进程与线程简单实验
Posted jhjgarden
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了进程与线程简单实验相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【实验要求】:
学习fork函数,exec函数,pthread函数的使用,阅读源码,分析三个函数的机理。
【代码实现】:
进程A创建子进程B
进程A打印hello world,进程B实现Sum累加
进程B有两个线程,主线程创建子线程实现Sum累加
分析各执行体处理器使用,内存使用等基本信息
【分析】
要写这个先得看fork exec pthread函数啦!
有几个博客很有帮助
https://www.cnblogs.com/amanlikethis/p/5537175.html
https://blog.csdn.net/nan_lei/article/details/81636473
https://blog.csdn.net/u011279649/article/details/18736181
看完了这个基本上可以开始写了
源代码很简单,分成两个文件,一个处理线程,一个创建进程B
处理进程的main.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <pthread.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <sys/types.h> 6 #include <wait.h> 7 8 int main() { 9 pid_t pid; 10 pid = fork(); 11 //devide father and child 12 if (pid < 0) { 13 printf("Fork failed "); 14 exit(-1); 15 } 16 17 else if (pid == 0) { 18 printf("This is child pid = %d. ",getpid()); 19 //exec 20 char *buf[]={"/home/ying/experi-os/child","child",NULL};//b‘s path. 21 execve("/home/ying/experi-os/child",buf,NULL); 22 } 23 24 else { 25 printf("Hello world! Father pid is %d. ",getpid()); 26 //Then wait the child(B) finished. 27 wait(NULL); 28 exit(0); 29 } 30 }
还有处理线程的child.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <pthread.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 6 int x = 0, sum = 0; 7 8 void *Sum(void* arg) { 9 //printf("sum begin successfully! "); 10 for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++) { 11 sum += i; 12 } 13 printf(" The result is %d ", sum); 14 } 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 printf("exec success. Input x:"); 19 if (scanf("%d", &x) != 1) { 20 return 0; 21 } 22 23 pthread_t id; 24 pthread_create(&id, NULL, Sum, (void*)NULL); 25 pthread_join(id, NULL);//wait thread end 26 27 exit(0); 28 return 0; 29 }
然后对它们分别编译
1 gcc child.c -o child -lpthread 2 gcc mian.c -o main
运行是
1 ./main
这个时候需要注意,对线程的编译需要加上-lpthread,因为好像Linux默认库里没有,不加会报错

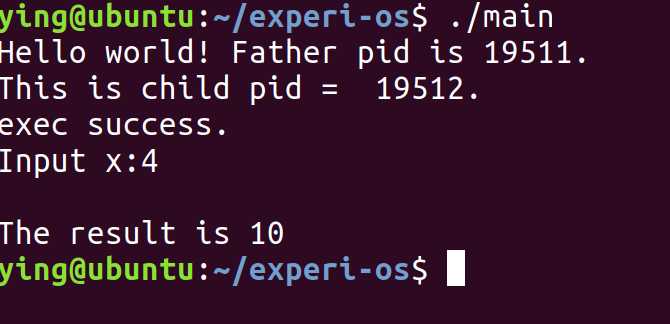
这样就完成啦!
【BUG总结】
在写的过程中有几次报错
1.Sum函数报错。Sum函数根据线程的形参要求应当是*Sum
2.main重复定义。两个文件通过 execve指令连接,而非连接编译
3.child.c编译时线程报错。原因是没有加上-lpthread
4.运行时bug。因为execve没有指向正确的线程可执行文件
注意以上几点基本上这个实验就没问题了,真的好简单
以上是关于进程与线程简单实验的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章