django 进阶之view layer
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了django 进阶之view layer相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一 基本环境1 环境处理
mkdir djanad
cd djanad/
pyenv virtualenv 3.6.5 djanad
pyenv local djanad结果如下

2 创建django和基本配置
pip install django==2.1django-admin startproject demo .
django-admin startapp app结果如下

数据库配置如下
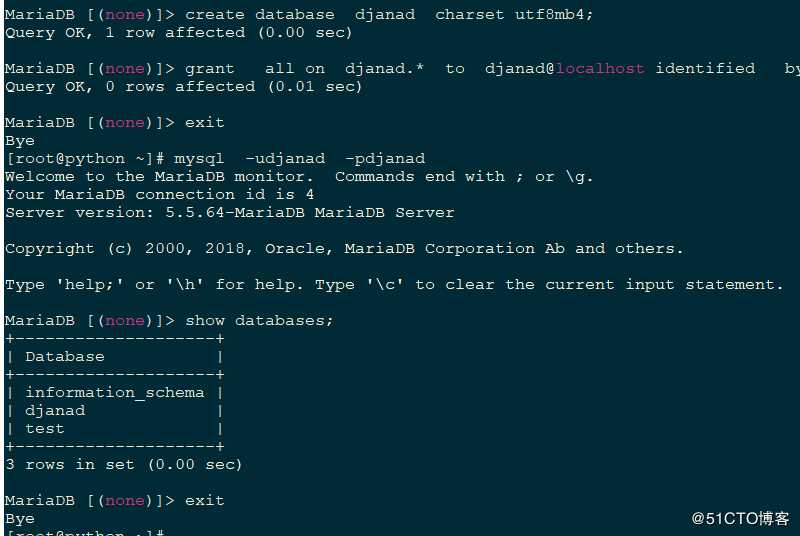
基本时区和mysql配置及相关时区配置请看django基础
https://blog.51cto.com/11233559/2444627
启动结果如下
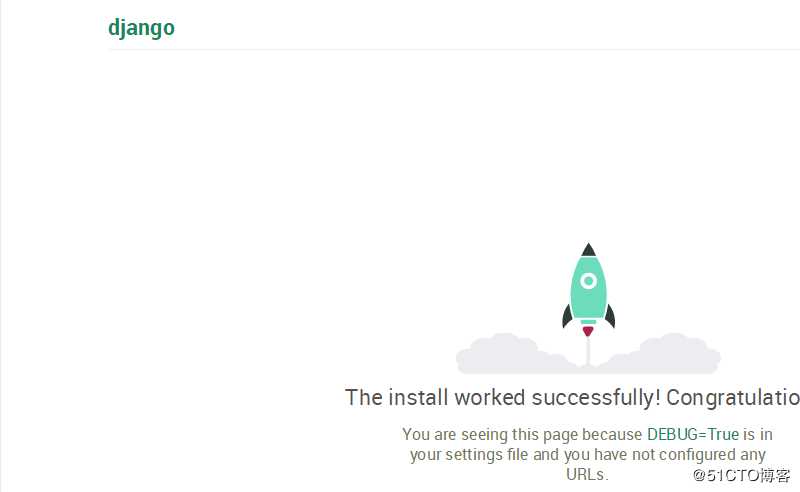
二 view基本使用
1 view中使用模板
1 概述
django内置了自己的模板引擎,和jinjia 很像,使用简单
使用 Template 进行定义模板,使用Context 将数据导入到该模板中,其导入默认使用字典
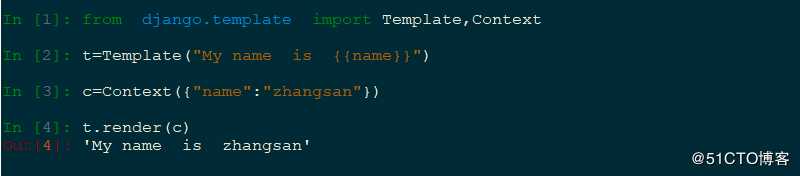
2 环境准备
1 创建models
django 默认会去到app_name/templates下寻找模板,这是settings中的默认设置,默认会去app_name/static找那个寻找静态文件(css,js,jpg,html)等
在 app/models.py 中创建数据库表模板,具体配置如下:
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
# 问题
class Question(models.Model):
question_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
pub_date = models.DateTimeField(‘date published‘)
def __str__(self):
return self.question_text
# 选择
# 配置选择为问题的外键,并配置选择的内容和选择的起始值
class Choice(models.Model):
question = models.ForeignKey(Question, on_delete=Question)
choice_text = models.CharField(max_length=200)
votes = models.IntegerField(default=0)
def __str__(self):
