机器学习4kmeans实际运用
Posted renshenbenzuig
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习4kmeans实际运用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
(1)图片压缩
以下为使用k-means代码进行图片压缩
from sklearn.datasets import load_sample_image
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
from pylab import mpl
# 指定默认字体
mpl.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘] = [‘FangSong‘]
# 解决保存图像是负号‘-‘显示为方块
mpl.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘] = False
##读取datasets库中的图片
image = load_sample_image("china.jpg")
#查看图片
plt.imshow(image)
plt.show()
##观察图片文件大小,数据结构
print("图片使用内存大小:",sys.getsizeof(image))
print("图片大小:",image.shape)
print(image)
##数据线性化
image1=image[::3, ::3]
X = image1.reshape(-1,3)
print(image.shape,X.shape)
###用kmeans对图片像素颜色进行聚类
n_colors = 64
K_model = KMeans(n_colors)
#归类以后的颜色分类期望值
y = K_model.fit_predict(X)
#每个类别的颜色,二维数组
colors = K_model.cluster_centers_
print(y.shape,colors.shape)
##压缩生成,还原为二维
new_image = colors[y].reshape(image1.shape)
new_image.shape
new_image.size
#对比
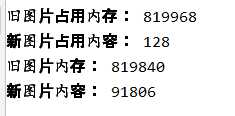
print("旧图片占用内存:",sys.getsizeof(image))
print("新图片占用内容:",sys.getsizeof(new_image))
print("旧图片内存:",image.shape)
print("新图片内容:",new_image.shape)
#生成图像
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))#画布
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.title("压缩前的图像")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.title("压缩后的图像")
plt.imshow(new_image.astype(np.uint8))
plt.suptitle("压缩前后对比图")
plt.show()
实际效果:


(2)实际运用
通过租房信息来预测该租房是否自带燃气
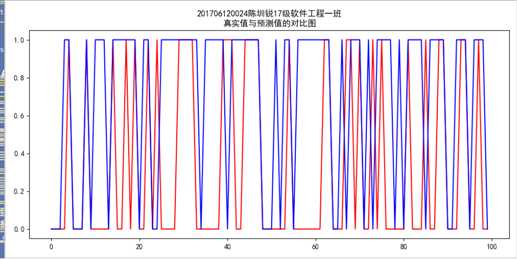
#K-meavn算法 import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.cluster import KMeans from sklearn import preprocessing from sklearn.metrics import jaccard_score,fowlkes_mallows_score,adjusted_rand_score data=pd.read_csv("201706120024陈圳锐(处理后).csv") y=data[‘燃气‘].values x=data.drop(‘燃气‘,axis=1).values #分箱处理调优 # a=0 # count1=0 # count2=0 # for i in range(2,20): # for index in range(2,20): # print(i,index) # #quantile # est = preprocessing.KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins=[i, index], encode=‘ordinal‘,strategy=‘uniform‘).fit(data[[‘面积‘,‘租金‘]].values) # x1=est.transform(data[[‘面积‘,‘租金‘]].values) # x=data.drop(‘面积‘,axis=1).drop(‘租金‘,axis=1).values # x=np.hstack((x1,x)) # # # #zscore标准化处理 # zscore_scaler = preprocessing.StandardScaler() # 建立StandardScaler对象 # x=zscore_scaler.fit_transform(data.drop(‘燃气‘,axis=1).values) # # x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=5) # # KMeans_model = KMeans(n_clusters=2) # KMeans_model.fit(x_train) # from sklearn import metrics # y_pre=KMeans_model.predict(x_test) # if a<metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pre): # count1=i # count2=index # a=metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pre) # # print(‘准确率指标:‘,metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,y_pre )) #分箱处理 est = preprocessing.KBinsDiscretizer(n_bins=[19, 19,19], encode=‘ordinal‘,strategy=‘uniform‘).fit(data[[‘面积‘,‘租金‘,‘楼层‘]].values) x1=est.transform(data[[‘面积‘,‘租金‘,‘楼层‘]].values) x=data.drop(‘面积‘,axis=1).drop(‘楼层‘,axis=1).drop(‘租金‘,axis=1).values x=np.hstack((x1,x)) #zscore标准化处理 zscore_scaler = preprocessing.StandardScaler() # 建立StandardScaler对象 x=zscore_scaler.fit_transform(data.drop(‘燃气‘,axis=1).values) #划分数据集 x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.2,random_state=5) #构建模型 KMeans_model = KMeans(n_clusters=2,random_state=5) #训练模型 KMeans_model.fit(x_train) #预测测试集 y_pre=KMeans_model.predict(x_test) from sklearn import metrics # KMeans_model.score(x_test,y_test) print("201706120024陈圳锐17级软件工程一班") print(‘准确率指标:‘,metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,y_pre )) print(‘聚类中心为: ‘,KMeans_model.cluster_centers_) #查看聚类中心 print(‘类别标签为: ‘,KMeans_model.labels_) print("参与的测试个数:",x_test.shape[0]) print("预测正确个数:",x_test.shape[0]*metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,y_pre )) print(‘准确率指标:‘,metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pre)) # 计算准确率 print(‘Kappa指标:‘,metrics.cohen_kappa_score(y_test, y_pre)) # Kappa 检验 print(‘混淆矩阵: ‘,metrics.confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pre)) # 混淆矩阵 print("201706120024陈圳锐17级软件工程一班") target_names = [‘无燃气‘,‘有燃气‘] print(‘分类报告: ‘,metrics.classification_report(y_test, y_pre,target_names=target_names))# 分类报告 print(‘汉明损失:‘,metrics.hamming_loss(y_test, y_pre)) #汉明损失 。在多分类中, 汉明损失对应于 y 和 y_pre 之间的s汉明距离 print(‘杰卡德系数:‘,metrics.jaccard_score(y_test, y_pre)) list1=[] list2=[] list3=[] for index in range(len(x_train)): center_index=KMeans_model.labels_ if int(center_index[index])==0: list1.append(np.sqrt(sum(abs((x[index,:]-KMeans_model.cluster_centers_[int(center_index[index]),:]))**2))) elif int(center_index[index])==1: list2.append(np.sqrt(sum(abs((x[index,:]-KMeans_model.cluster_centers_[int(center_index[index]),:]))**2))) cp1=np.mean(list1) cp2=np.mean(list2) cp_mean=(cp1+cp2)/2 print("该聚类的cp为:"+str(cp_mean)) #求sp list4=[] for index in range(len(KMeans_model.cluster_centers_)): for index1 in range(index+1,len(KMeans_model.cluster_centers_)): #print(index,index1) list4.append(np.sqrt(sum(abs(KMeans_model.cluster_centers_[index, :] - KMeans_model.cluster_centers_[index1, :]) ** 2))) sp=np.mean(list4) print("该聚类的sp为:"+str(sp)) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 可视化绘制 plt.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘] = ‘SimHei‘# 设置中文显示 fig = plt.figure(figsize = (10,5)) plt.plot(range(100), KMeans_model.predict(x_test)[0:100],color="red") plt.plot(range(100), y_test[0:100],color="blue") plt.title(‘201706120024陈圳锐17级软件工程一班 真实值与预测值的对比图‘) plt.savefig(‘k-means真实值与预测值的对比图.png‘) plt.show()
该模型的实际效果

以上是关于机器学习4kmeans实际运用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章