Sched_Boost小结
Posted lingjiajun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Sched_Boost小结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
之前遇到一个耗电问题,最后发现是/proc/sys/kernel/sched_boost节点设置异常,一直处于boost状态。导致所有场景功耗上升。
现在总结一下sched_boost的相关知识。
Sched_Boost
sched_boost主要是通过影响Task placement的方式,来进行boost。它属于QTI EAS中的一部分。
默认task placement policy
计算每个cpu的负载,并将task分配到负载最轻的cpu上。如果有多个cpu的负载相同(一般是都处于idle),那么就会把task分配到系统中capacity最大的cpu上。
设置sched_boost
通过设置节点:/proc/sys/kernel/sched_boost 或者内核调用sched_set_boost()函数,可以进行sched_boost,并且在分配任务时,忽略对energy的消耗。
boost一旦设置之后,就必须显示写0来关闭。同时也支持个应用同时调用设置,设置会选择boost等级最高的生效; 而当所有应用都都关闭boost时,boost才会真正失效。
boost等级
sched_boost一共有4个等级,除了0代表关闭boost以外,其他3个等级灵活地控制功耗和性能的不同倾向程度。
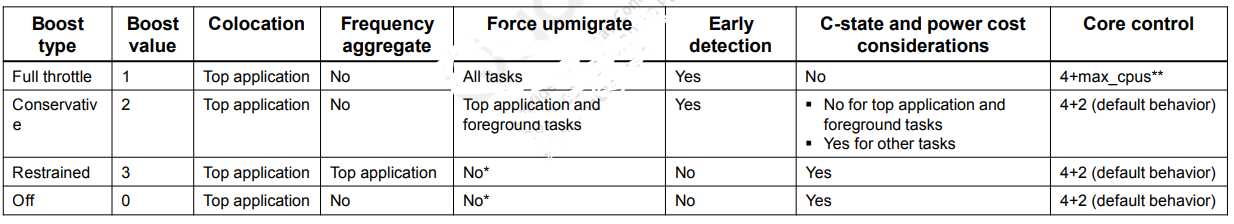
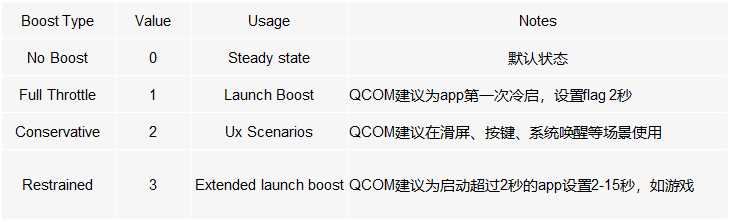

在通过节点设置,会调用sched_boost_handler
{ .procname = "sched_boost", .data = &sysctl_sched_boost, .maxlen = sizeof(unsigned int), .mode = 0644, .proc_handler = sched_boost_handler, .extra1 = &neg_three, .extra2 = &three, },
经过verify之后,调用_sched_set_boost来设置boost。
int sched_boost_handler(struct ctl_table *table, int write, void __user *buffer, size_t *lenp, loff_t *ppos) { int ret; unsigned int *data = (unsigned int *)table->data; mutex_lock(&boost_mutex); ret = proc_dointvec_minmax(table, write, buffer, lenp, ppos); if (ret || !write) goto done; if (verify_boost_params(*data)) _sched_set_boost(*data); else ret = -EINVAL; done: mutex_unlock(&boost_mutex); return ret;
而通过内核调用的方式,同样最后也是调用_sched_set_boost来设置boost。
int sched_set_boost(int type) { int ret = 0; mutex_lock(&boost_mutex); if (verify_boost_params(type)) _sched_set_boost(type); else ret = -EINVAL; mutex_unlock(&boost_mutex); return ret; }
接下来,我们看关键的设置函数_sched_set_boost:
static void _sched_set_boost(int type) { if (type == 0) //通过type参数判断是否enable/disable boost sched_boost_disable_all(); //(1)disable all boost else if (type > 0) sched_boost_enable(type); //(2) enable boost else sched_boost_disable(-type); //(3) disable boost /* * sysctl_sched_boost holds the boost request from * user space which could be different from the * effectively enabled boost. Update the effective * boost here. */ sched_boost_type = sched_effective_boost(); sysctl_sched_boost = sched_boost_type; set_boost_policy(sysctl_sched_boost); //(3) trace_sched_set_boost(sysctl_sched_boost); }
首先看一下sched_boost的4个用于控制配置的结构体:
其中refcount来记录设置的次数。enter函数表示切换到该boost配置的动作;exit则是退出该boost配置的动作。
static struct sched_boost_data sched_boosts[] = { [NO_BOOST] = { .refcount = 0, .enter = sched_no_boost_nop, .exit = sched_no_boost_nop, }, [FULL_THROTTLE_BOOST] = { .refcount = 0, .enter = sched_full_throttle_boost_enter, .exit = sched_full_throttle_boost_exit, }, [CONSERVATIVE_BOOST] = { .refcount = 0, .enter = sched_conservative_boost_enter, .exit = sched_conservative_boost_exit, }, [RESTRAINED_BOOST] = { .refcount = 0, .enter = sched_restrained_boost_enter, .exit = sched_restrained_boost_exit, }, };
(1)disable all boost
调用除no boost外,所有boost配置的exit函数并且将他们的refcount清0。
#define SCHED_BOOST_START FULL_THROTTLE_BOOST #define SCHED_BOOST_END (RESTRAINED_BOOST + 1 static void sched_boost_disable_all(void) { int i; for (i = SCHED_BOOST_START; i < SCHED_BOOST_END; i++) { if (sched_boosts[i].refcount > 0) { sched_boosts[i].exit(); sched_boosts[i].refcount = 0; } } }
