设计模式-行为型模式-模板方法模式(Template Method)
Posted sxrtb
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设计模式-行为型模式-模板方法模式(Template Method)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
行为型-模板方法模式
个人理解,通俗的说,就是我们将实现某功能的模板写好,其中实现这个功能的具体步骤可以抽离出来,由子类来写具体的实现。
其实抽象类就体现了模板方法这个思想,抽象类将子类需要实现的方法抽象出来,形成抽象方法;也可以理解为抽象类作为了子类的通用模板。设计模板方法时,我们的父类一般都是抽象类。
类图:
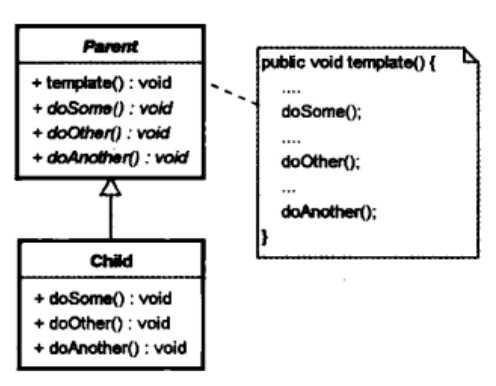
1.定义AbstractClass
public abstract class TemplateMethod { protected abstract void doOperation1(); public void doOperation2(){ System.out.println("TemplateMethod doOperation2"); } /** * 模板方法 */ public void templateMethod(){ doOperation1(); doOperation2(); } }
2.实现具体步骤的子类
public class FirstSubTemplateMethod extends TemplateMethod { @Override protected void doOperation1() { System.out.println("FirstSubTemplateMethod doOperation1"); } @Override public void doOperation2() { System.out.println("FirstSubTemplateMethod doOperation2"); } }
public class SecodeSubTemplateMethod extends TemplateMethod{ @Override protected void doOperation1() { System.out.println("SecodeSubTemplateMethod doOperation1"); } }
3.测试模板方法
public class TemplateMethodTest { public static void main(String[] args) { TemplateMethod templateMethod1 = new FirstSubTemplateMethod(); TemplateMethod templateMethod2 = new SecodeSubTemplateMethod(); templateMethod1.templateMethod(); templateMethod2.templateMethod(); } }
4.输出
FirstSubTemplateMethod doOperation1
FirstSubTemplateMethod doOperation2
SecodeSubTemplateMethod doOperation1
TemplateMethod doOperation2
其实这样,模板方法模式就结束了。
那么我们的父类能不能是普通的类,或者是接口呢,这个问题讲完模板方法后再将。
个人理解,其实模板方法体现在,有一个模板方法,这个方法中调用了中另外一个或这几个方法。而被调用的方法需要子类实现(或者提供了默认实现,子类可以重写),则它的修饰符可以使public,protected,甚至可以省略(一般不使用这种方式)。
这里我们再说父类能不能是普通的类和接口。先说接口,JDK1.8之前,接口中的方法只能是抽象方法,JDK1.8之后,接口中可以有类方法和默认方法,而设计模式这种思想早就被人提出,所以我们没有看到使用接口来写模板模式的(如果那一天看到别人用默认将默认的方法写出一种模板方法,我个人还是觉得可以接受的,java语言使我们手中的工具,我们可以用java编写能带给人们便利的软件)。
再说父类能不能是普通的类。如果父类是普通的类,而父类中的方法就都不能用abstract,那么这样,。。。感觉也未尝不可。
再说模板方法,感觉在编程中,某个方法调用一个到几个其他方法的方法感觉到处都是。若父类是普通的类,那么,无处不是模板方法(那么父类到底可不可以是普通类呢,实在要这个编程,那也没错)。
模板方法是人们对常用编程方式的一种提炼,很好的体现了开闭原则和里氏替换原则。通常上,人们将父类定义为抽象类。
抽象类中不一定有抽象方法,模板方法中也不是一定要有抽象方法。
设计模式,或者我们现在讨论的模板方法设计模式,体现的一种编程思想。
使用模板方法的例子:
JAVA WEB程序离不开Servlet(SpringMVC底层就封装了Servlet,虽然有可能我们平时开发中没有直接使用到Servlet)。编写一个Servlet,可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/a376298333/article/details/79121548。
public class FirstServlet extends javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet { protected void doPost(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response) throws javax.servlet.ServletException, IOException { } protected void doGet(javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response) throws javax.servlet.ServletException, IOException { } }
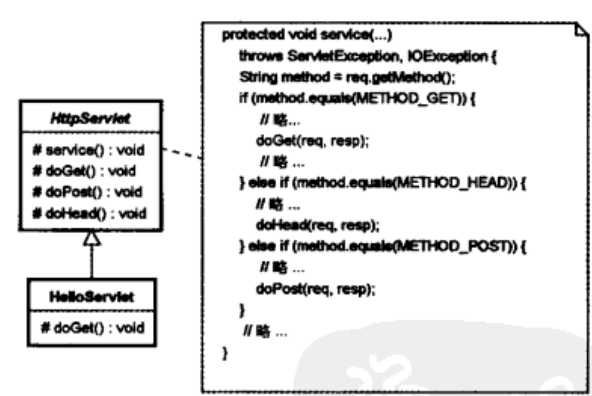
而javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet的源码
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private static final String METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE"; private static final String METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD"; private static final String METHOD_GET = "GET"; private static final String METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS"; private static final String METHOD_POST = "POST"; private static final String METHOD_PUT = "PUT"; private static final String METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE"; private static final String HEADER_IFMODSINCE = "If-Modified-Since"; private static final String HEADER_LASTMOD = "Last-Modified"; private static final String LSTRING_FILE = "javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings"; private static final ResourceBundle lStrings = ResourceBundle.getBundle("javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings"); public HttpServlet() { } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String protocol = req.getProtocol(); String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported"); if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { resp.sendError(405, msg); } else { resp.sendError(400, msg); } } protected long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest req) { return -1L; } protected void doHead(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { if (DispatcherType.INCLUDE.equals(req.getDispatcherType())) { this.doGet(req, resp); } else { NoBodyResponse response = new NoBodyResponse(resp); this.doGet(req, response); response.setContentLength(); } } protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String protocol = req.getProtocol(); String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported"); if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { resp.sendError(405, msg); } else { resp.sendError(400, msg); } } protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String protocol = req.getProtocol(); String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_put_not_supported"); if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { resp.sendError(405, msg); } else { resp.sendError(400, msg); } } protected void doDelete(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String protocol = req.getProtocol(); String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_delete_not_supported"); if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { resp.sendError(405, msg); } else { resp.sendError(400, msg); } } private static Method[] getAllDeclaredMethods(Class<?