return self.choice_text
2 执行生成迁移文件和迁移并查看
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate结果如下
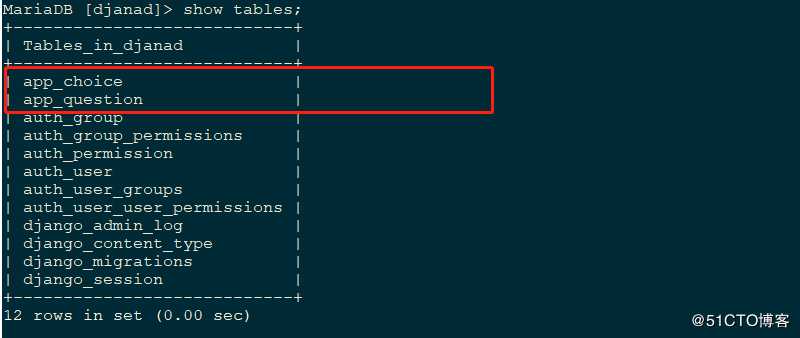
3 添加数据进入表中
创建后台登陆用户,设置用户名为admin,密码为admin@123
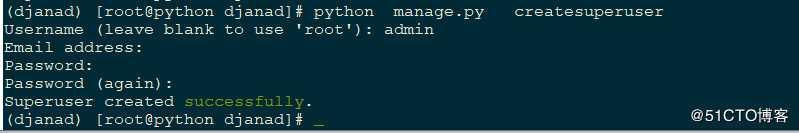
4 将model中的模型添加进入django admin 后台管理界面
app/admin.py中添加
# Register your models here.
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Question, Choice
# Register your models here.
class ChoiceInline(admin.TabularInline):
model = Choice
extra = 3
class QuestionAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
fieldsets = [
(None, {‘fields‘: [‘question_text‘]}),
(‘Date information‘, {‘fields‘: [‘pub_date‘], ‘classes‘: [‘collapse‘]}),
]
inlines = [ChoiceInline]
list_display = (‘question_text‘, ‘pub_date‘)
admin.site.register(Choice)
admin.site.register(Question, QuestionAdmin)url : localhost:port/admin/
5 登陆后台并添加数据如下
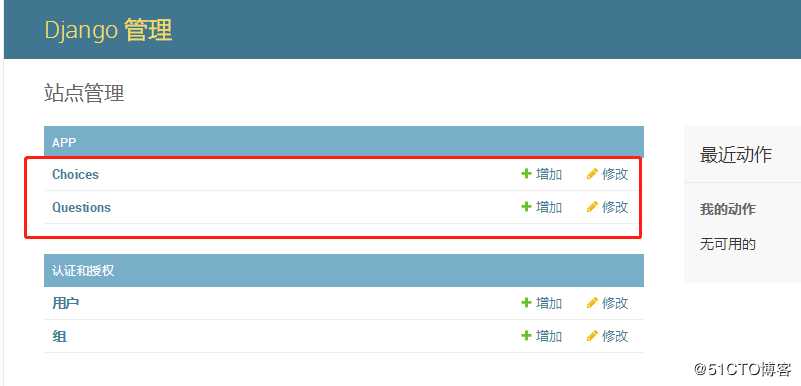
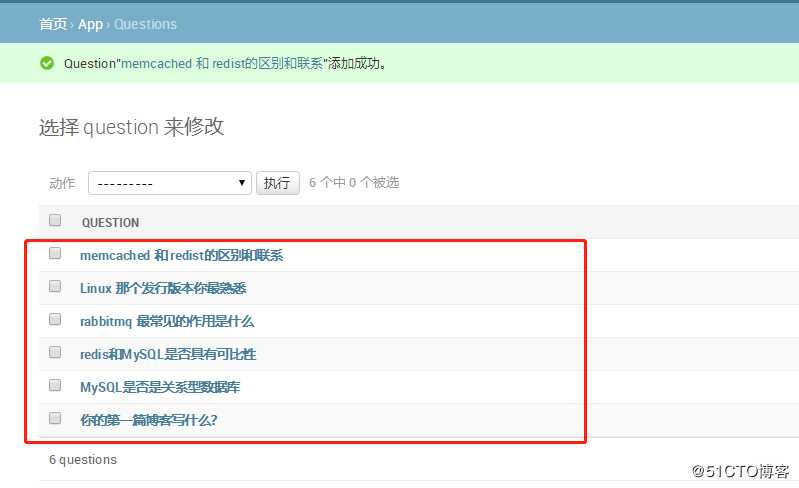
6 配置静态文件
demo/setting.py 中配置添加
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ‘static‘)
]项目中创建static 并上传图片django.jpg
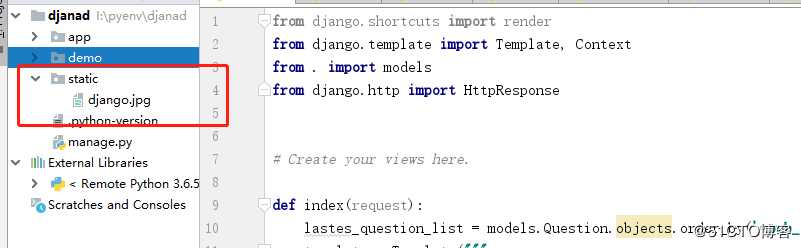
7 配置 url
demo/urls.py中配置如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls",namespace="app")), #此处配置名称空间,用于处理后面的翻转
]
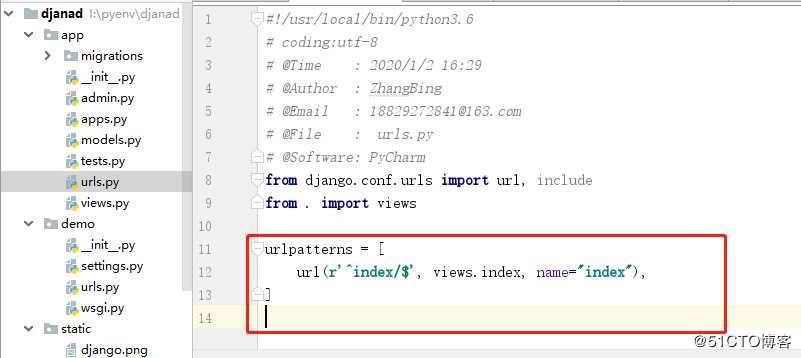
8 app中创建 urls.py 文件,内容如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^index/$‘, views.index, name="index"), # name 指定名称,
]
3 view 使用
1 在view中直接嵌入模板,结果如下
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.template import Template, Context
from . import models
from django.http import HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
lastes_question_list = models.Question.objects.order_by(‘-pub_date‘)[:5]
template = Template("""
<img src="/static/django.jpg">
{% if lastes_question_list %}
<ul>
{% for question in lastes_question_list %}
<li> <a href="/app/ {{question.id}}/"> {{ question.question_text }} </a> </li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endif %}
""")
context = Context({"lastes_question_list": lastes_question_list})
return HttpResponse(template.render(context))访问配置,结果如下

2 使用html 模板如下
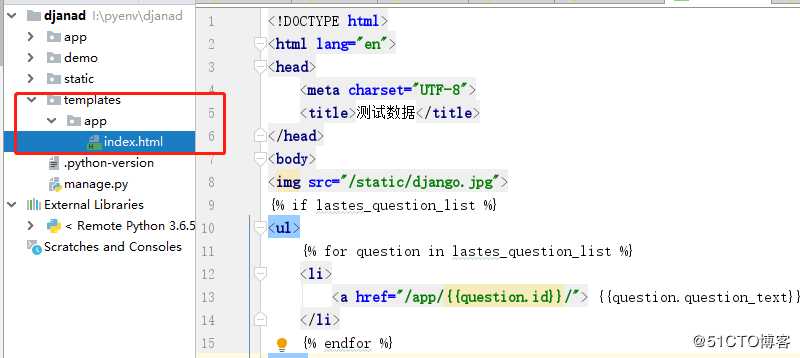
index 代码如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>测试数据</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="/static/django.jpg">
{% if lastes_question_list %}
<ul>
{% for question in lastes_question_list %}
<li>
<a href="/app/{{question.id}}/"> {{question.question_text}} </a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endif%}
</body>
</html>app/view.py 中代码如下
from . import models
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.template import loader
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
lastes_question_list = models.Question.objects.order_by(‘-pub_date‘)[:5]
template = loader.get_template("app/index.html")
context = {"lastes_question_list": lastes_question_list}
return HttpResponse(template.render(context))3 index.html不变,app/view 修改
