Sta----树的深度
Posted z8875
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Sta----树的深度相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题目
给出一个N个点的树,找出一个点来,以这个点为根的树时,所有点的深度之和最大
Input
给出一个数字N,代表有N个点.N<=1000000 下面N-1条边.
Output
输出你所找到的点,如果具有多个解,请输出编号最小的那个.
Sample Input
8
1 4
5 6
4 5
6 7
6 8
2 4
3 4
Sample Output
7
题解
解题思路
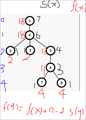
(下面的树没说明就是是以1为根)
(s(i)) 表示的是以i为根的子树中节点个数,
(f(i)) 在(dfs1)中表示以i为根的子树中节点的深度和,
在(dfs2)中表示以I为根的树的深度和,
进过(dfs1)后(f(1)) 已求出
那么(f(i))该怎么求呢?
我们可以想到应该是子树的深度加上父亲及父亲连着的其他节点的深度
子树每个节点的深度都比以父亲为根的小1,而父亲那里是多了1
所以
(f(y) = f(x) - s(y) + (n - s(i)))
(f(y) = f(x) + n - 2 * s(y))
可以对照着图模拟一下
代码
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+5;
struct side {
int t, next;
}a[N*2];
int tot, head[N];
void add(int x, int y) {
a[++tot].next = head[x];
head[x] = tot;
a[tot].t = y;
}
int n, d[N], s[N], ans;
long long f[N];
void dfs1(int x, int fa) {
s[x] = 1;
f[x] = d[x];
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = a[i].next) {
int y = a[i].t;
if (y == fa) continue;
d[y] = d[x] + 1;
dfs1(y, x);
f[x] += f[y];
s[x] += s[y];
}
}
void dfs2(int x, int fa) {
for(int i = head[x]; i; i = a[i].next) {
int y = a[i].t;
if (y == fa) continue;
f[y] = f[x] + n - 2 * s[y];
dfs2(y, x);
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1, x, y; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y),
add(x, y), add(y, x);
dfs1(1, -1);
dfs2(1, -1);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (f[ans] < f[i]) ans = i;
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
以上是关于Sta----树的深度的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章