机器学习(ML)十四之凸优化
Posted jaww
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习(ML)十四之凸优化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
优化与深度学习
优化与估计
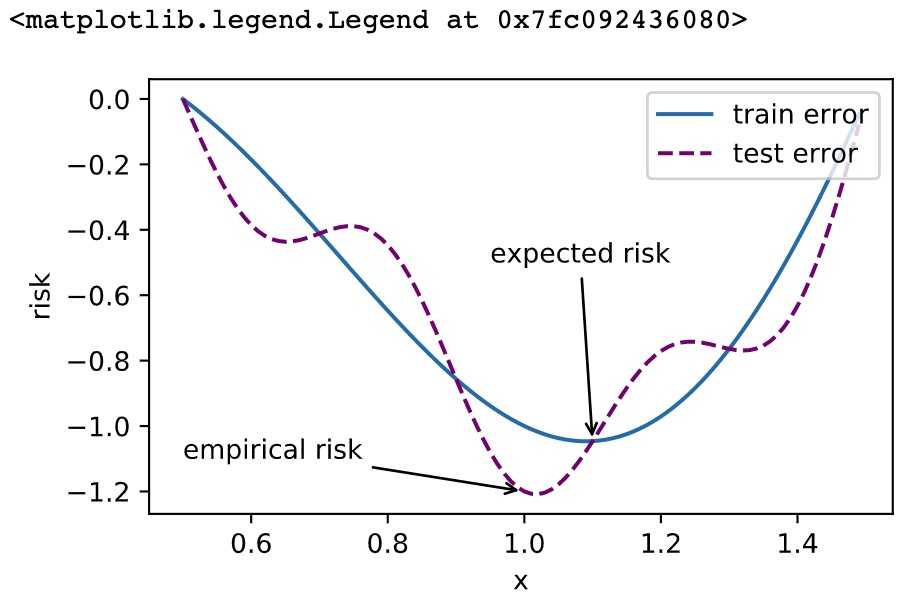
尽管优化方法可以最小化深度学习中的损失函数值,但本质上优化方法达到的目标与深度学习的目标并不相同。
- 优化方法目标:训练集损失函数值
- 深度学习目标:测试集损失函数值(泛化性)

1 %matplotlib inline 2 import sys 3 import d2lzh1981 as d2l 4 from mpl_toolkits import mplot3d # 三维画图 5 import numpy as np 6 def f(x): return x * np.cos(np.pi * x) 7 def g(x): return f(x) + 0.2 * np.cos(5 * np.pi * x) 8 9 d2l.set_figsize((5, 3)) 10 x = np.arange(0.5, 1.5, 0.01) 11 fig_f, = d2l.plt.plot(x, f(x),label="train error") 12 fig_g, = d2l.plt.plot(x, g(x),‘--‘, c=‘purple‘, label="test