数据结构-链表
Posted moyuduo
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构-链表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
链表
链表是一个以节点存储的有序列表,每个节点包括data域和next域,data域是用来保存值的,next域是保存下一个节点的地址,根据有无头节点,链表可分为带头节点的链表和不带头节点的链表
单链表
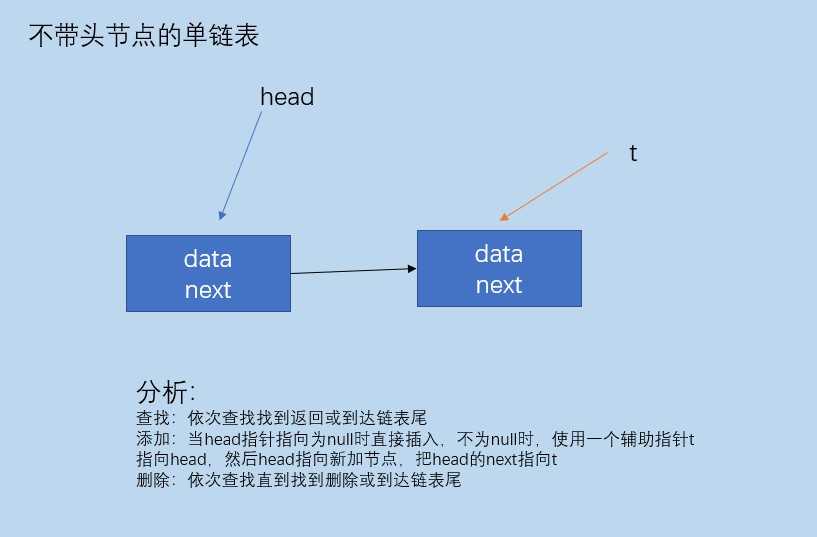
不带头节点的单链表
public class SingleLinkedList<E> {
static class Node<E>{
E data;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E e) {
this.data=e;
}
}
private Node<E> head;
public SingleLinkedList() {
}
//向链表这中添加数据
public void add(E e) {
Node<E> node=new Node(e);
if(head==null) {
head=node;
return;
}
Node<E> t=head;
head=node;
head.next=t;
}
//从链表中查找数据,使用equals判断两个对象是否相等
public E search(E e) {
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
if(e.equals(node.data)) {
return node.data;
}
node=node.next;
}
return null;
}
//从链表中删除数据,使用equals判断是否相等
public E delete(E e) {
if(head==null) {
return null;
}
Node<E> node=head;
//如果头节点就是要删除的数据
if(e.equals(head.data)) {
head=node.next;
return node.data;
}
//遍历找到要删除的数据
while(node.next!=null) {
if(e.equals(node.next.data)) {
E val=node.next.data;
node.next=node.next.next;
return val;
}
node=node.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String str= "SingleLinkedList [";
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
str+=node.data.toString()+",";
node=node.next;
}
if(head!=null) {
str=str.substring(0, str.length()-1);
}
return str+"]";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList<Stu> list=new SingleLinkedList<>();
list.add(new Stu(1,"张三",20));
list.add(new Stu(2,"李四",21));
list.add(new Stu(3,"王五",22));
System.out.println(list);
Stu query=new Stu(2);
Stu search = list.search(query);
System.out.println(search);
list.delete(new Stu(2));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu(1));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu(3));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
class Stu{
private Integer idcard;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Stu(Integer idcard) {
super();
this.idcard = idcard;
}
public Stu(Integer idcard, String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.idcard = idcard;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getIdcard() {
return idcard;
}
public void setIdcard(Integer idcard) {
this.idcard = idcard;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stu [idcard=" + idcard + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj==null) {
return false;
}
if(obj instanceof Stu) {
Stu o=(Stu)obj;
return this.idcard==o.idcard;
}
return false;
}
}
输出:
SingleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21],Stu [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
Stu [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21]
SingleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
SingleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22]]
SingleLinkedList []
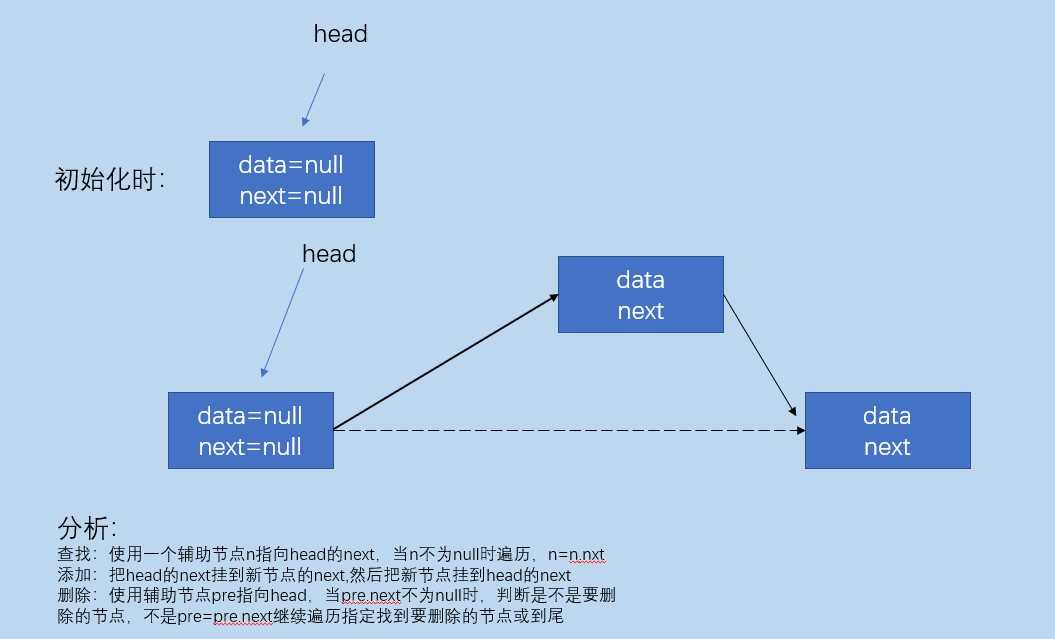
带头节点的单链表
public class SingleLinkedList2<E> {
static class Node<E>{
E data;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E e) {
this.data=e;
}
public Node() {}
}
private Node<E> head;
public SingleLinkedList2() {
head=new Node<E>();
}
//向链表这中添加数据
public void add(E e) {
Node<E> newNode=new Node<E>(e);
newNode.next=head.next;
head.next=newNode;
}
//从链表中查找数据,使用equals判断两个对象是否相等
public E search(E e) {
Node<E> node=head.next;
while(node!=null) {
if(e.equals(node.data)) {
return node.data;
}
node=node.next;
}
return null;
}
//从链表中删除数据,使用equals判断是否相等
public E delete(E e) {
//使用pre来保存要删除节点的前一个节点,以便在删除时断链
Node<E> pre=head;
while(pre.next!=null) {
if(e.equals(pre.next.data)) {
E val=pre.next.data;
pre.next=pre.next.next;
return val;
}
pre=pre.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String str= "SingleLinkedList2 [";
Node<E> node=head.next;
while(node!=null) {
str+=node.data.toString()+",";
node=node.next;
}
if(head.next!=null) {
str=str.substring(0, str.length()-1);
}
return str+"]";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList2<Stu2> list=new SingleLinkedList2<>();
list.add(new Stu2(1,"张三",20));
list.add(new Stu2(2,"李四",21));
list.add(new Stu2(3,"王五",22));
System.out.println(list);
Stu2 query=new Stu2(2);
Stu2 search = list.search(query);
System.out.println(search);
list.delete(new Stu2(2));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu2(1));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu2(3));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
class Stu2{
private Integer idcard;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Stu2(Integer idcard) {
super();
this.idcard = idcard;
}
public Stu2(Integer idcard, String name, Integer age) {
super();
this.idcard = idcard;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getIdcard() {
return idcard;
}
public void setIdcard(Integer idcard) {
this.idcard = idcard;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Stu2 [idcard=" + idcard + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj==null) {
return false;
}
if(obj instanceof Stu2) {
Stu2 o=(Stu2)obj;
return this.idcard==o.idcard;
}
return false;
}
}
输出:
