) #wrapper()
bbs()
运行结果:
auth func: local
auth func: ldap
welcome to index page!
wrapper func args:
Username:Huan
Password:123
User has passed authentication!
welcome to home page!
-----after authentication---
from home
wrapper func args:
ldap....

以上是关于装饰器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章