结对项目
Posted zjh233
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了结对项目相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
项目合作者 张宇芃3118004987 朱杰晖3118004989
1.Github项目地址:https://github.com/786095601/Pairing-Project
2.
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 20 | |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 20 | |
| Development | 开发 | 1200 | |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 240 | |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 60 | |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 20 | |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 120 | |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 620 | |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 60 | |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | |
| Reporting | 报告 | 100 | |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 60 | |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | |
| 合计 | 1840 |
3.效能分析
- 规范化的四则表达式的生成,耗费了很久时间,想了两种情况,还是采用了存两个数组一个int型一个char型,因为没有查重所以效率低了很多。在生成答案的函数中,一开始是想先把中缀表达式转换成后缀表达式,再对后缀表达式进行运算,后来思考发现在转换的过程中可以完成计算,减少了栈的使用。但是由于判断过程比较复杂,加上结果保留分数,效率不是很高。
4.设计实现过程
- 函数一共两个主要的,一个生成题目,一个生成答案,根据答案的情况来看题目是否生成生成题目的函数先随机生成8个数字,随机生成操作数个数,再生成运算符个数,运算符随机取,调用生成答案函数,根据答案来判定此题是否生成。若生成,打印时要注意分数的变换。
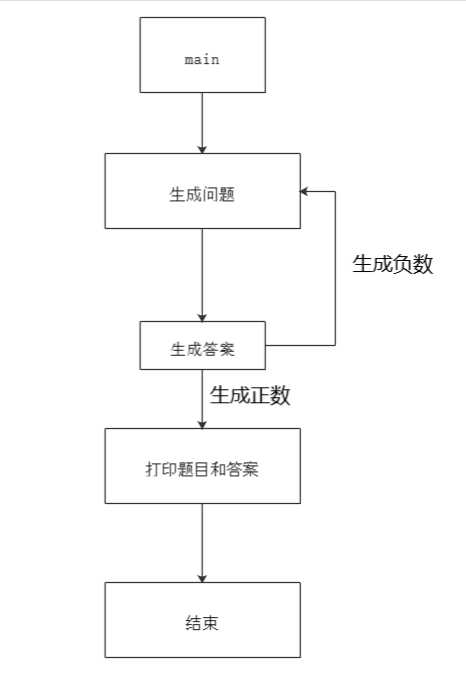
- 生成答案的流程图:
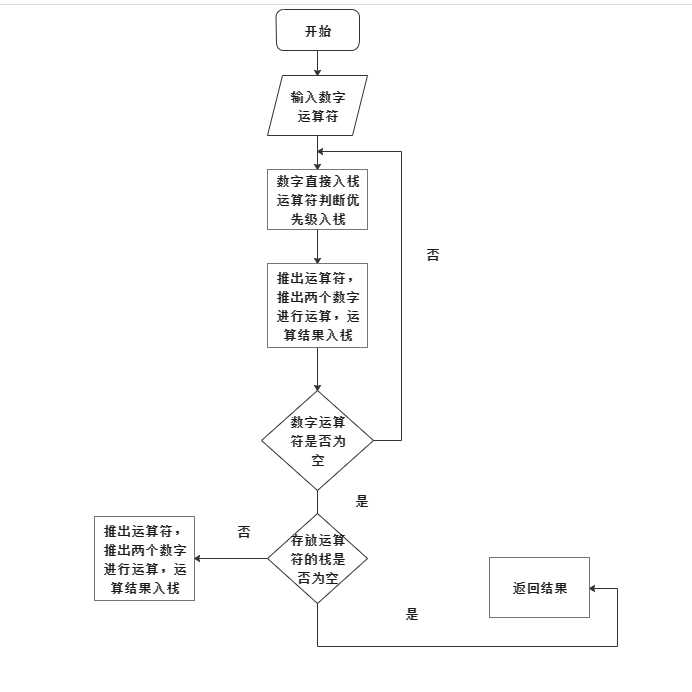
5.关键代码
- 先生成八个随机数,因为最坏的情况是4个分数,需要8个数字。随机生成运算符存在字符数组operate数组内。组内约定好整数数组结束标志是0,字符数组结束标志是‘�‘。最后根据答案函数的返回值来控制答案的输出。
void Question(int n, int r, FILE *f) {//生成随机四则运算
int i, j, k,m, x, t, l;
int flag;
int o,p,q;
int count;//操作数数
int onum;//运算符数
int y=0;
int num[9]={0};
char operate[10]={‘�‘};//括号加三个运算符加上分数的除号,最多9个
int tag;
char c[6] = { ‘+‘,‘-‘,‘*‘,‘/‘,‘(‘,‘.‘};
FILE *Path;
Path = fopen("A.txt","a");
f = fopen("Q.txt", "a");
if (f == NULL){
printf("打开失败
");
fclose(f);
}
if (Path == NULL){
printf("打开失败
");
fclose(Path);
}
for (x = 0; x < n;) {
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {//三个运算符以下所以最多四个操作数,最多四个分数,一共八个数