SingleLinkedList2 [Stu2 [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu2 [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21],Stu2 [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
Stu2 [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21]
SingleLinkedList2 [Stu2 [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu2 [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
SingleLinkedList2 [Stu2 [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22]]
SingleLinkedList2 []
双链表
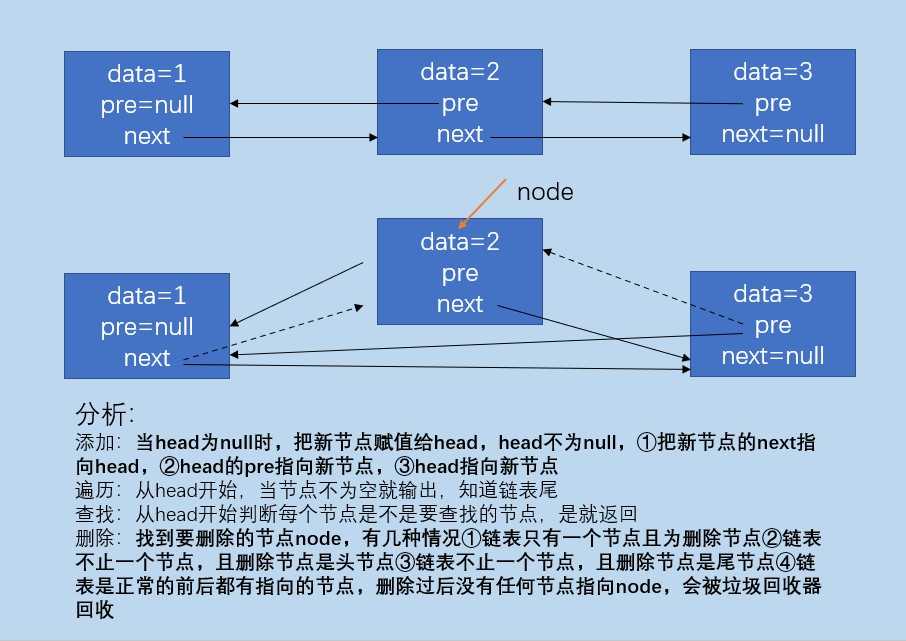
分析为什么要双链表
- 单链表每个节点只保存了后继节点,只能单向遍历,使用双链表可以双向遍历
- 单链表在删除时需要找到删除节点的前一个节点,然后删除,双链表可以实现自删除
不带头节点的双链表
public class DoubleLinkedList<E> {
static class Node<E>{
E data;
Node<E> pre;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E e) {
this.data=e;
}
}
private Node<E> head;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
}
//头插法向链表这中添加数据
public void add(E e) {
Node<E> newNode=new Node<E>(e);
if(head==null) {
head=newNode;
return;
}
//新节点的next指向head
newNode.next=head;
//head的pre更新为新节点
head.pre=newNode;
//把head指向添加的新节点
head=newNode;
}
//从链表中查找数据,使用equals判断两个对象是否相等
public E search(E e) {
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
if(e.equals(node.data)) {
return node.data;
}
node=node.next;
}
return null;
}
//从链表中删除数据,使用equals判断是否相等
public E delete(E e) {
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
if(e.equals(node.data)) {//找到要删除的节点
if(node.pre==null&&node.next==null) {//如果链表只有一个节点且为删除节点
head=null;
return node.data;
}
if(node.pre==null) {//如果链表不止一个节点,且删除节点是头节点
head=head.next;
head.pre=null;
return node.data;
}
if(node.next==null) {//如果链表不止一个节点,且删除节点是尾节点
node.pre.next=null;
return node.data;
}
//删除中间节点
node.pre.next=node.next;
node.next.pre=node.pre;
return node.data;
}
node=node.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String str= "DoubleLinkedList [";
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
str+=node.data+",";
node=node.next;
}
if(head!=null) {
str=str.substring(0,str.length()-1);
}
return str+"]";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLinkedList<Stu> list=new DoubleLinkedList<>();
list.add(new Stu(1,"张三",20));
list.add(new Stu(2,"李四",21));
list.add(new Stu(3,"王五",22));
System.out.println(list);
Stu query=new Stu(2);
Stu search = list.search(query);
System.out.println(search);
list.delete(new Stu(2));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu(1));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu(3));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
输出:
DoubleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21],Stu [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
