HDU--1198 Farm Irrigation (并查集做法+DFS做法)
Posted liyexin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HDU--1198 Farm Irrigation (并查集做法+DFS做法)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Problem Description
Benny has a spacious farm land to irrigate. The farm land is a rectangle, and is divided into a lot of samll squares. Water pipes are placed in these squares. Different square has a different type of pipe. There are 11 types of pipes, which is marked from A to K, as Figure 1 shows.
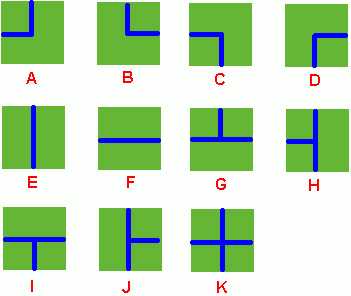
Benny has a map of his farm, which is an array of marks denoting the distribution of water pipes over the whole farm. For example, if he has a map
ADC
FJK
IHE
then the water pipes are distributed like
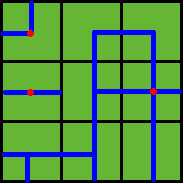
Several wellsprings are found in the center of some squares, so water can flow along the pipes from one square to another. If water flow crosses one square, the whole farm land in this square is irrigated and will have a good harvest in autumn.
Now Benny wants to know at least how many wellsprings should be found to have the whole farm land irrigated. Can you help him?
Note: In the above example, at least 3 wellsprings are needed, as those red points in Figure 2 show.
Input
There are several test cases! In each test case, the first line contains 2 integers M and N, then M lines follow. In each of these lines, there are N characters, in the range of ‘A‘ to ‘K‘, denoting the type of water pipe over the corresponding square. A negative M or N denotes the end of input, else you can assume 1 <= M, N <= 50.
Output
For each test case, output in one line the least number of wellsprings needed.
Sample Input
2 2
DK
HF
3 3
ADC
FJK
IHE
-1 -1
Sample Output
2
3
题意:给出一个n*m的图,每个字母代表对应的田地类型。田地上的线表示水流,相通的水流可以流通。问最少需要几个出水点来灌溉所有土地。
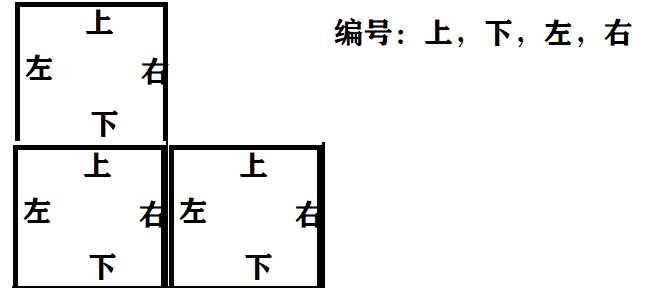
以下都以:上下左右顺序来构造的图:
int mp[12][4]={ {1,0,1,0}, {1,0,0,1}, {0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1}, {1,1,0,0}, {0,0,1,1}, {1,0,1,1}, {1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1}, {1,1,0,1}, {1,1,1,1}, };
以此为判定连通:
1:DFS做法:以now[][]来储存输入的图,由now2[][]来记录对应mp[][]里的类型编号。每次深搜把四周搜一遍,可以连通就消掉,dfs的次数就是答案。类似之前的油田问题,只是这个题需要把地图转化。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<set> using namespace std; const int maxn=60; int mp[12][4]={ {1,0,1,0}, {1,0,0,1}, {0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1}, {1,1,0,0}, {0,0,1,1}, {1,0,1,1}, {1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1}, {1,1,0,1}, {1,1,1,1}, }; char now[maxn][maxn]; int now2[maxn][maxn]; bool vis[maxn][maxn]; int n,m; void dfs(int i,int j) { vis[i][j]=false; int s=now2[i][j]; int s2=now2[i-1][j]; int s3=now2[i+1][j],s4=now2[i][j-1],s5=now2[i][j+1]; for(int x=0;x<4;x++)//这wa了一次,因为我传入的是i,j,所以for里不要再int i了。 { if(x==0)//上 { if(mp[s][0]==1&&mp[s2][1]==1&&i-1>=0&&vis[i-1][j]==true) dfs(i-1,j); } if(x==1)//下 { if(mp[s][1]==1&&mp[s3][0]==1&&i+1<n&&vis[i+1][j]==true) dfs(i+1,j); } if(x==2)//左 { if(mp[s][2]==1&&mp[s4][3]==1&&j-1>=0&&vis[i][j-1]==true) dfs(i,j-1); } if(x==3)//右 { if(mp[s][3]==1&&mp[s5][2]==1&&j+1<m&&vis[i][j+1]==true) dfs(i,j+1); } } } int main() { while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)&&n!=-1&&m!=-1) { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%s",now[i]); memset(vis,true,sizeof(vis)); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { for(int j=0;j<m;j++) { now2[i][j]=now[i][j]-‘A‘; } } int ans=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { for(int j=0;j<m;j++) { if(vis[i][j]==true) { ans++; dfs(i,j); } } } cout<<ans<<endl; } }
2:并查集做法。
看图可以看出,相连通的块可以放入一个集合里。结尾遍历一下所有点,有几个集合,就需要几个出水点。n*m,那么就是n*m个点,对它们进行合并操作即可。判断过程是,遍历每一个田地,对它进行check():看它的四周(注意出界情况),如果可以连通,就把本田地编号与可连通田地的编号进行合并。find()以及jion()均为并查集的最基本操作,没有进行改动。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<set> using namespace std; const int maxn=60; int mp[12][4]={ {1,0,1,0}, {1,0,0,1}, {0,1,1,0}, {0,1,0,1}, {1,1,0,0}, {0,0,1,1}, {1,0,1,1}, {1,1,1,0}, {0,1,1,1}, {1,1,0,1}, {1,1,1,1}, }; int pr[maxn]; int n,m; char now[maxn][maxn]; void init() { for(int i=1;i<=n*m;i++) pr[i]=i; } int find(int x) { if(x!=pr[x]) return pr[x]=find(pr[x]); return x; } void join(int x,int y) { int fx=find(x),fy=find(y); if(fx!=fy) pr[fx]=fy; return ; } void check(int i,int j,int k) { int s1=now[i][j]-‘A‘; if(i!=n-1) { int s2=now[i+1][j]-‘A‘; if(mp[s1][1]==1&&mp[s2][0]==1) join(k,k+m); } if(i!=0) { int s2=now[i-1][j]-‘A‘; if(mp[s1][0]==1&&mp[s2][1]==1) join(k,k-m); } if(j!=0) { int s2=now[i][j-1]-‘A‘; if(mp[s1][2]==1&&mp[s2][3]==1) join(k,k-1); } if(j!=m-1) { int s2=now[i][j+1]-‘A‘; if(mp[s1][3]==1&&mp[s2][2]==1) join(k,k+1); } } int main() { while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)&&n!=-1&&m!=-1) { init(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%s",&now[i]); int k=1; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { for(int j=0;j<m;j++) { check(i,j,k); k++; } } int ans=0; for(int i=1;i<=n*m;i++) { if(pr[i]==i) ans++; // cout<<pr[i]<<" "; } cout<<ans<<endl; } }
PS:就本人代码来讲,dfs的速度比并查集快了将近一倍
以上是关于HDU--1198 Farm Irrigation (并查集做法+DFS做法)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章