数据结构PTA(浙大mooc)
Posted blogofzzx
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构PTA(浙大mooc)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
04-树5 Root of AVL Tree (25分)
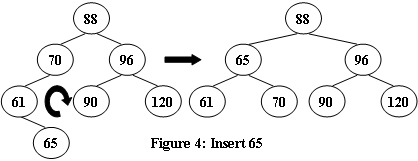
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
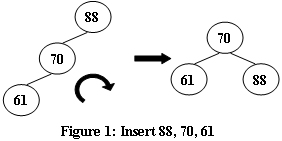
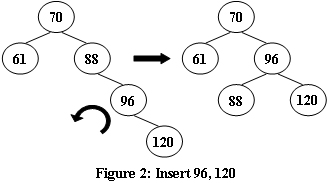
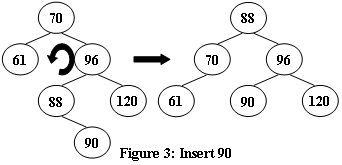
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted.
Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
#include<stdio.h> #include<malloc.h> #define EH 0 //等高 #define RH -1 //右高 #define LH 1 //左高 typedef struct BSTNode *BSTree; void L_Rotate(BSTree &p); void R_Rotate(BSTree &p); void LeftBalance(BSTree &T); void RightBalance(BSTree &T); int InsertAVL(BSTree &T, int e, bool &taller); struct BSTNode { int data; int bf; //-1代表右高,1代表左高,0代表左右一样高 BSTree lchild; BSTree rchild; }; int main() { int n; scanf_s("%d", &n); int x; BSTree T=NULL; bool taller = false; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf_s("%d", &x); InsertAVL(T, x, taller); } printf("%d ", T->data); return 0; } //右旋 void R_Rotate(BSTree &p) { BSTree lc; lc = p->lchild; //lc指向p的左子树的根结点 p->lchild = lc->rchild; //p的左子树接lc的右子树 lc->rchild = p; //lc的右子树接p p = lc; //p指向新的根结点 } //左旋 void L_Rotate(BSTree &p) { BSTree rc = p->rchild; //rc指向p的右子树的根结点 p->rchild = rc->lchild; //p的右子树接rc的左子树 rc->lchild = p; //rc的左子树接为p p = rc; //p指向新的根结点 } int InsertAVL(BSTree &T, int e, bool &taller) { //若在平衡的二叉搜索树T中不存在和e相同的结点则插入一个新结点,返回1,否则返回0 //若因插入使二叉搜索树失去平衡,则做平衡旋转处理,bool类型判断T是否长高 if (!T){//插入新结点,树长高,taller置为True T = (BSTree)malloc(sizeof(BSTNode)); T->data = e; T->lchild = T->rchild = NULL; T->bf = EH; taller = true; } else { if (e == T->data) //存在和e相同的结点不插入 { taller = false; return 0; } if (e < T->data) //应在T的左子树中进行搜索 { if (!InsertAVL(T->lchild, e, taller)) //返回值为0说明左子树中存在相同的结点,则直接return 0; return 0; if (taller) //如果树长高了,判断是否需要平衡 { switch (T->bf) //检查T的平衡因子 { case LH: //原来左子树比右子数高,又插入在左子树中,需要做平衡 LeftBalance(T); taller = false; break; case EH: T->bf = LH; taller = true; break; case RH: T->bf = EH; taller = false; break; } } } else //在T的右子树种进行搜索 { if (!InsertAVL(T->rchild, e, taller)) //返回值为0,说明右子树种存在相同的结点,不用插入 return 0; if (taller) { switch (T->bf) { case LH: T->bf = EH; taller = false; break; case EH: T->bf = RH; taller = true; break; case RH: RightBalance(T); taller = false; break; } } } } return 1; } void LeftBalance(BSTree &T) { //对以T为根结点的二叉树做左平衡旋转,结束后,指针T指向新的根结点 BSTree lc = T->lchild; switch (lc->bf) //检查T的左子树的平衡因子 { case LH: //如果左边高,则做右旋操作 T->bf = lc->bf = EH; //先修改平衡因子,右旋后,平衡因子置为EH R_Rotate(T); break; case RH: //如果右高,新结点插在T的左子树的右子树上,应做左右双旋 BSTree rd = lc->rchild; switch (rd->bf) //按照三种情况修改,T和lc的平衡因子 { case LH:lc->bf = EH; T->bf = RH; break; case EH:lc->bf = T->bf = EH; break; case RH:T->bf = EH; lc->bf = LH; break; } rd->bf = EH; //修改rd的平衡因子 L_Rotate(T->lchild); //对T的左子树进行左旋,旋转之后T的左孩子变为rd; R_Rotate(T); //然后对T进行右旋操作 break; } } void RightBalance(BSTree &T) { BSTree rc = T->rchild; //rc指向T的右子树 switch (rc->bf) { case RH: //插入在T的右子树的右子树上,应进行右旋操作 T->bf = rc->bf = EH;//先修改T和T的右子树的平衡因子 L_Rotate(T); break; case LH: //插入在T的右子树的左子树上,应进行右左双选操作 BSTree ld = rc->lchild; switch (ld->bf) { case LH:T->bf = EH; rc->bf = RH; break; case EH:T->bf = rc->bf = EH; break; case RH:T->bf = LH; rc->bf = EH; break; } ld->bf = EH; R_Rotate(T->rchild); //对T的右子树进行右旋,旋转后T的右子树的根结点变成ld L_Rotate(T); //然后对T进行左旋 break; } }
以上是关于数据结构PTA(浙大mooc)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章