HDU 4121Xiangqi
Posted fang-hao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HDU 4121Xiangqi相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目描述
Xiangqi is one of the most popular two-player board games in China. The game represents a battle between two armies with the goal of capturing the enemy’s “general” piece. In this problem, you are given a situation of later stage in the game. Besides, the red side has already “delivered a check”. Your work is to check whether the situation is “checkmate”.
Now we introduce some basic rules of Xiangqi. Xiangqi is played on a 10×9 board and the pieces are placed on the intersections (points). The top left point is (1,1) and the bottom right point is (10,9). There are two groups of pieces marked by black or red Chinese characters, belonging to the two players separately. During the game, each player in turn moves one piece from the point it occupies to another point. No two pieces can occupy the same point at the same time. A piece can be moved onto a point occupied by an enemy piece, in which case the enemy piece is "captured" and removed from the board. When the general is in danger of being captured by the enemy player on the enemy player’s next move, the enemy player is said to have "delivered a check". If the general‘s player can make no move to prevent the general‘s capture by next enemy move, the situation is called “checkmate”.
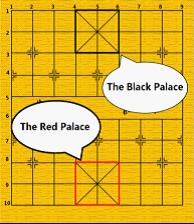
We only use 4 kinds of pieces introducing as follows: General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called “flying general” (see the figure above). “Flying general” means that one general can “fly” across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces.
General: the generals can move and capture one point either vertically or horizontally and cannot leave the “palace” unless the situation called “flying general” (see the figure above). “Flying general” means that one general can “fly” across the board to capture the enemy general if they stand on the same line without intervening pieces. Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces
Chariot: the chariots can move and capture vertically and horizontally by any distance, but may not jump over intervening pieces Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target.
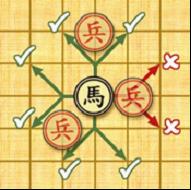
Cannon: the cannons move like the chariots, horizontally and vertically, but capture by jumping exactly one piece (whether it is friendly or enemy) over to its target. Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called “hobbling the horse’s leg”.
Horse: the horses have 8 kinds of jumps to move and capture shown in the left figure. However, if there is any pieces lying on a point away from the horse horizontally or vertically it cannot move or capture in that direction (see the figure below), which is called “hobbling the horse’s leg”.
Now you are given a situation only containing a black general, a red general and several red chariots, cannons and horses, and the red side has delivered a check. Now it turns to black side’s move. Your job is to determine that whether this situation is “checkmate”.
题目翻译
给你一副棋盘,判断是否处于将死状态。
解题思路
首先想到的思路是判断一下红色子能到达的所有地方,看看黑将能走的地方是不是都被覆盖了,但是这样还有一个问题,就是黑将有可能走到一个地方,吃掉了那里的红子,所以这样写起来可能有点麻烦,所以我们换一种写法,我们假设现在黑将走到了它能走到的地方,然后我们判断红的能不能吃到黑子就好了。
代码
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #define G 1 6 #define R 2 7 #define H 3 8 #define C 4 9 #define BG 5 10 using namespace std; 11 int n,bx,by,map[20][20]; 12 int nx[]={1,0,-1,0}; 13 int ny[]={0,1,0,-1}; 14 //G R H C BG 15 //1 2 3 4 5 16 inline void read(int &x){ 17 x=0; register char ch=getchar(); 18 while(ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘)ch=getchar(); 19 while(ch>=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘)x=x*10+ch-‘0‘,ch=getchar(); 20 } 21 inline int judge(int x,int y){ 22 int temp[20][20]; 23 memcpy(temp,map,sizeof(map)); 24 temp[bx][by]=0,temp[x][y]=BG; 25 for(register int i=1;i<=10;i++){ 26 for(register int j=1;j<=9;j++){ 27 if(i==x&&j==y)continue; 28 if(temp[i][j]==G){ 29 if(j!=y)continue; 30 else { 31 int flag=0; 32 for(register int k=i-1;k>x;k--){ 33 if(flag)break; 34 if(temp[k][j])flag++; 35 } 36 if(!flag)return 1; 37 } 38 } 39 else if(temp[i][j]==C){ 40 if(j!=y)continue; 41 else { 42 int flag=0; 43 for(register int k=i-1;k>x;k--)if(temp[k][j])flag++; 44 if(flag==1)return 2; 45 } 46 } 47 else if(temp[i][j]==H){//up 48 if(!temp[i-1][j]&&i>2){ 49 if(temp[i-2][j-1]==BG||temp[i-2][j+1]==BG)return 3; 50 }//down 51 if(!temp[i+1][j]&&i<9){ 52 if(temp[i+2][j-1]==BG||temp[i+2][j+1]==BG)return 3; 53 }//left 54 if(!temp[i][j-1]&&j>2){ 55 if(temp[i-1][j-2]==BG||temp[i+1][j-2]==BG)return 3; 56 }//right 57 if(!temp[i][j+1]&&j<8){ 58 if(temp[i-1][j+2]==BG||temp[i+1][j+2]==BG)return 3; 59 } 60 } 61 else if(temp[i][j]==R){ 62 for(register int k=i-1;k>=1;k--){ 63 if(temp[k][j]&&temp[k][j]!=BG)break; 64 if(temp[k][j])return 4; 65 } 66 for(register int k=i+1;k<=10;k++){ 67 if(temp[k][j]&&temp[k][j]!=BG)break; 68 if(temp[k][j])return 4; 69 } 70 for(register int k=j-1;k>=1;k--){ 71 if(temp[i][k]&&temp[i][k]!=BG)break; 72 if(temp[i][k])return 4; 73 } 74 for(register int k=j+1;k<=9;k++){ 75 if(temp[i][k]&&temp[i][k]!=BG)break; 76 if(temp[i][k])return 4; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 } 81 return 0; 82 } 83 int main(){ 84 while(1){ 85 memset(map,0,sizeof(map)); 86 read(n),read(bx),read(by); 87 if(n==0&&bx==0&&by==0)return 0; 88 map[bx][by]=BG; 89 char ch; 90 register int x,y; 91 for(register int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 92 scanf("%c",&ch); 93 read(x),read(y); 94 if(ch==‘G‘)map[x][y]=G; 95 else if(ch==‘R‘)map[x][y]=R; 96 else if(ch==‘H‘)map[x][y]=H; 97 else if(ch==‘C‘)map[x][y]=C; 98 } 99 int flag=0; 100 for(register int i=0;i<4;i++){ 101 register int nextx=bx+nx[i],nexty=by+ny[i]; 102 if(nextx>=1&&nextx<=3&&nexty>=4&&nexty<=6){ 103 //cout<<nextx<<‘ ‘<<nexty<<‘ ‘<<judge(nextx,nexty)<<endl; 104 if(flag)break; 105 if(!judge(nextx,nexty))flag=1; 106 } 107 } 108 if(flag)printf("NO "); 109 else printf("YES "); 110 } 111 }
以上是关于HDU 4121Xiangqi的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章