> c) { if (c.equals(HttpServlet.class)) { return null; } else { Method[] parentMethods = getAllDeclaredMethods(c.getSuperclass()); Method[] thisMethods = c.getDeclaredMethods(); if (parentMethods != null && parentMethods.length > 0) { Method[] allMethods = new Method[parentMethods.length + thisMethods.length]; System.arraycopy(parentMethods, 0, allMethods, 0, parentMethods.length); System.arraycopy(thisMethods, 0, allMethods, parentMethods.length, thisMethods.length); thisMethods = allMethods; } return thisMethods; } } protected void doOptions(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { Method[] methods = getAllDeclaredMethods(this.getClass()); boolean ALLOW_GET = false; boolean ALLOW_HEAD = false; boolean ALLOW_POST = false; boolean ALLOW_PUT = false; boolean ALLOW_DELETE = false; boolean ALLOW_TRACE = true; boolean ALLOW_OPTIONS = true; Class clazz = null; try { clazz = Class.forName("org.apache.catalina.connector.RequestFacade"); Method getAllowTrace = clazz.getMethod("getAllowTrace", (Class[])null); ALLOW_TRACE = (Boolean)getAllowTrace.invoke(req, (Object[])null); } catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException | IllegalAccessException | IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException | ClassNotFoundException var14) { ; } for(int i = 0; i < methods.length; ++i) { Method m = methods[i]; if (m.getName().equals("doGet")) { ALLOW_GET = true; ALLOW_HEAD = true; } if (m.getName().equals("doPost")) { ALLOW_POST = true; } if (m.getName().equals("doPut")) { ALLOW_PUT = true; } if (m.getName().equals("doDelete")) { ALLOW_DELETE = true; } } String allow = null; if (ALLOW_GET) { allow = "GET"; } if (ALLOW_HEAD) { if (allow == null) { allow = "HEAD"; } else { allow = allow + ", HEAD"; } } if (ALLOW_POST) { if (allow == null) { allow = "POST"; } else { allow = allow + ", POST"; } } if (ALLOW_PUT) { if (allow == null) { allow = "PUT"; } else { allow = allow + ", PUT"; } } if (ALLOW_DELETE) { if (allow == null) { allow = "DELETE"; } else { allow = allow + ", DELETE"; } } if (ALLOW_TRACE) { if (allow == null) { allow = "TRACE"; } else { allow = allow + ", TRACE"; } } if (ALLOW_OPTIONS) { if (allow == null) { allow = "OPTIONS"; } else { allow = allow + ", OPTIONS"; } } resp.setHeader("Allow", allow); } protected void doTrace(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String CRLF = " "; StringBuilder buffer = (new StringBuilder("TRACE ")).append(req.getRequestURI()).append(" ").append(req.getProtocol()); Enumeration reqHeaderEnum = req.getHeaderNames(); while(reqHeaderEnum.hasMoreElements()) { String headerName = (String)reqHeaderEnum.nextElement(); buffer.append(CRLF).append(headerName).append(": ").append(req.getHeader(headerName)); } buffer.append(CRLF); int responseLength = buffer.length(); resp.setContentType("message/http"); resp.setContentLength(responseLength); ServletOutputStream out = resp.getOutputStream(); out.print(buffer.toString()); out.close(); } protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod(); long lastModified; if (method.equals("GET")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); if (lastModified == -1L) { this.doGet(req, resp); } else { long ifModifiedSince; try { ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since"); } catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) { ifModifiedSince = -1L; } if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified / 1000L * 1000L) { this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doGet(req, resp); } else { resp.setStatus(304); } } } else if (method.equals("HEAD")) { lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); this.doHead(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("POST")) { this.doPost(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("PUT")) { this.doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("DELETE")) { this.doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) { this.doOptions(req, resp); } else if (method.equals("TRACE")) { this.doTrace(req, resp); } else { String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method}; errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(501, errMsg); } } private void maybeSetLastModified(HttpServletResponse resp, long lastModified) { if (!resp.containsHeader("Last-Modified")) { if (lastModified >= 0L) { resp.setDateHeader("Last-Modified", lastModified); } } } public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException { HttpServletRequest request; HttpServletResponse response; try { request = (HttpServletRequest)req; response = (HttpServletResponse)res; } catch (ClassCastException var6) { throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response"); } this.service(request, response); } }
这里就使用到了模板方法设计模式。
类图:
·
以上是关于设计模式-行为型模式-模板方法模式(Template Method)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章