Quantum Hierarchical State Machine (量子层级状态机)
Posted yuzaihuan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Quantum Hierarchical State Machine (量子层级状态机)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言:一直想把这种好的代码应用与实际项目中,尤其是像状态机这种,这样,在多线程控制方面能够减小调试时间。
印象中,状态机类似这样:
switch(item):
{
case A:
break;
case B:
break;
default:
break;
}
最好能找到一种通用的格式就好,顺便完成常用的Pause和Continue功能(自己写的时候,这部分是挺麻烦的)。
下面只是对qf4net中的实例代码的解读,可能有不对的地方,请指正。
Samek量子层级状态机
源代码(qf4net)是用C/C++写的,主要用于嵌入式系统,没有C#版本的,不利于使用。
不同于使用固定大小的数组,新的方法采用数组列表的方式,可以适用于任意复杂度,和深度的层级状态机。
完整翻译文章挺困难的,我还是比较喜欢应用的角度来解读代码,并用于实际工作中。只是一个梳理的过程,随着自己理解的程度,对代码的理解又是不一定对。
问题描述(以下描述来自百度百科)
筷子是临界资源,一段时间只允许一位哲学家使用。为了表示互斥,用一个信号量表示一只筷子,五个信号量构成信号量数组。
管程机制
代码解读
问题的描述可以简化为下图:
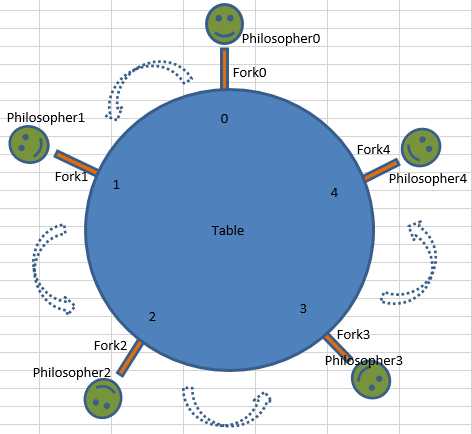
使用qf4net库文件在C#下实现。
首先标识所有可能使用到的信号:
1 public enum DPPSignal : int 2 { 3 Hungry = QSignals.UserSig, // Sent by philosopher when becoming hungry 4 Done, // Sent by philosopher when done eating 5 Eat, // Sent by table to let philosopher eat 6 Timeout, // Timeout to end thinking or eating 7 MaxSignal // Keep this signal always last 8 };
其中Hungry,Done,Timeout是由哲学家自己发出的,Eat才是桌子发出的。需保证UserSig为用户自定义的第一个信号,MaxSignal为用户自定义的最后一个信号。
同时我们看到QSignals的原始定义:
1 public enum QSignals : int 2 { 3 /// <summary> 4 /// Signal that is used to retrieve the super state (must not be used externally). 5 /// </summary> 6 Empty, 7 /// <summary> 8 /// 9 /// </summary> 10 Init, 11 /// <summary> 12 /// 13 /// </summary> 14 Entry, 15 /// <summary> 16 /// 17 /// </summary> 18 Exit, 19 /// <summary> 20 /// Entry in the enumeration that marks the first slot that is available for custom signals. 21 /// </summary> 22 UserSig 23 };
看到QSignals的定义,发现DPPSignal有点类似继承的形式,因为信号为空(Empty),信号初始化(Init),进入(Entry),退出(Exit)基本上每个状态(State)都有的信号。
哲学家类:哲学家只有三种状态:思考,肚子饿,吃饭需要关注,因此,创建这三种状态的处理过程;同时,每个哲学家需要一个唯一的ID便于标识;提供计时器用于跟踪思考和吃饭的时间,由此,得到哲学家类的变量定义如:
1 //思考时间,类型为时间间隔 2 private readonly TimeSpan c_ThinkTime = new TimeSpan(0, 0, 7); // last parameter represents seconds 3 //吃饭时间 4 private readonly TimeSpan c_EatTime = new TimeSpan(0, 0, 5); // last parameter represents seconds 5 6 private QTimer m_Timer; 7 private int m_PhilosopherId; 8 9 //哲学家只有三种状态:思考,肚子饿,吃饭 10 private QState m_StateThinking; 11 private QState m_StateHungry; 12 private QState m_StateEating; 13 14 //带参数的构造函数 15 public Philosopher(int philosopherId) 16 { 17 m_PhilosopherId = philosopherId; 18 19 m_StateThinking = new QState(this.Thinking); 20 m_StateHungry = new QState(this.Hungry); 21 m_StateEating = new QState(this.Eating); 22 23 m_Timer = new QTimer(this); 24 }
实例化之前,需要重写如下函数。这只在类内部使用。系统内部可能有很多其它信号,但哲学家只关注是否可以吃饭这一个信号;同时,把哲学家的初始状态更改为思考的状态。
1 protected override void InitializeStateMachine() 2 { 3 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = this.ToString(); 4 LogMessage(String.Format("Initializing philosopher {0}.", m_PhilosopherId)); 5 //需要关注的外部信号是:可以吃饭了 6 QF.Instance.Subscribe(this, (int)DPPSignal.Eat); 7 InitializeState(m_StateThinking); // initial state=thinking 8 }
接下来看看Thinking状态函数:
Thinking:
Entry:给系统发布一个计时器,描述思考结束事件;
TImout:思考结束了,需要转换状态为肚子饿
Exit:退出Thinking状态