error") 13 fig_f.axes.annotate(‘empirical risk‘, (1.0, -1.2), (0.5, -1.1),arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘)) 14 fig_g.axes.annotate(‘expected risk‘, (1.1, -1.05), (0.95, -0.5),arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘)) 15 d2l.plt.xlabel(‘x‘) 16 d2l.plt.ylabel(‘risk‘) 17 d2l.plt.legend(loc="upper right")
优化在深度学习中的挑战
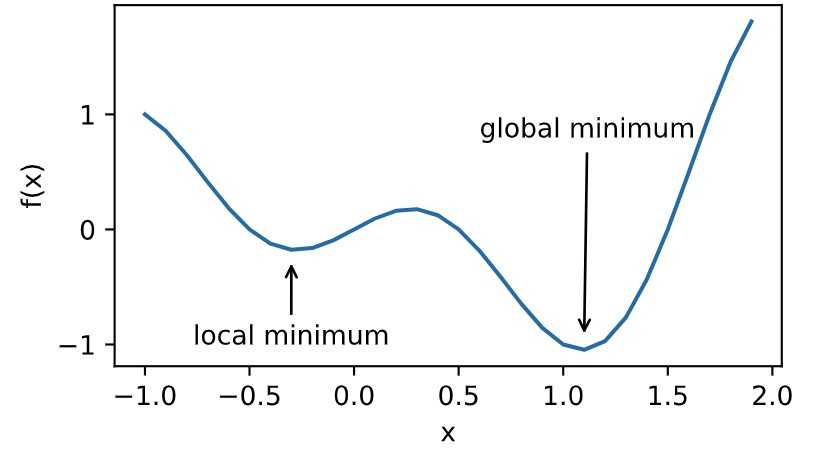
- 局部最小值
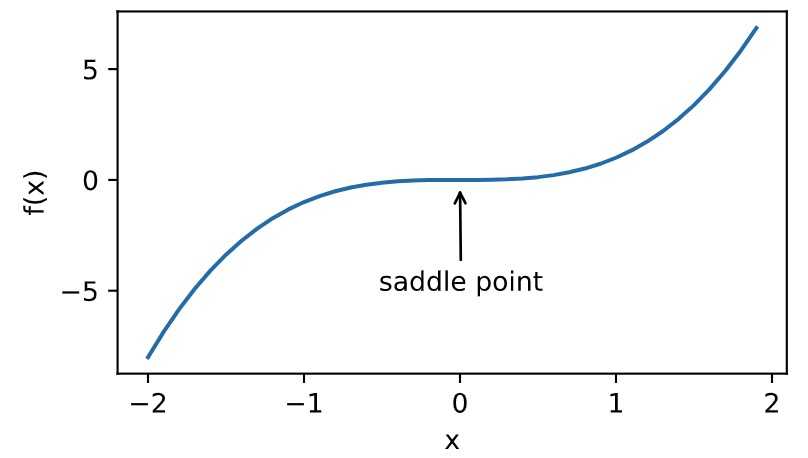
- 鞍点
- 梯度消失
局部最小值
![]()

1 def f(x): 2 return x * np.cos(np.pi * x) 3 4 d2l.set_figsize((4.5, 2.5)) 5 x = np.arange(-1.0, 2.0, 0.1) 6 fig, = d2l.plt.plot(x, f(x)) 7 fig.axes.annotate(‘local minimum‘, xy=(-0.3, -0.25), xytext=(-0.77, -1.0), 