from . import models
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
lastes_question_list = models.Question.objects.order_by(‘-pub_date‘)[:5]
context = {"lastes_question_list": lastes_question_list}
return render(request, template_name="app/index.html", context=context)4 去掉static 和 url中的硬编码及反向解析
根据根路由中注册的namespace和子路由中注册的name来动态获取路径。在模板中使用"{% url namespace:name %}"
如果携带位置参数
“{% url namespace:name args %}"
如果携带关键字参数
“{% url namespace:name k1=v1 k2=v2 %}"
配置 详情页面添加数据
app/view.py 中添加数据如下
from . import models
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
lastes_question_list = models.Question.objects.order_by(‘-pub_date‘)[:5]
context = {"lastes_question_list": lastes_question_list}
return render(request, template_name="app/index.html", context=context)
def detal(request, question_id):
detal = models.Question.objects.get(pk=question_id)
context = {"detal": detal}
return render(request, template_name="app/detal.html", context=context)
app/urls.py中如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^index/$‘, views.index, name="index"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/$‘, views.detal, name="detal"),# name 指定名称,用于后面的反向解析
]
]
详情页html 配置如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>测试数据</title>
</head>
<body>
{% if detal %}
<h1>{{ detal.question_text }}</h1>
{% for question in detal.choice_set.all %}
<li>
{{ question.votes }}
{{ question.choice_text }}
</li>
{% endfor %}
{% endif %}
</body>
</html>index.html 修改如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
{% load static %}
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>测试数据</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="{% static ‘django.jpg‘%}">
{% if lastes_question_list %}
<ul>
{% for question in lastes_question_list %}
<li>
<a href="{% url ‘detal‘ question.id %}"> {{question.question_text}} </a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endif%}
</body>
</html>2 针对上述项目实现投票机制
1 修改detal 结果如下
此处的app:vote 是对应的namespace 和 name ,及名称空间和名称
<!DOCTYPEhtml>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>测试数据</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>{{ detal.question_text }}</h1>
<p>
<strong>{{error_message}}</strong>
</p>
<form action="{% url ‘app:vote‘ detal.id %}" method="post">
{% for choice in detal.choice_set.all %}
<input type="radio" name="choice" id="choice {{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id }}"/>
<label for="choice {{ forloop.counter }}"> {{ choice.choice_text }} </label>
<br/>
{% endfor %}
<input type="submit" value="投票"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>2 app/views.py
from . import models
from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import render, get_object_or_404, reverse
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
lastes_question_list = models.Question.objects.order_by(‘-pub_date‘)[:5]
context = {"lastes_question_list": lastes_question_list}
return render(request, template_name="app/index.html", context=context)
