动态数组
Posted aacfhfzfze
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了动态数组相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
数组的概念
数组(Array)是一种线性表数据结构。它用一组连续的内存空间,来存储一组具有相同类型的数据。
线性表就是数据排成像一条线一样的结构。每个线性表上的数据最多只有前和后两个方向。除了数组,链表、队列、栈等也是线性表结构。
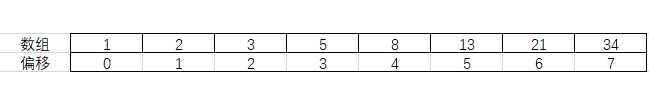
使用数组的优势在于:数组支持随机访问,根据下标随机访问的时间复杂度为O(1)。
为什么很多编程语言里面的数组都从0开始编号?
如果数组从0开始计数,那么计算a[i]的内存地址只需要用这个公式:
a[i]_address = base_address + i * type_size
如果数组从1开始计数,那么公式变成:
a[i]_address = base_address + (i-1)*type_size
那样每次随机访问数组元素都多了一次减法运算,也就是多了一次减法指令,数组作为非常基础的数据结构,通过下标随机访问数组元素又是其非常基础的编程操作,效率的优化就要尽可能做到极致。所以选择了从0开始编号数组,而不是从1开始。
动态数组的简单实现:
import java.util.Objects;
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
public Array(E[] arr){
data = (E[]) new Objects[arr.length];
for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length;i++)
data[i] = arr[i];
size = arr.length;
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
public void swap(int i, int j){
if(i < 0 || i >= size || j < 0 || j >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index is illegal.");
E t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d
", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}动态数组的复杂度:
addLast(e) O(1)
addFirst(e) O(n)
add(index,e) O(n)
整体来说添加的操作是O(n)的复杂度
removeLast(e) O(1)
removeFirst(e) O(n)
remove(index,e) O(n)
整体来说删除的操作是O(n)的复杂度
set(index,e) O(1)
get(index) O(1)
contains(e) O(n)
find(e) O(n)
以上是关于动态数组的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章