1086 Tree Traversals Again
Posted ruruozhenhao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了1086 Tree Traversals Again相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
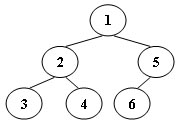
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1Code:
#include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<stack> using namespace std; typedef struct Node *node; struct Node { int value; node leftSon; node rightSon; node father; Node():value(), leftSon(), rightSon(), father(){} }; void postOrder(node h) { if (h != NULL) { postOrder(h->leftSon); postOrder(h->rightSon); cout << h->value << " "; } } int main() { int n; cin >> n; getchar(); string str, op, num; int pos; queue<string> q; stack<int> s; stack<string> leftOrRight; for (int i = 0; i < n*2; ++i) { getline(cin, str); if (str[1] == ‘u‘) { pos = str.find(‘ ‘); op = str.substr(0, pos); num = str.substr(pos+1); q.push(op); q.push(num); } else { q.push(str); } } node head = new Node(); node prt = head; while (!q.empty()) { if (q.front() == "Push") { q.pop(); int value = stoi(q.front()); s.push(value); q.pop(); node temp = new Node(); if (prt->leftSon) { leftOrRight.push("right"); prt->rightSon = temp; temp->father = prt; } else { leftOrRight.push("left"); prt->leftSon = temp; temp->father = prt; } prt = temp; } else { q.pop(); if (leftOrRight.top() == "left") prt = prt->father; prt->value = s.top(); if (leftOrRight.top() == "right") prt = prt->father; s.pop(); leftOrRight.pop(); } } postOrder(prt); return 0; }
以上是关于1086 Tree Traversals Again的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章