# 详情页面
def detal(request, question_id):
detal = models.Question.objects.get(pk=question_id)
context = {"detal": detal}
return render(request, template_name="app/detal.html", context=context)
# 投票结果显示
def vote(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(models.Question, pk=question_id)
if request.method == "POST":
choice_id = request.POST.get(‘choice‘, 0)
try:
selected_choice = question.choice_set.get(pk=choice_id)
except models.Choice.DoesNotExist:
return render(request, ‘app/detal.html‘, {
‘qestion‘: question,
"error_message": "You didn‘t select a choice",
})
else:
selected_choice.votes += 1
selected_choice.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse(‘app:results‘, args=(question.id,)))
# 投票结果显示
def results(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(models.Question, pk=question_id)
print(question, type(question))
return render(request, ‘app/results.html‘, {"question": question})
3 templates/app/results.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> {{ question.question_text }} </h1>
<h1> 测试 </h1>
<ul>
{% for choice in question.choice_set.all %}
<li>
{{ choice.choice_text }} -- {{ choice.votes }} vote {{ choice.votes |pluralize }}
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
</body>
</html>4 投票程序结果如下:
3 错误页面处理
1 基本页面处理
def test(request):
# return HttpResponse(‘Not Found‘, status=404)
return HttpResponseNotFound(‘Not Found‘)
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls"), {"question_id": 1}), # 此处配置直接捕获question_id 进行处理
url(r‘^test/$‘, test)
]上述两种返回错误方式结果相同
2 自定义错误视图
在url中导入,在其他页面使用即可
在 demo/urls.py中导入
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin
from django.http import HttpResponse, HttpResponseNotFound
def test(request):
return HttpResponse(‘Not Found‘, status=404)
handler404 = ‘demo.views.my_custom_page_not_found_view‘
handler500 = ‘demo.views.my_custom_error_found_view‘
handler403 = ‘demo.views.my_custom_permission_denied_view‘
handler400 = ‘demo.views.my_custom_bad_request_request_view‘
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls")), # 此处配置直接捕获question_id 进行处理
url(r‘^test/$‘, test)
]demo/views.py中配置如下
from django.http import HttpResponse
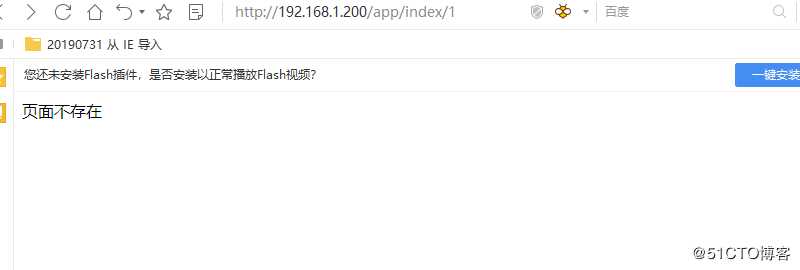
def my_custom_page_not_found_view(request):
return HttpResponse("页面不存在", status=404)
def my_custom_error_found_view(request):
return HttpResponse("服务器错误", status=500)
def my_custom_permission_denied_view(request):
return HttpResponse("拒绝访问", status=403)
def my_custom_bad_request_request_view(request):
return HttpResponse("请求错误", status=400)
此处需要将demo/setting.py 中的DEBUG修改为False,才会出现此处定义的情况

结果如下
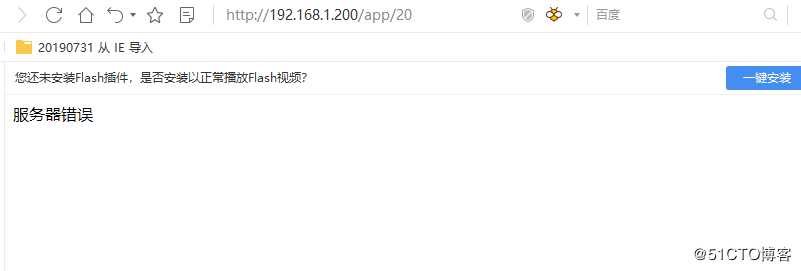
4 相关函数
1 render函数
用于渲染模板和传递参数
def render(request, template_name, context=None, content_type=None, status=None, using=None):
"""
Returns a HttpResponse whose content is filled with the result of calling
django.template.loader.render_to_string() with the passed arguments.