num[i] = rand() % (r-1)+1;
}
for(i = 0; i < 9; i++){ //每一轮出题都清空
operate[i] = ‘�‘;
}
l=0;
count = (rand() % 3) + 2;//操作数取2~4
flag=0;
onum=0;
tag=0;
y = 0;
while(onum - count < -1)//定义运算符
{
t = rand() % 6;
switch (c[t]) {
case ‘+‘:
if(operate[l]==‘)‘){
operate[l+1] = ‘+‘;
l+=2;
onum++;
}
else{
operate[l++] = ‘+‘;
onum++;
}
break;
case ‘-‘:
if(operate[l]==‘)‘){
operate[l+1] = ‘-‘;
l+=2;
onum++;
}
else{
operate[l++] = ‘-‘;
onum++;
}
break;
case ‘*‘:
if(operate[l]==‘)‘){
operate[l+1] = ‘*‘;
l+=2;
onum++;
}
else{
operate[l++] = ‘*‘;
onum++;
}
break;
case ‘/‘:
if(operate[l]==‘)‘){
operate[l+1] = ‘/‘;
l+=2;
onum++;
}
else{
operate[l++] = ‘/‘;
onum++;
}
break;
case ‘(‘:
if(tag==0&&onum<1&&count>2){
operate[l+2]=‘)‘;
operate[l++] = ‘(‘;
tag=1;
}
break;
case ‘.‘:
if(operate[l-1]==‘.‘){
flag=1;
continue;
}
if(operate[l+1]==‘)‘){
operate[l+2]=operate[l+1];
operate[l+1]=‘ ‘;
operate[l++] = ‘.‘;
}
else{
operate[l++]=‘.‘;
}
y++;
break;
}
}
num[count+y]=0;
answer(num,operate,o,p,q);
if(o<0)
continue;
fprintf(f, "%d、 ", x + 1);
for(j=0,m=0,k=0;j<count;){
if(operate[m]==‘(‘){
fprintf(f,"( ");
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘.‘){
if(num[k] > num[k + 1] && num[k] % num[k + 1] != 0){//加测是否为假分数
fprintf(f, "%d‘%d/%d ", num[k] / num[k + 1], num[k] % num[k + 1], num[k + 1]);
k+=2;
m++;
j++;
if(operate[m]==‘+‘||operate[m]==‘-‘)
{
fprintf(f, "%c ", operate[m]);
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘*‘)
{
fprintf(f, "× ");
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘/‘)
{
fprintf(f, "÷ ");
m++;
}
}
else if (num[k] < num[k + 1] ) {//检测是否为真分数
fprintf(f, "%d/%d ", num[k], num[k + 1]);
k+=2;
m++;
j++;
if(operate[m]==‘+‘||operate[m]==‘-‘)
{
fprintf(f, "%c ", operate[m]);
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘*‘)
{
fprintf(f, "× ");
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘/‘)
{
fprintf(f, "÷ ");
m++;
}
}
else if(num[k] % num[k+1] == 0){//若出现整除,则直接输出自然数