1 private static TransitionChain s_Tran_Thinking_Hungry; 2 private QState Thinking(IQEvent qEvent) 3 { 4 switch (qEvent.QSignal) 5 { 6 case (int)QSignals.Entry: 7 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is thinking.", m_PhilosopherId)); 8 //进来后,思考一段时间,发布思考完了信号,只发送一次 9 m_Timer.FireIn(c_ThinkTime, new PhilosopherEvent(DPPSignal.Timeout)); 10 return null; 11 12 case (int)DPPSignal.Timeout: 13 //思考结束后,得转换状态为肚子饿了的状态 14 TransitionTo(m_StateHungry, ref s_Tran_Thinking_Hungry); 15 return null; 16 17 case (int)QSignals.Exit: 18 //退出时,记录信息,方便调试 19 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is exiting thinking state.", m_PhilosopherId)); 20 return null; 21 } 22 return this.TopState; 23 }
肚子饿的状态函数也需要考虑以下几个信号:
Hungry:
Entry:给桌子发布事件,信息包括饿了信号及当前哲学家ID
Eat:需要转换状态到吃
Exit:推出Hungry状态
1 private static TransitionChain s_Tran_Hungry_Eating; 2 private QState Hungry(IQEvent qEvent) 3 { 4 switch (qEvent.QSignal) 5 { 6 case (int)QSignals.Entry: 7 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is hungry.", m_PhilosopherId)); 8 //创建一个要吃饭的桌子事件,状态为肚子饿了,发呆哲学家的Id,申请对应的碗筷 9 TableEvent tableEvent = new TableEvent(DPPSignal.Hungry, m_PhilosopherId); 10 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} publishes Hungry event.", m_PhilosopherId)); 11 //发布一个要吃饭的事件 12 QF.Instance.Publish(tableEvent); 13 return null; 14 15 case (int)DPPSignal.Eat: 16 //等待桌子发送可以吃饭的信号 17 if (((TableEvent)qEvent).PhilosopherId == m_PhilosopherId) 18 { 19 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} receives eat signal.", m_PhilosopherId)); 20 //正常过度到可以吃饭的状态 21 TransitionTo(m_StateEating, ref s_Tran_Hungry_Eating); 22 } 23 return null; 24 25 case (int)QSignals.Exit: 26 //记录退出肚子饿了的状态 27 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is exiting hungry state.", m_PhilosopherId)); 28 return null; 29 } 30 return this.TopState; 31 }
Eating的状态也是如此:
Eating:
Entry:发布·一个计时器,等待Timeout信号
TImeout:吃完了,需要转换信号到思考的状态
Exit:推出Eating状态,同时给桌子发布吃完了得信号。
1 private static TransitionChain s_Tran_Eating_Thinking; 2 private QState Eating(IQEvent qEvent) 3 { 4 switch (qEvent.QSignal) 5 { 6 case (int)QSignals.Entry: 7 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is eating.", m_PhilosopherId)); 8 //吃饭中,结束后,发送一次吃饭结束信号 9 m_Timer.FireIn(c_EatTime, new PhilosopherEvent(DPPSignal.Timeout)); 10 return null; 11 12 case (int)DPPSignal.Timeout: 13 //吃饭结束后,转换状态到思考的状态 14 TransitionTo(m_StateThinking, ref s_Tran_Eating_Thinking); 15 return null; 16 17 case (int)QSignals.Exit: 18 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is exiting eating state.", m_PhilosopherId)); 19 //创建桌子事件:信号状态为吃好了,发呆哲学家Id,可以释放碗筷 20 TableEvent tableEvent = new TableEvent(DPPSignal.Done, m_PhilosopherId); 21 LogMessage(String.Format("Philosopher {0} publishes Done event.", m_PhilosopherId)); 22 //发布上面的事件 23 QF.Instance.Publish(tableEvent); 24 return null; 25 } 26 return this.TopState; 27 }
为了简化问题,在哲学家得事件类中,作者只是打印输出当前状态字符串:
1 public override string ToString() 2 { 3 switch (this.QSignal) 4 { 5 case (int)DPPSignal.Done: 6 case (int)DPPSignal.Hungry: 7 case (int)DPPSignal.Timeout: 8 return ((DPPSignal)this.QSignal).ToString(); 9 default: return base.ToString(); 10 } 11 }
接下来考虑桌子类.