"""
content = loader.render_to_string(template_name, context, request, using=using)
return HttpResponse(content, content_type, status)选项:
request : 请求参数
template_name:对应的html模板名称
context:渲染模板的context字典,默认是空 {}
content_type : Response MIME type,默认使用DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE 设置
2 redirect 函数
用于页面跳转
def redirect(to, *args, **kwargs):
pass 选项
to :
此选项可以是
1 模块
2 视图名称
3 absolute或者回调 urlperments 是否永久重定向
为 True 表示永久重定向,否则表示临时重定向
3 get_object_or_404 函数
当对象不存在时返回特定页面404
def get_object_or_404(class, *args, **kwargs):
pass 第一个参数: 可为Model中对应的数据库表类,后面可为对应的过滤方法
question = get_object_or_404(models.Question, pk=question_id)当对象执行成功时,返回对应的值,否则返回404 错误
4 get_list_or_404 函数
当对象不存在时返回特定页面404
question = get_list_or_404(models.Question, pk=question_id)5 装饰器
require_http_methods(request_method_list)
用于限制请求类型,在此中以列表的形式显示
require_GET()
用于限制请求类型为GET请求
require_POST()
用于限制请求类型为POST 请求
require_safe()
用于限制安全的请求,如get和head
gzip_page()
用于启用gzip压缩功能
cache_control(**kwargs)
缓存相关函数
never_cache()
用于配置永久不缓存
login_required()
用于处理登录后的用户才能访问对应的属性
三 urlconf
1 django 路由匹配概述
1 项目启动后根据 setting ROOT_URLCONF 决定跟URLconf,默认是object中的urls.py
2 它是django.conf.urls.url()实例的一个python 列表
3 django 依次匹配每个URL模式,在于请求的URL匹配的第一个模式停下来。
4 一旦其中的一个正则表达式匹配上,django将导入并调用给出的视图,它是一个简单的python函数(或者一个基于类的视图)。视图将获得如下参数:
一个HttpRequest 实例。
如果匹配的正则表达式返回来了没有命名的组,那么正则表达式匹配的内容将作为位置参数提供给视图。
关键字参数由正则表达式匹配的命名组成,但是可以被django.conf.urls.url()的可选参数kwargs 覆盖。
5 如果没有匹配到正则表达式,或者如果过程中抛出一个异常,django将调用一个适当的错误处理试图。
2 用户请求数据处理过程
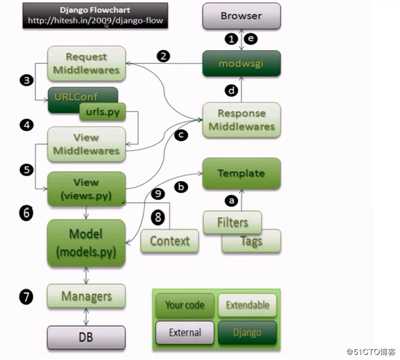
Middlewares: 过滤函数,俗称过滤器,在执行之前和执行之后进行某些操作
3 URL 命名空间
1 两种命名空间
app namespace
instance namespace
2 app namespace
app/urls.py
app_name=‘app‘ # 此中方式和在demo/urls.py中的
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls",namespace="app")), 作用相同命名空间的作用主要用作隔离
上述表示使用了此配置后,此配置文件中的所有数据都在此名称空间下,在使用url时,需要在其上面加上名称空间的名称
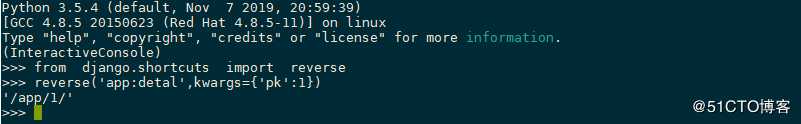
3 instance namespace
instance 级别,名称不可以重复
在demo/urls.py中的
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls",namespace="app")), 用于在项目的urls.py中的include()中指定,作用和上面的相同,均可用于反向解析
说明:
app namespace 使用场景: 通常使用此方式 ,除非有多个include则使用instance namespace
3 url 反向解析
1 解析概述
如果在你的代码中,需要使用一些类似url模板标签,Django提供了下列功能:
正解析: url ->view
反解析: view name -> url
2 reverse
此函数用于通过url中指定的name来返回对应的url
格式如下
reverse(viewname,urlconf=None,args=None,Kwargs=None,current_app=None)
viewname 可以是一个url模式名称或一个可调用的视图对象
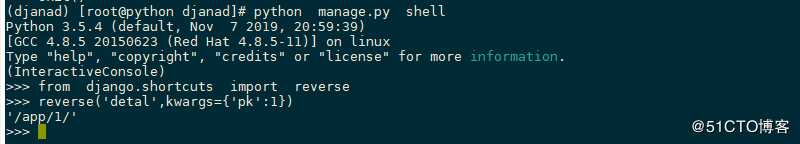
3 reverse_lazy
懒加载下的 reverse
格式如下:
reverse_lazy(viewname, urlconf=None, args=None, kwargs=None, current_app=None)
作用:
提供反向URL作为url基于类的通用视图的属性。
向装饰器提供反向URL(例如装饰器的login_url参数django.contrib.auth.decorators.permission_required() )。
提供反向URL作为函数签名中参数的默认值。
1 在模板中: 使用url 模板标签
2 在python 代码中,使用django.core.urlresolvers.reverse() 函数
3 在更高层的与处理django模型实例相关的代码中,使用get_absolute_url() 方法
4 多种URL
demo.urls.py 中配置如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin
from django.http import HttpResponse
def year(request):
return HttpResponse("year")
def month(request):
return HttpResponse("month")
def ymd(request):
return HttpResponse("year-month-days")
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls")),
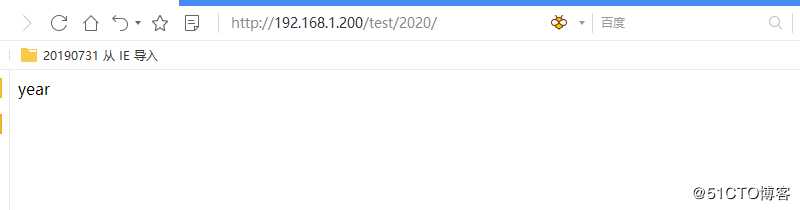
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/$‘, year),