8 arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘)) 9 fig.axes.annotate(‘global minimum‘, xy=(1.1, -0.95), xytext=(0.6, 0.8), 10 arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘)) 11 d2l.plt.xlabel(‘x‘) 12 d2l.plt.ylabel(‘f(x)‘);
鞍点

1 x = np.arange(-2.0, 2.0, 0.1) 2 fig, = d2l.plt.plot(x, x**3) 3 fig.axes.annotate(‘saddle point‘, xy=(0, -0.2), xytext=(-0.52, -5.0), 4 arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘)) 5 d2l.plt.xlabel(‘x‘) 6 d2l.plt.ylabel(‘f(x)‘);

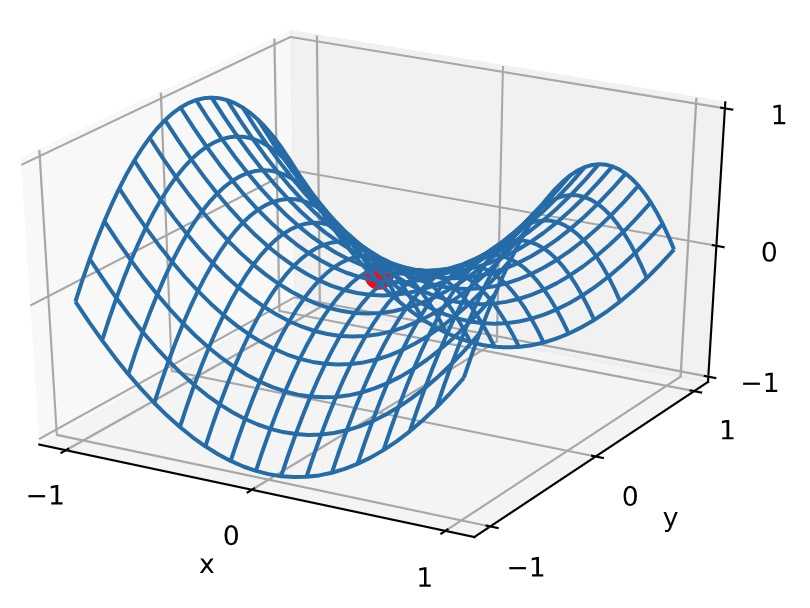
1 x, y = np.mgrid[-1: 1: 31j, -1: 1: 31j] 2 z = x**2 - y**2 3 4 d2l.set_figsize((6, 4)) 5 ax = d2l.plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection=‘3d‘) 6 ax.plot_wireframe(x, y, z, **{‘rstride‘: 2, ‘cstride‘: 2}) 7 ax.plot([0], [0], [0], ‘ro‘, markersize=10) 8 ticks = [-1, 0, 1] 9 d2l.plt.xticks(ticks) 10 d2l.plt.yticks(ticks) 11 ax.set_zticks(ticks) 12 d2l.plt.xlabel(‘x‘) 13 d2l.plt.ylabel(‘y‘);
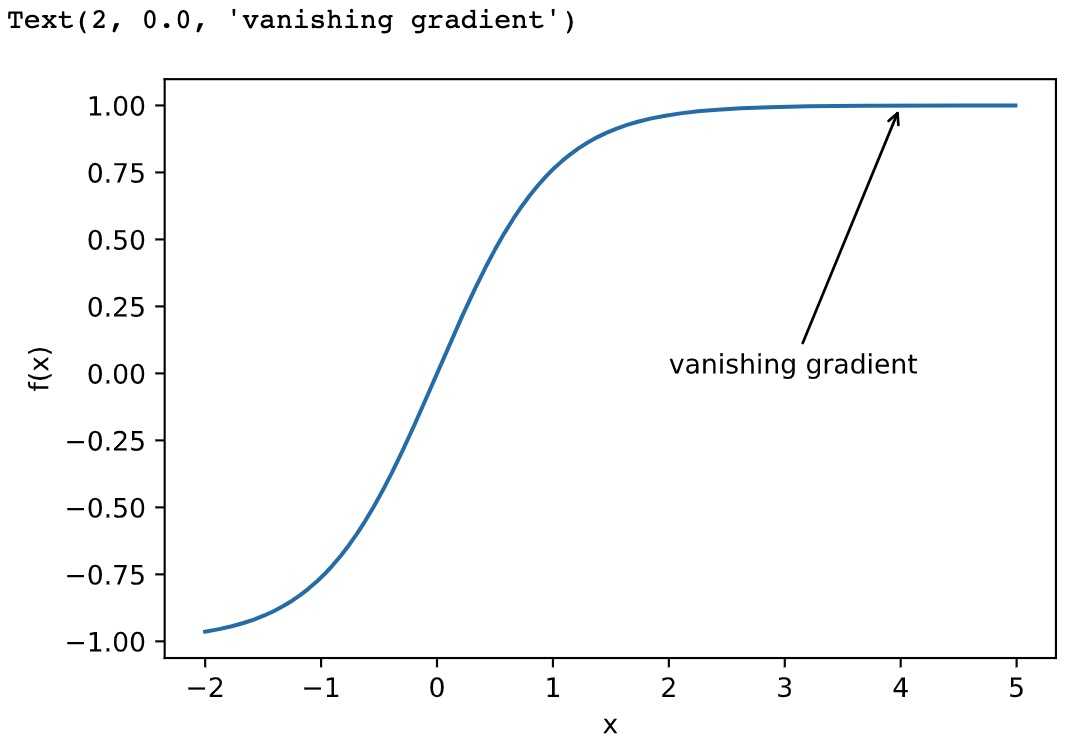
梯度消失

1 x = np.arange(-2.0, 5.0, 0.01) 2 fig, = d2l.plt.plot(x, np.tanh(x)) 3 d2l.plt.xlabel(‘x‘) 4 d2l.plt.ylabel(‘f(x)‘) 5 fig.axes.annotate(‘vanishing gradient‘, (4, 1), (2, 0.0) ,arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘))
凸性 (Convexity)
基础
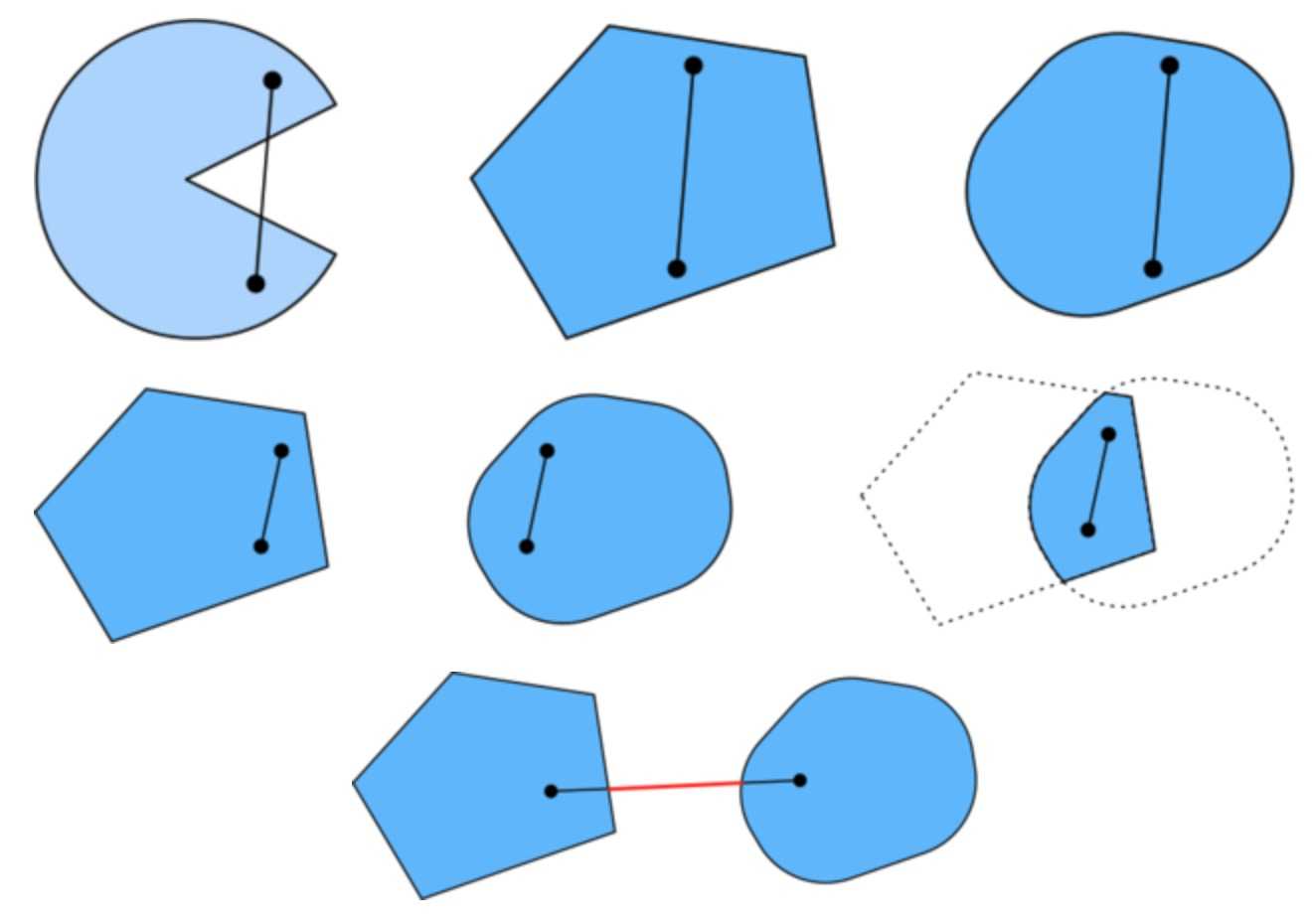
集合
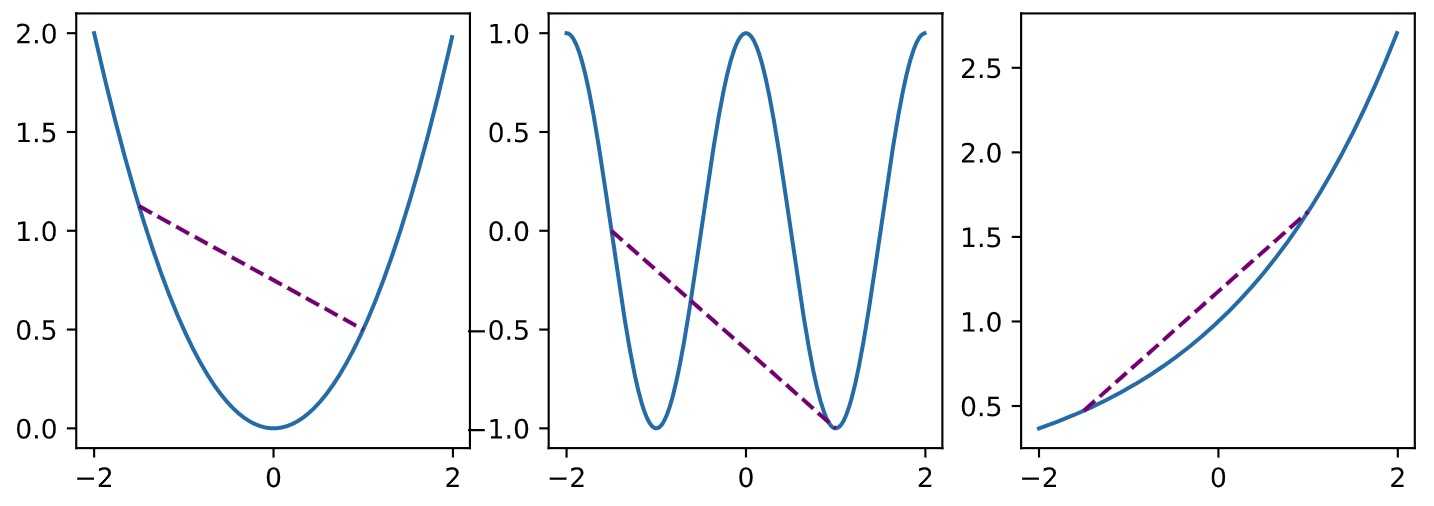