桌子只有一个状态Serving,它需要监控筷子和每个哲学家的状态(数组)。
1 //只有一种状态:提供服务 2 private QState m_StateServing; 3 private int m_NumberOfPhilosophers; 4 private bool[] m_ForkIsUsed; 5 private bool[] m_PhilosopherIsHungry; 6 7 public Table(int numberOfPhilosophers) 8 { 9 //创建哲学家,记录筷子被使用的个数及未被使用的个数(有人在挨饿) 10 m_NumberOfPhilosophers = numberOfPhilosophers; 11 m_ForkIsUsed = new bool[m_NumberOfPhilosophers]; 12 m_PhilosopherIsHungry = new bool[m_NumberOfPhilosophers]; 13 14 for (int i = 0; i < m_NumberOfPhilosophers; i++) 15 { 16 m_ForkIsUsed[i] = false; 17 m_PhilosopherIsHungry[i] = false; 18 } 19 //初始状态:可以服务了 20 m_StateServing = new QState(this.Serving); 21 }
桌子状态机初始化时需要注册这两个信号,就是来自哲学家的饿了和吃好了的信号。
1 protected override void InitializeStateMachine() 2 { 3 Thread.CurrentThread.Name = this.ToString(); 4 // Subscribe for the relevant events raised by philosophers 5 //桌子只关注外部的两种信号:有人肚子饿,有人吃好了 6 QF.Instance.Subscribe(this, (int)DPPSignal.Hungry); 7 QF.Instance.Subscribe(this, (int)DPPSignal.Done); 8 9 //起始状态:可以服务了 10 InitializeState(m_StateServing); // initial transition 11 }
Serving状态函数只提供对信号Hungry和Done的处理,没有像哲学家类那样处理Entry和Exit。
Serving:
Hungry:判断是否有空的筷子,如果有就吃,否则的话,标注哲学家的状态
Done:吃完饭就释放筷子,依次判断左右哲学家及筷子的状态,并且,以左优先。
1 private QState Serving(IQEvent qEvent) 2 { 3 int philosopherId; 4 5 switch (qEvent.QSignal) 6 { 7 case (int)DPPSignal.Hungry: 8 philosopherId = GetPhilosopherId(qEvent); 9 //确保哲学家的起始状态不是肚子饿的状态 10 Debug.Assert(!m_PhilosopherIsHungry[philosopherId], "Philosopher must not be already hungry"); 11 12 Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is hungry.", philosopherId)); 13 14 //是否有闲置的筷子 15 if (ForksFree(philosopherId)) 16 { 17 LetPhilosopherEat(philosopherId); 18 } 19 else 20 { 21 // The philosopher has to wait for free forks 22 m_PhilosopherIsHungry[philosopherId] = true; // mark philosopher as hungry 23 Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Philosopher {0} has to wait for forks.", philosopherId)); 24 } 25 return null; 26 27 case (int)DPPSignal.Done: 28 philosopherId = GetPhilosopherId(qEvent); 29 Console.WriteLine(String.Format("Philosopher {0} is done eating.", philosopherId)); 30 //更新标志位 31 m_PhilosopherIsHungry[philosopherId] = false; 32 33 // free up the philosopher‘s forks:释放使用中的筷子 34 FreeForks(philosopherId); 35 36 // Can the left philosopher eat?