url(r‘^[0-9]{2}/$‘, month),
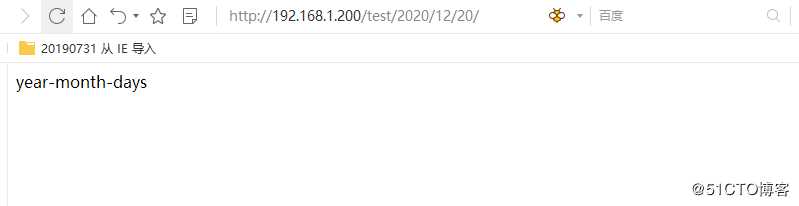
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/[0-9]{2}/[0-9]{2}/$‘, ymd),
]说明:
1 若要从URL中捕获一个值,只需要在它周围放置一对圆括号
2 不需要添加一个前导的反斜杠,因为每个URL都有,
3 每个正则表达式前面的‘r‘ 是可选的,建议加上,它告诉python这个字符串是原始的字符串,字符串中的任何意义都不应该被转义。
4 默认捕捉到的都是字符串
5 上述的匹配方式因为加上了$,因此其是绝对匹配
5 URL 无法匹配的错误处理
当django找不到一个匹配请求的URL的正则表达式时,或者当抛出一个异常时,django会将调用有个错误处理视图
默认的错误处理视图
-handler404
-handler500
-handler403
-handler400
6 url 多种组合写法
1 引入配置
demo/urls.py 中如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin
from django.http import HttpResponse
def year(request):
return HttpResponse("year")
def month(request):
return HttpResponse("month")
def ymd(request):
return HttpResponse("year-month-days")
extra_patters = [
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/$‘, year),
url(r‘^[0-9]{2}/$‘, month),
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/[0-9]{2}/[0-9]{2}/$‘, ymd),
]
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls"), name="app"),
url(r‘test/‘, include(extra_patters)), # 引入上述配置的匹配规则
]
2 多层级配置
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin
from django.http import HttpResponse
def year(request):
return HttpResponse("year")
def month(request):
return HttpResponse("month")
def ymd(request):
return HttpResponse("year-month-days")
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls"), name="app"),
url(r‘test/‘, include([
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/$‘, year),
url(r‘^[0-9]{2}/$‘, month),
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/[0-9]{2}/[0-9]{2}/$‘, ymd),
])), # 引入上述配置的匹配规则
]3 追加配置
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin
from django.http import HttpResponse
def year(request):
return HttpResponse("year")
def month(request):
return HttpResponse("month")
def ymd(request):
return HttpResponse("year-month-days")
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^app/‘, include("app.urls"), name="app"),
url(r‘test/‘, include([
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/$‘, year),
url(r‘^[0-9]{2}/$‘, month),
url(r‘^[0-9]{4}/[0-9]{2}/[0-9]{2}/$‘, ymd),
])), # 引入上述配置的匹配规则
]
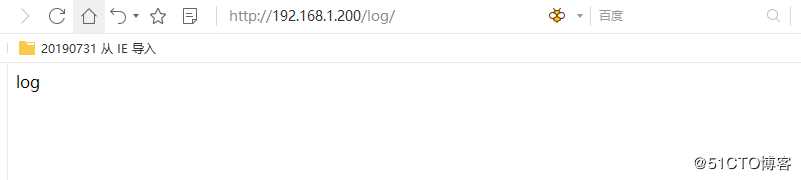
def log(request):
return HttpResponse("log")
urlpatterns += [
url(r‘log/‘, log)
]
结果如下
6 URL 参数的捕获和继承
demo/urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from django.contrib import admin
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/app/‘, include("app.urls"), name="app"), # 此处配置直接捕获question_id 进行处理
]
app/urls.py 中配置如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from . import views
app_name = "app"
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^index/$‘, views.index, name="index"),
url(r‘^$‘, views.detal, name="detal"),
url(r‘^result$‘, views.result, name="result"),
url(r‘^vote$‘, views.vote, name="vote"),
]去除了之前的(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)
app/view.py
修改 index接受参数,需要添加接受此参数,否则其无法访问
def index(request, question_id):
lastes_question_list = models.Question.objects.order_by(‘-pub_date‘)[:5]
context = {"lastes_question_list": lastes_question_list}
return render(request, template_name="app/index.html", context=context)
传递额外参数
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/app/‘, include("app.urls"), {"question_id": 1}), # 此处配置直接捕获question_id 进行处理
