lecture 2
Posted eleni
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了lecture 2相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. circuit switching
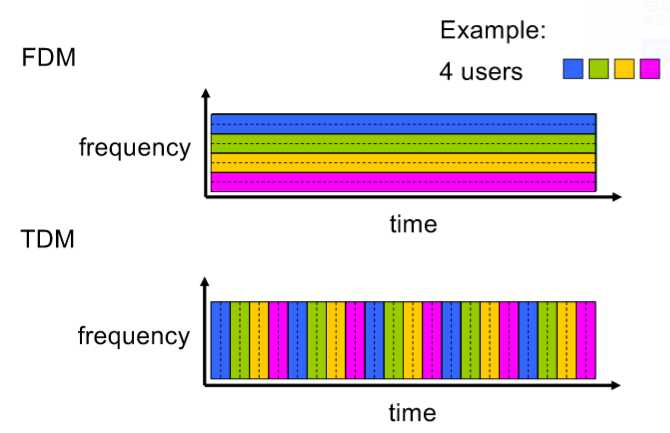
对于FDM而言,资源不会共享,如何分配取决于frequency,frequency越大,占用的资源越多(need to divided into small number of frequency)
对于TDM而言,资源归一个user所有,其他user需要排队等待
2. circuit switching的优点是no lost problem, no delay problem during transform; 缺点是need to set up以及not feasible
not feasible体现在:
a) inefficient
计算机通信突发状态很多(bursty);in periods of silence不能使用或共享专用电路;无法采用网络动态
b) fixed data rate
计算机通信速度不同,如观看视频与浏览网页时;fixed data rate不实用
c) connection state maintenance
每个通信状态都需要维持,开销大;不可扩展
3. packet switching
packet是独立的,不需要提前set up;包含payload+header,payload包含所携带data,header包含对packet的处理方法
4. switches有三种转发模式
a) cut through
switch will start transmitting as soon as it has processed the header
延迟最小,但是无法进行错误检测
b) FragmentFree(课上没有涉及)
switches将读至collision window,几乎没有延迟的进行error checking
c) store and forward
switch will processes a packet after it has received entirely
主流交换机首选方案,交换机将整个帧拷贝到板载缓存中,进行CRC校验;包含CRC error以及帧太长太短都会被丢掉
5. packet switching事先没有预留链接资源,switches将对其统计复用(statistical multiplexing)
统计复用依赖于并非所有流都同时爆发的假设(可类比为保险,有失败风险,出现overload)
6. Transient Overload瞬态过载:通过一个,别的进入buffer中等待 (delay problem)
Persistent Overload 持续过载:buffer出现overload,会开始drop packets(lose problem)
7. packet switching的优点是多个用户可同时使用且没有set up; 缺点是可能出现delay以及lost problem
8. 多个用户同时使用的证明用到probability计算公式,计算多个user时overload可能性
9. packet也可以使用circuit switch,set up时就决定了使用哪一个circuit,如quiz:
A message from device A to B consists of packet X and packet Y. In a circuit switched network, packet Y’s path___________________packet X’s path
A. is the same
B. is independent
C. is always different from
answer:A
10. end systems connect to Internet via access ISPs(Internet Service Providers)
因为两两互连太过复杂,只跟global ISPs连接可能出现经济问题;同时如果出现多个ISps可能出现竞争问题;目前的解决方案是不同地区有自己的regional ISP,各个公司有自己的ISP并与对应地区的ISP连接
11. 四种packet delay的来源
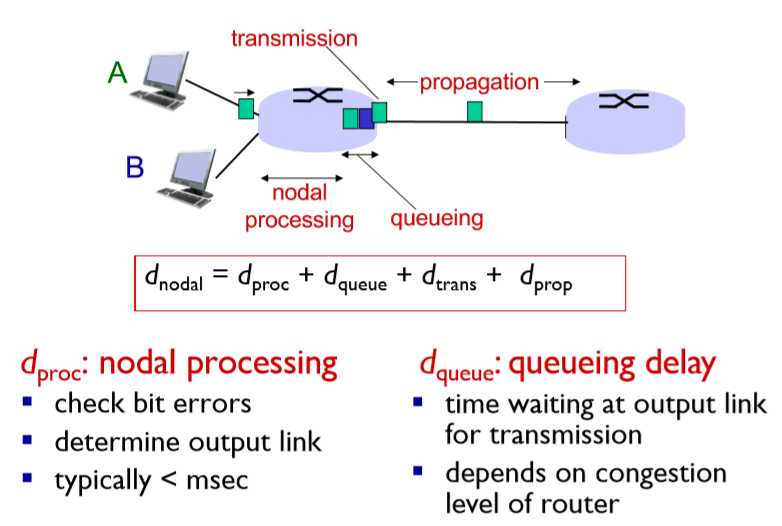
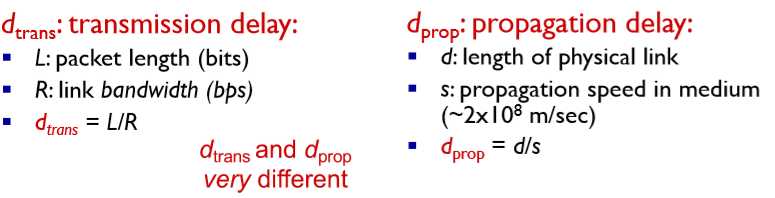
progation delay: progation time to travel along the link
12. queueing delay is the most important one
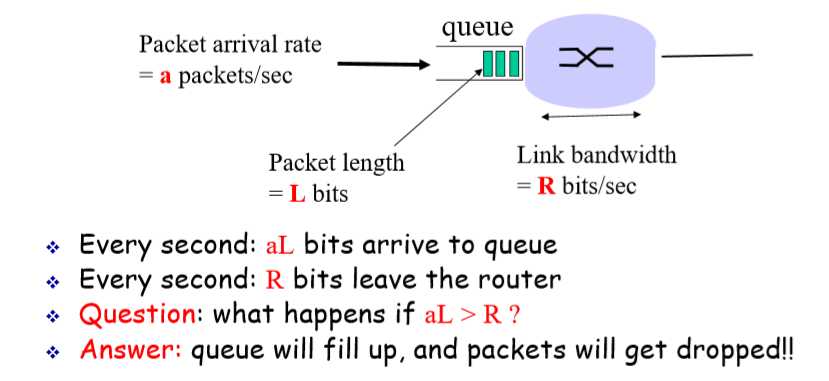
N packet arrives simultaneously every LN/R seconds
arrive rate: a = N/(LN/R) = R/L(packet/second)
traffic intensity = aL/R = (R/L)(L/R) = 1
Average queueing delay (queue is empty at time 0) :
{0 + L/R + 2L/R + … + (N-1)L/R}/N = L/(RN){1+2+…+(N-1)} =L(N-1)/(2R)
第一个为0是因为queue最开始为空故而没有delay
13. Consider a packet that has just arrived at a router. What is the correct order of the delays encountered bythe packet until itreachesthe next-hop router?
A. Transmission, processing,propagation,queuing
B. Propagation, processing,transmission, queuing
C. Processing, queuing, transmission, propagation
D. Queuing, processing,propagation,transmission
answer: C
14. throughput: rate(bits/time unit) at which bits transferred between sender/receiver
即最终的传输量
instananeous: rate at given point in time
average: rate over longer period of time
以上是关于lecture 2的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章