函数
![]()

1 def f(x): 2 return 0.5 * x**2 # Convex 3 4 def g(x): 5 return np.cos(np.pi * x) # Nonconvex 6 7 def h(x): 8 return np.exp(0.5 * x) # Convex 9 10 x, segment = np.arange(-2, 2, 0.01), np.array([-1.5, 1]) 11 d2l.use_svg_display() 12 _, axes = d2l.plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(9, 3)) 13 14 for ax, func in zip(axes, [f, g, h]): 15 ax.plot(x, func(x)) 16 ax.plot(segment, func(segment),‘--‘, color="purple") 17 # d2l.plt.plot([x, segment], [func(x), func(segment)], axes=ax)
Jensen 不等式
![]()
性质
- 无局部极小值
- 与凸集的关系
- 二阶条件
无局部最小值
![]()
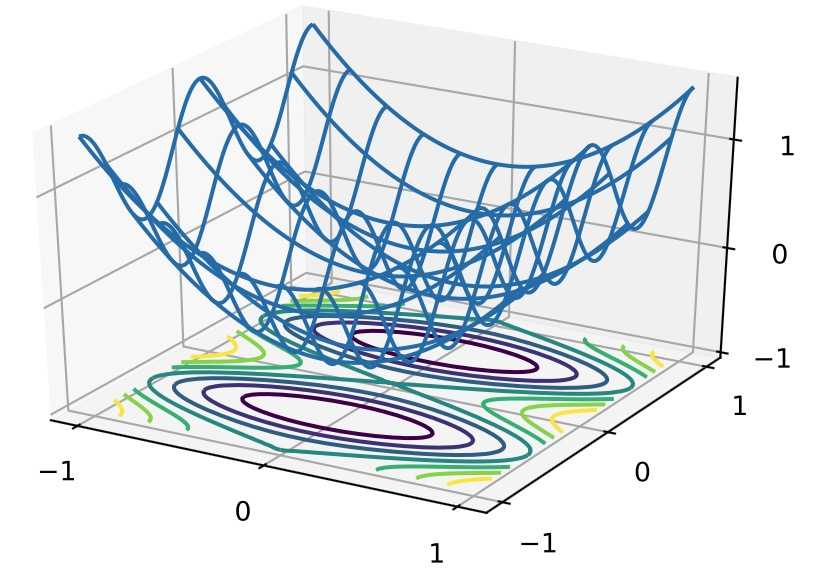
与凸集的关系
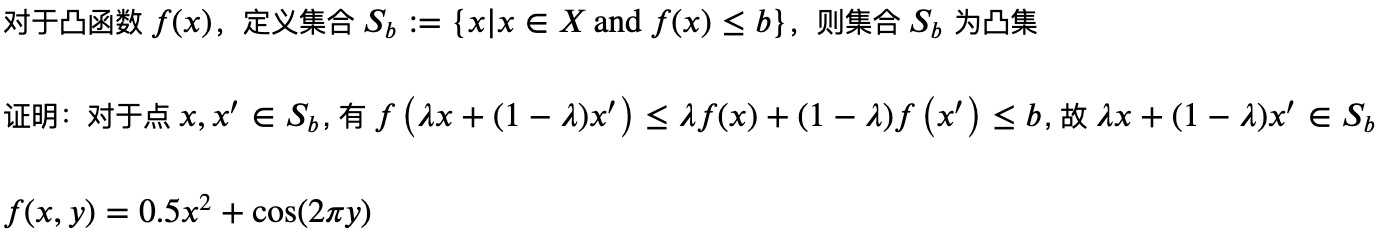