]说明: 此处配置的必须是正则表达式中匹配的值,此处会覆盖正则表达式中匹配的值,此处的question_id,为1
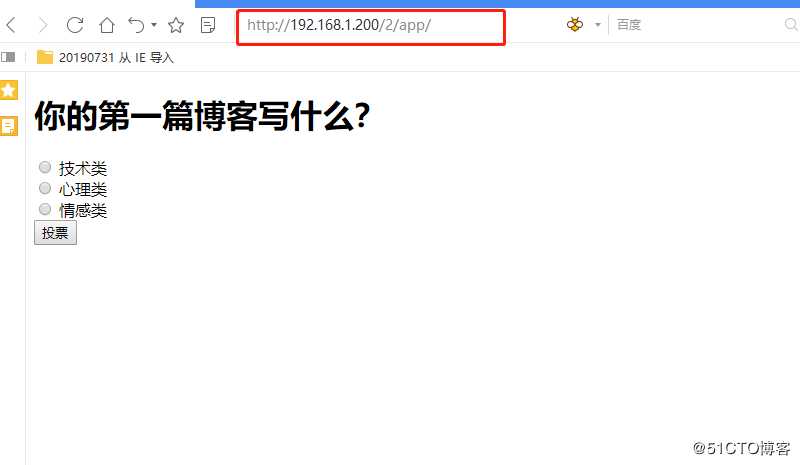
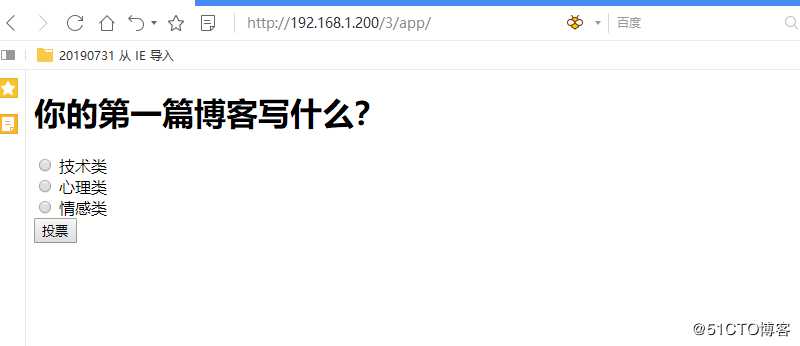
五 view 高级部分
1 发送邮件
1 setting.py 中配置如下
需要在项目project.setting.py 中配置相关参数
本项目是在 demo/setting.py 中配置
# 邮件发送相关配置
EMAIL_HOST = "smtp.163.com" # 服务地址
EMAIL_PORT = 25 # 发送使用的端口
EMAIL_HOST_USER = "" # 发送邮件使用的账号
EMAIL_HOST_PASSWORD = "" # 发送授权密码
# EMAIL_USE_TLS=True # 是否启用TLS
# EMAIL_USE_SSL=True # 是否启用SSL 2 send_mail 格式含义如下
def send_mail(subject, message, from_email, recipient_list,
fail_silently=False, auth_user=None, auth_password=None,
connection=None, html_message=None):
pass 其中:
subject 表示邮件的标题
message 表示邮件内容
from_email 表示发件人
recipient_list 表示收件人列表
3 app/views.py 中代码如下
from django.core.mail import send_mail
def sendemail(request):
if request.method == "POST":
subject = request.POST.get(‘subject‘, ‘‘)
message = request.POST.get(‘message‘, ‘‘)
recipient_list = request.POST.get(‘recipient_list‘, ‘‘)
print(recipient_list)
if subject and message and recipient_list:
try:
send_mail(subject, message=message, from_email=‘18829272841@163.com‘,
recipient_list=[‘zhangbing@zhishoubao.com‘])
except Exception as e:
return HttpResponse("Invalid header found.")
return HttpResponseRedirect(‘/app/index‘)
else:
return HttpResponse("Make sure all fields are entered and valid.")
return render(request, ‘app/sendemail.html‘)4 app/urls.py 中修改如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from . import views
app_name = "app"
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^index/$‘, views.index, name="index"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)$‘, views.detal, name="detal"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/result$‘, views.result, name="result"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/vote$‘, views.result, name="vote"),
url(r‘^sendemail/$‘, views.sendemail, name="sendemail"),5 templates/app/sendemail.html中修改如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>邮件发送</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
<label> 主题 </label>
<input type="text" name="subject">
<br/>
<label> 内容 </label>
<input type="text" name="message">
<br/>
<label> 发件人列表</label>
<input type="email" name="recipient_list">
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>6 结果如下
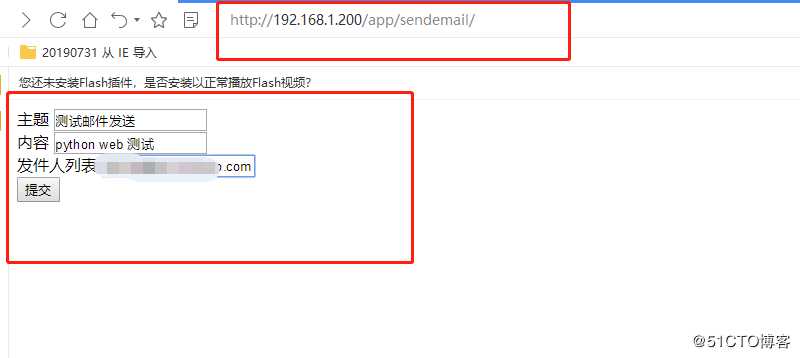
7 跳转到如下页面
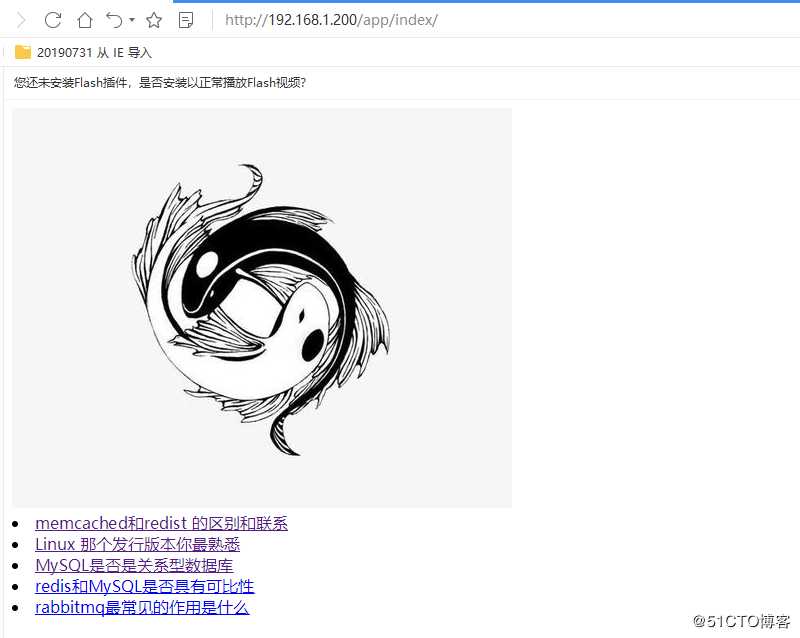
2 导出CSV 文件
1 app/views.py中配置如下
import csv
import datetime
def get_csv(request):
if request.method == "POST":
response = HttpResponse(content_type="text/csv")
response[‘Content-Disposition‘] = ‘attachment;filename={}.csv‘.format(
datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d"))
writer = csv.writer(response)
writer.writerow(["第一行", 1, 2, 3, 4])
writer.writerow(["第二行", ‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘, ‘D‘])
return response
return render(request, ‘app/get_csv.html‘)2 app/urls.py 中配置如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from . import views
app_name = "app"
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^index/$‘, views.index, name="index"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)$‘, views.detal, name="detal"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/result$‘, views.result, name="result"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/vote$‘, views.result, name="vote"),