Stu [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21]
DoubleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
DoubleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22]]
DoubleLinkedList []
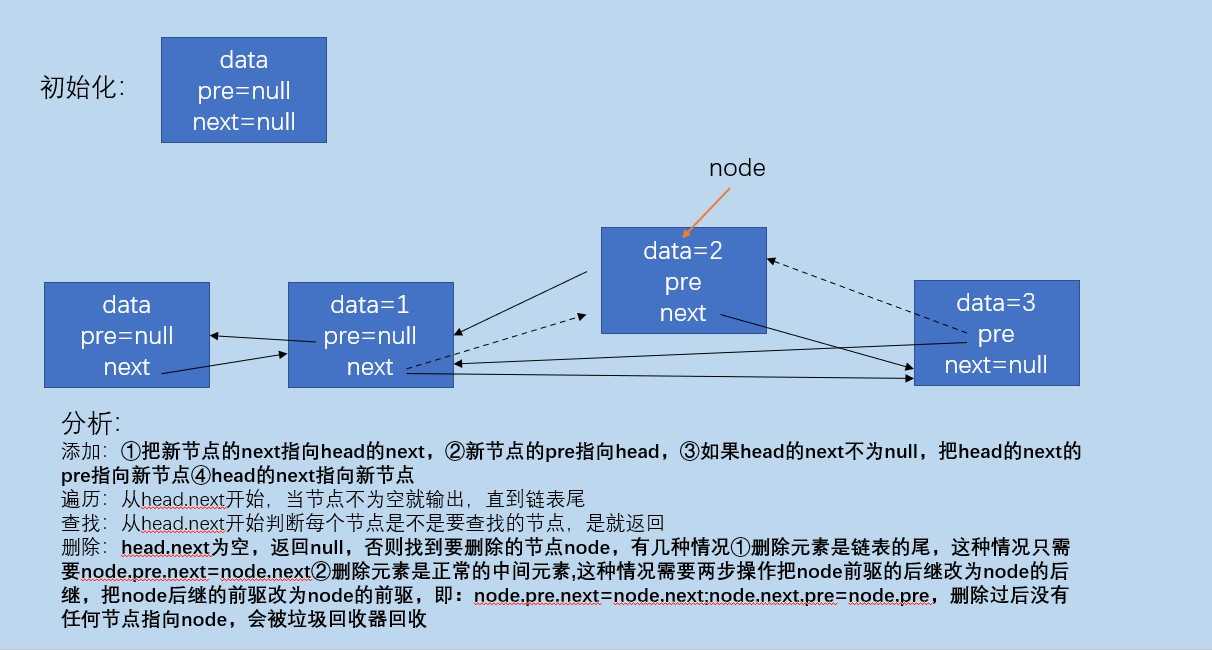
带头节点的双链表
public class DoubleLinkedList<E> {
static class Node<E>{
E data;
Node<E> pre;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E e) {
this.data=e;
}
}
private Node<E> head;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
}
//头插法向链表这中添加数据
public void add(E e) {
Node<E> newNode=new Node<E>(e);
if(head==null) {
head=newNode;
return;
}
//新节点的next指向head
newNode.next=head;
//head的pre更新为新节点
head.pre=newNode;
//把head指向添加的新节点
head=newNode;
}
//从链表中查找数据,使用equals判断两个对象是否相等
public E search(E e) {
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
if(e.equals(node.data)) {
return node.data;
}
node=node.next;
}
return null;
}
//从链表中删除数据,使用equals判断是否相等
public E delete(E e) {
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
if(e.equals(node.data)) {//找到要删除的节点
if(node.pre==null&&node.next==null) {//如果链表只有一个节点且为删除节点
head=null;
return node.data;
}
if(node.pre==null) {//如果链表不止一个节点,且删除节点是头节点
head=head.next;
head.pre=null;
return node.data;
}
if(node.next==null) {//如果链表不止一个节点,且删除节点是尾节点
node.pre.next=null;
return node.data;
}
//删除中间节点
node.pre.next=node.next;
node.next.pre=node.pre;
return node.data;
}
node=node.next;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String str= "DoubleLinkedList [";
Node<E> node=head;
while(node!=null) {
str+=node.data+",";
node=node.next;
}
if(head!=null) {
str=str.substring(0,str.length()-1);
}
return str+"]";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLinkedList<Stu> list=new DoubleLinkedList<>();
list.add(new Stu(1,"张三",20));
list.add(new Stu(2,"李四",21));
list.add(new Stu(3,"王五",22));
System.out.println(list);
Stu query=new Stu(2);
Stu search = list.search(query);
System.out.println(search);
list.delete(new Stu(2));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu(1));
System.out.println(list);
list.delete(new Stu(3));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
输出:
DoubleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21],Stu [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
Stu [idcard=2, name=李四, age=21]
DoubleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22],Stu [idcard=1, name=张三, age=20]]
DoubleLinkedList [Stu [idcard=3, name=王五, age=22]]
DoubleLinkedList []
以上是关于数据结构-链表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章