fprintf(f, "%d ", num[k]/num[k+1]);
k+=2;
m++;
j++;
if(operate[m]==‘+‘||operate[m]==‘-‘)
{
fprintf(f, "%c ", operate[m]);
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘*‘)
{
fprintf(f, "× ");
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘/‘)
{
fprintf(f, "÷ ");
m++;
}
}
}
if(k<count+y)
{
fprintf(f, "%d ", num[k]);
k++;
j++;
}
if(operate[m]==‘)‘)
{
fprintf(f, ") ");
m++;
}
if(operate[m]==‘+‘||operate[m]==‘-‘)
{
fprintf(f, "%c ", operate[m]);
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘*‘)
{
fprintf(f, "× ");
m++;
}
else if(operate[m]==‘/‘)
{
fprintf(f, "÷ ");
m++;
}
}
fprintf(f, "=
");
fprintf(Path,"%d、",x+1);
if(o==0&&p>0){
fprintf(Path,"%d/%d
",p,q);
}
else if(o>0&&p!=0){
fprintf(Path,"%d‘%d/%d
",o,p,q);
}
else if(o>0&&p==0){
fprintf(Path,"%d
",o);
}
else if(p==0&&o==0){
fprintf(Path,"0
");
}
x++;
}
fclose(f);
fclose(Path);
}
- 中缀表达式转后缀表达式并求值。由于考虑到结果要保留成分数,因此采用了结构体数组来存放操作数。
//结构体数组,用于存放操作数
struct Number{
int num;
int son;//分子
int mot;//分母
};
void answer(int b[], char c[],int &o,int &p,int &q) { //计算中缀表达式
struct Number OPS[100]; int top1 = -1; //存放数字的结构体数组
char OPF[100]; int top2 = -1; //存放运算符的栈
int i = 0, x = 0, y = 0;
// 遍历中缀表达式
while (b[x] != 0 || c[y] != ‘�‘) {
if ((x == 0) && (y == 0) && (c[y] == ‘(‘)) {
OPF[++top2] = c[y++];
continue;
}
if (i == 1) {
if (c[y] == ‘�‘) {
i--;
continue;//数组空了
}
// 运算符的栈为空,直接入栈
if (top2 == -1) {
OPF[++top2] = c[y++];//入栈
}
// 运算符的栈不为空,要比较和栈顶的优先级
else if (c[y] == ‘+‘ || c[y] == ‘-‘) {
while (OPF[top2] == ‘+‘ || OPF[top2] == ‘-‘ || OPF[top2] == ‘*‘ || OPF[top2] == ‘/‘ || OPF[top2] == ‘.‘) {
opr(OPS, top1, OPF, top2); //计算
}
OPF[++top2] = c[y++]; //运算完后,c[i]入栈
}
else if (c[y] == ‘*‘ || c[y] == ‘/‘) {
while (OPF[top2] == ‘*‘ || OPF[top2] == ‘/‘ || OPF[top2] == ‘.‘) {
opr(OPS, top1, OPF, top2); //计算
}
OPF[++top2] = c[y++]; //运算完后,c[i]入栈
}
else if (c[y] == ‘.‘) {
while (OPF[top2] == ‘.‘) {
opr(OPS, top1, OPF, top2); //计算
}