url(r‘^sendemail/$‘, views.sendemail, name="sendemail"),
url(r‘^get_csv/$‘, views.get_csv, name="getcsv"),
]3 templates/app/get_csv.html中配置如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>触发获取get_csv</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="获取csv">
</form>
</body>
</html>4 结果如下
3 上传文件
1 app/views.py 中配置如下
def upload_file(request):
if request.method == "POST":
print(request.FILES)
upload_file = request.FILES.get(‘file‘, None)
if upload_file is None:
return HttpResponse("Not file get")
else:
with open(‘/tmp/{}‘.format(upload_file.name), ‘wb‘) as f:
f.write(upload_file.read())
return HttpResponse("{} 文件上传成功,大小为:{}".format(upload_file.name, upload_file.size))
else:
return render(request, ‘app/upload_file.html‘)2 app/urls.py 中配置如下
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from . import views
app_name = "app"
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^index/$‘, views.index, name="index"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)$‘, views.detal, name="detal"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/result$‘, views.result, name="result"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/vote$‘, views.result, name="vote"),
url(r‘^sendemail/$‘, views.sendemail, name="sendemail"),
url(r‘^get_csv/$‘, views.get_csv, name="getcsv"),
url(r‘^upload_file/$‘, views.upload_file, name="upload_file"),
]3 templates/app/upload_file.html中配置如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>上传文件</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post" ENCTYPE="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file">
<br/>
<input type="submit" value="上传文件">
</form>
</body>
</html>4 结果如下
5 说明
-request.FILES
- enctype 默认是 "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",上传文件时需要修改为"multipart/form-data"
4 下载文件
1 app.views.py 中配置如下
def download_file(request):
if request.method == "POST":
f = open(‘/tmp/2020-01-03.csv‘, ‘rb‘)
response = HttpResponse(f, content_type="application/csv")
response[‘Content-Disposition‘] = ‘attachment;filename={}.csv‘.format(
datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d"))
f.close()
return response
else:
return render(request, ‘app/download_file.html‘)2 app/urls.py中配置
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from . import views
app_name = "app"
urlpatterns = [
url(r‘^index/$‘, views.index, name="index"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)$‘, views.detal, name="detal"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/result$‘, views.result, name="result"),
url(r‘^(?P<question_id>[0-9]+)/vote$‘, views.result, name="vote"),
url(r‘^sendemail/$‘, views.sendemail, name="sendemail"),
url(r‘^get_csv/$‘, views.get_csv, name="getcsv"),
url(r‘^upload_file/$‘, views.upload_file, name="upload_file"),
url(r‘^download_file/$‘, views.download_file, name="download_file"),
]3 templates/app/download_file.html中配置如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>下载数据</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="下载文件">
</form>
</body>
</html>
以上是关于django 进阶之view layer的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章