1 x, y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-1, 1, 101), np.linspace(-1, 1, 101), 2 indexing=‘ij‘) 3 4 z = x**2 + 0.5 * np.cos(2 * np.pi * y) 5 6 # Plot the 3D surface 7 d2l.set_figsize((6, 4)) 8 ax = d2l.plt.figure().add_subplot(111, projection=‘3d‘) 9 ax.plot_wireframe(x, y, z, **{‘rstride‘: 10, ‘cstride‘: 10}) 10 ax.contour(x, y, z, offset=-1) 11 ax.set_zlim(-1, 1.5) 12 13 # Adjust labels 14 for func in [d2l.plt.xticks, d2l.plt.yticks, ax.set_zticks]: 15 func([-1, 0, 1])
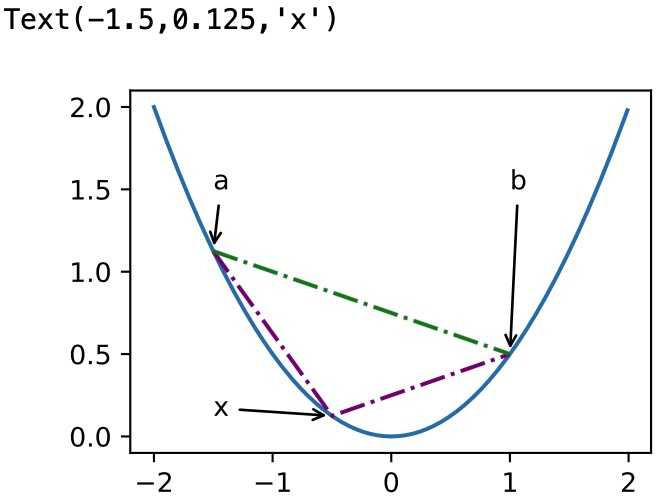
凸函数与二阶导数


1 def f(x): 2 return 0.5 * x**2 3 4 x = np.arange(-2, 2, 0.01) 5 axb, ab = np.array([-1.5, -0.5, 1]), np.array([-1.5, 1]) 6 7 d2l.set_figsize((3.5, 2.5)) 8 fig_x, = d2l.plt.plot(x, f(x)) 9 fig_axb, = d2l.plt.plot(axb, f(axb), ‘-.