OPF[++top2] = c[y++]; //运算完后,c[i]入栈
}
else if (c[y] == ‘(‘) { //左括号,直接入栈
OPF[++top2] = c[y++];
}
else if (c[y] == ‘)‘) { //右括号,处理到把‘(‘抵消
while (OPF[top2] != ‘(‘) {
opr(OPS, top1, OPF, top2); //计算
}
top2--;
y++;//弹出左括号
}
if (c[y] != ‘(‘&&c[y - 1] != ‘)‘) {
i--;
}
}
else if (i == 0) {
// str[i]是数字,直接入栈
if (b[x] == 0) {
i++;
continue;
}
OPS[++top1].num = b[x++];
OPS[top1].mot = 0;
OPS[top1].son = 0;
i++;
}
}
// 遍历完成后,检查栈是否计算完
while (top2 != -1) {
opr(OPS, top1, OPF, top2); //计算
}
o=OPS[top1].num;
p=OPS[top1].son;
q=OPS[top1].mot;//返回计算结果
}
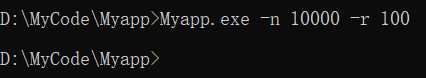
6.测试运行
- 通过命令行控制
可以生成一万道题目
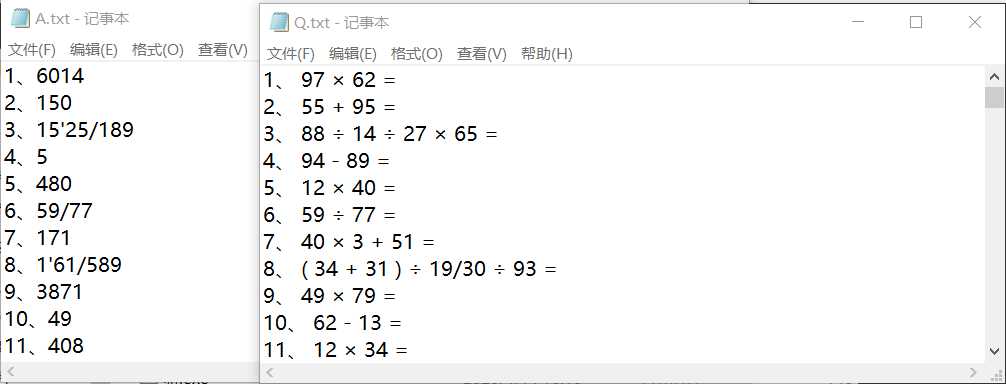
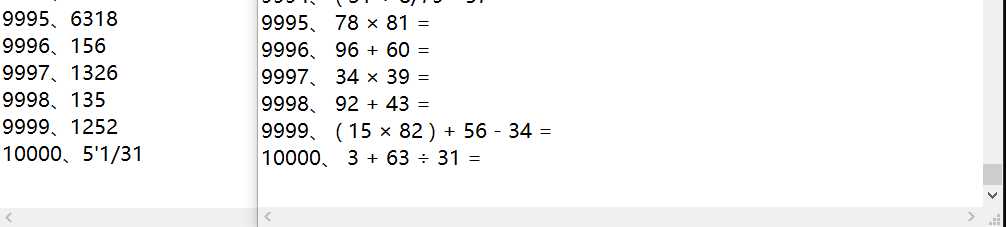
我们对生成的式子和答案进行了大量随机的抽样和检查,发现结果都是对的。
7.
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 20 | 15 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 20 | 15 |
| Development | 开发 | 1200 | 1155 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 240 | 240 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 60 | 30 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 20 | 20 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 15 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 120 | 100 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 620 | 600 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 60 | 30 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 100 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 100 | 70 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 60 | 40 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 20 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 20 |
| 合计 | 1320 | 1240 |
8.项目小结
- 张宇芃:二人合作确实比个人难度大一点,因为要协调好各方面。两个人对接代码的时候基本都是互相找bug。第一次进行二人合作很不适应,并且犯了很多小失误,并且因为交流频率略低所以项目进展缓慢。这一次的作业并没有完成查重和判断对错非常遗憾,但是确实是能力不足。希望下次能更好的规划和优化。
- 朱杰晖:在本次的结对项目中,我体会到了合作的力量,有了不少的收获。我对表达式的求值方法,栈的使用有了进一步的理解。在结对的过程中,我慢慢适应了合作,同时积累了经验和教训,合作的过程中应该加强交流沟通。
以上是关于结对项目的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章