题解 LG P2264
Posted ct666rp
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了题解 LG P2264相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这是题解P2264
先讲一下Trie,其实Trie也名前缀树,就是说:如果Trie中某串是某串的前缀,那么我们可以共用这个串也就是这样:
插入h、hk、jc,jcfa
那么,h节点会给h和hk共用,jc串也会给jcfa共用。
对于本题来说,因为要考虑每个句子后要标记次数,所以Trie要有附加数组。
拿样例为例,我们原本会构建这样的一棵TRIE树:
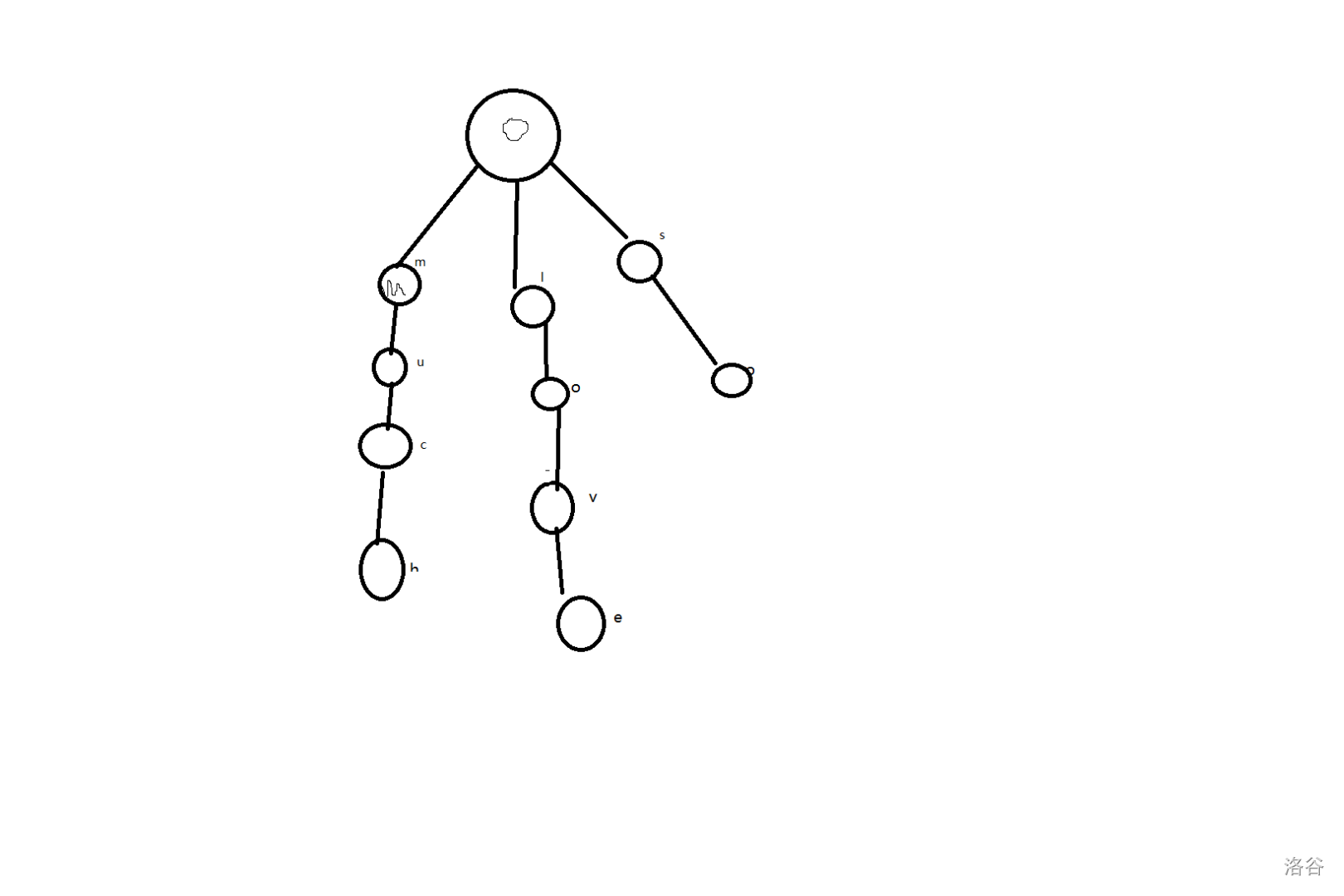
但我们只要在底下最后一个点附加一个val数组来记录次数,因为要记录次数。
那么trie就沉了这样:
int ch[N][C],tot=1;
int check[N];
怎么写也就更简单了:
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; #define N 50005 #define rr register #define C 27 string s,w; int n; int ch[N][C],tot=1,ans; string w1[N]; int check[N]; int idx(char s); void insert(string s); int find(string s); char turn(char x); int main() { cin>>n; for(rr int i=1;i<=n;i++) { cin>>w1[i]; for(rr int j=0;j<=w1[i].size()-1;j++) w1[i][j]=turn(w1[i][j]); insert(w1[i]); } int len; getchar(); getline(cin,s); len=s.size()-1; for(rr int i=0;i<=len;i++) { s[i]=turn(s[i]); if(s[i]==‘.‘ or s[i]==‘,‘ or s[i]==‘ ‘) { if(find(w)==1) ans++; if(s[i]==‘.‘) for(rr int j=1;j<=n;j++) insert(w1[j]); w=""; } else w+=s[i]; } cout<<ans; return 0; } int idx(char x) { int v; v=(int)(x-‘a‘); return v; } void insert(string s) { int len=s.size()-1; int las=0,w; for(rr int i=0;i<=len;i++) { w=idx(s[i]); if(ch[las][w]==0) ch[las][w]=++tot; las=ch[las][w]; } check[las]=1; return; } int find(string s) { int len=s.size()-1; int las=0,w; for(rr int i=0;i<=len;i++) { w=idx(s[i]); if(ch[las][w]==0) return 0; las=ch[las][w]; } if(check[las]==1) { check[las]++; return 1; } else return 0; } char turn(char x) { if(x>=‘A‘&&x<=‘Z‘) return (x+32); else return x; }
Update 2020.2.14 祝大家情人节快乐!
二分答案:
N方过百万,暴力碾标程
这是对不会STL+Trie的福音。
这是P2264的第2种做法。
我们想一下,题目中说了有N个可以加好感度的字符串。
众所周知,我们只需要按字典序排好序,那么N个字符串就会呈单调上升。
单调上升的话,我们就可以进行二分查找是否可以加好感度。
而二分查找的时间是logn,整个程序的时间就是O(Slogn)。
其中S是字符串长度。
以上是关于题解 LG P2264的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章