‘,color="purple") 10 fig_ab, = d2l.plt.plot(ab, f(ab),‘g-.‘) 11 12 fig_x.axes.annotate(‘a‘, (-1.5, f(-1.5)), (-1.5, 1.5),arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘)) 13 fig_x.axes.annotate(‘b‘, (1, f(1)), (1, 1.5),arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘)) 14 fig_x.axes.annotate(‘x‘, (-0.5, f(-0.5)), (-1.5, f(-0.5)),arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle=‘->‘))
限制条件
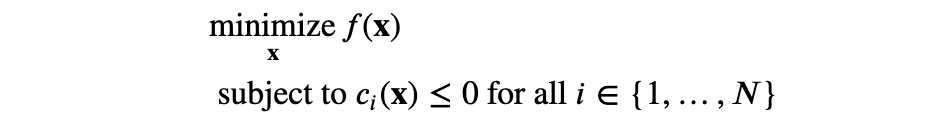
拉格朗日乘子法
![]()
惩罚项
![]()
投影
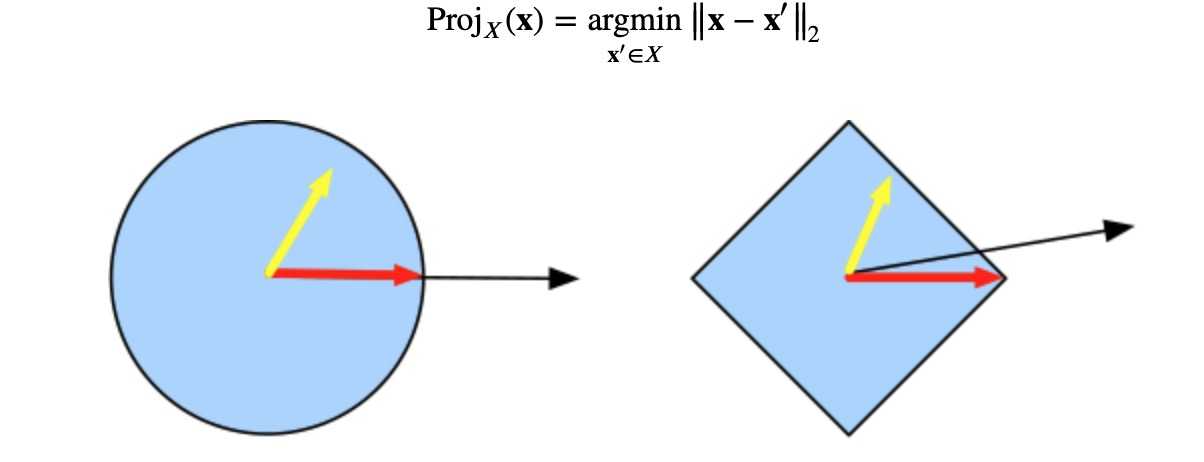
以上是关于机器学习(ML)十四之凸优化的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章