当前的筷子左边的邻居需要吗,需要的话就给他 37 int neighborPhilosopher = LeftIndex(philosopherId); 38 if (m_PhilosopherIsHungry[neighborPhilosopher] && ForksFree(neighborPhilosopher)) 39 { 40 LetPhilosopherEat(neighborPhilosopher); 41 // The left philosopher could eat; mark philosopher as no longer hungry 42 m_PhilosopherIsHungry[neighborPhilosopher] = false; 43 } 44 45 // Can the right philosopher eat?筷子如果左边没人要,那就表明ForksFree为真,那就给右边的人 46 neighborPhilosopher = RightIndex(philosopherId); 47 if (m_PhilosopherIsHungry[neighborPhilosopher] && ForksFree(neighborPhilosopher)) 48 { 49 LetPhilosopherEat(neighborPhilosopher); 50 // The right philosopher could eat; mark philosopher as no longer hungry 51 m_PhilosopherIsHungry[neighborPhilosopher] = false; 52 } 53 54 return null; 55 } 56 return this.TopState; 57 }
上面对几个函数的处理没有提供代码,可以参考原始代码。
对应简化版的TableEvent类,也只是打印当前状态信息并输出。
1 public override string ToString() 2 { 3 switch (this.QSignal) 4 { 5 case (int)DPPSignal.Hungry: 6 case (int)DPPSignal.Eat: 7 case (int)DPPSignal.Done: 8 return String.Format("Signal {0}; Philosopher {1}", ((DPPSignal)this.QSignal).ToString(), PhilosopherId); 9 default: return base.ToString(); 10 } 11 }
运行主程序:
1 [STAThread] 2 static void Main(string[] args) 3 { 4 QF.Instance.Initialize((int)DPPSignal.MaxSignal - 1); 5 6 //创建可以坐5个哲学家的桌子 7 IQActive table = new Table(c_NumberOfPhilosophers); 8 IQActive[] philosophers = new IQActive[c_NumberOfPhilosophers]; 9 10 for (int i = 0; i < c_NumberOfPhilosophers; i++) 11 { 12 philosophers[i] = new Philosopher(i); 13 } 14 15 Console.WriteLine(c_NumberOfPhilosophers + " philosophers gather around a table thinking ..."); 16 table.Start(c_NumberOfPhilosophers); 17 for (int i = 0; i < c_NumberOfPhilosophers; i++) 18 { 19 philosophers[i].Start(i); 20 } 21 }
得到打印输出部分结果如下:
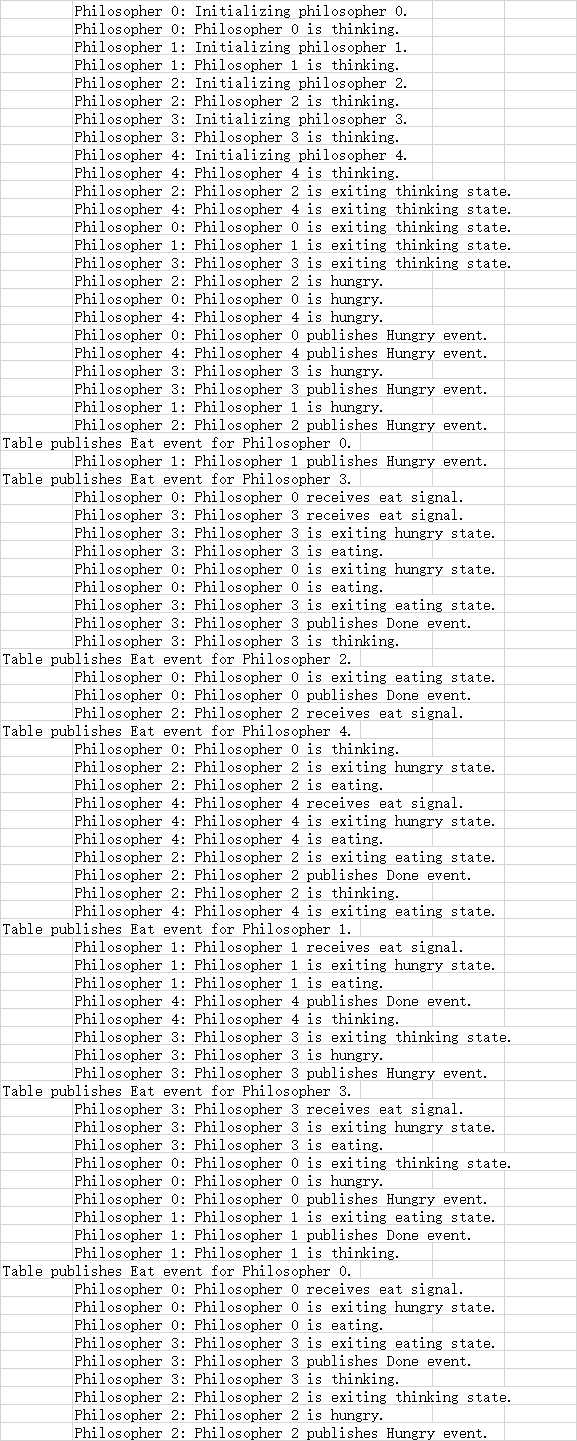
以上是关于Quantum Hierarchical State Machine (量子层级状态机)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
系统聚类(hierarchical clustering analysis)
Managing Hierarchical Data in MySQL(邻接表模型)