(2) enable boost
refcount记录调用次数+;
由于sched+boost支持多应用同时调用的,所以在设置boost之前,要先检查当前有效的boost配置。
优先级是No boost > Full Throttle > Conservative > Restrained。
static void sched_boost_enable(int type) { struct sched_boost_data *sb = &sched_boosts[type]; int next_boost, prev_boost = sched_boost_type; sb->refcount++; //refcount记录次数+1 if (sb->refcount != 1) return; /* * This boost enable request did not come before. * Take this new request and find the next boost * by aggregating all the enabled boosts. If there * is a change, disable the previous boost and enable * the next boost. */ next_boost = sched_effective_boost(); //设置boost之前,检查当前有效的boost配置 if (next_boost == prev_boost) return; sched_boosts[prev_boost].exit(); //调用之前配置的exit,退出之前的boost sched_boosts[next_boost].enter(); //调用现在配置的enter,进入当前boost状态
通过检查refcount,来确认当前有效的boost。
static int sched_effective_boost(void) { int i; /* * The boosts are sorted in descending order by * priority. */ for (i = SCHED_BOOST_START; i < SCHED_BOOST_END; i++) { if (sched_boosts[i].refcount >= 1) return i; } return NO_BOOST; }
接下来详细分析3种boost设置的原理:
Full Throttle
full throttle(全速)模式下的sched boost,主要有如下2个动作:
(1)core control
(2)freq aggregation
static void sched_full_throttle_boost_enter(void) { core_ctl_set_boost(true); //(1)core control walt_enable_frequency_aggregation(true); //(2)freq aggregation }
(1)core control
int core_ctl_set_boost(bool boost) { unsigned int index = 0; struct cluster_data *cluster; unsigned long flags; int ret = 0; bool boost_state_changed = false; if (unlikely(!initialized)) return 0; spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, flags); for_each_cluster(cluster, index) { //修改并记录每个cluster的boost状态 if (boost) { boost_state_changed = !cluster->boost; ++cluster->boost; } else { if (!cluster->boost) { ret = -EINVAL; break; } else { --cluster->boost; boost_state_changed = !cluster->boost; } } } spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, flags); if (boost_state_changed) { index = 0; for_each_cluster(cluster, index) //针对每个cluster,apply boost设置 apply_need(cluster); } trace_core_ctl_set_boost(cluster->boost, ret); return ret; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(core_ctl_set_boost);
static void apply_need(struct cluster_data *cluster) { if (eval_need(cluster)) //判断是否需要 wake_up_core_ctl_thread(cluster); //唤醒cluster的core control thread }
具体如何判断的:
enable boost时:判断是否需要unisolate cpu,
disable boost时:判断need_cpus < active_cpus是否成立。
并且与上一次更新的间隔时间满足 > delay time。
static bool eval_need(struct cluster_data *cluster) { unsigned long flags; struct cpu_data *c; unsigned int need_cpus = 0, last_need, thres_idx; int ret = 0; bool need_flag = false; unsigned int new_need; s64 now, elapsed; if (unlikely(!cluster->inited)) return 0; spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, flags); if (cluster->boost || !cluster->enable) { need_cpus = cluster->max_cpus; //当enable boost时,设置need_cpus为所有cpu } else { cluster->active_cpus = get_active_cpu_count(cluster); //当disable boost时,首先获取active的cpu thres_idx = cluster->active_cpus ? cluster->active_cpus - 1 : 0; list_for_each_entry(c, &cluster->lru, sib) { bool old_is_busy = c->is_busy; if (c->busy >= cluster->busy_up_thres[thres_idx] || sched_cpu_high_irqload(c->cpu)) c->is_busy = true; else if (c->busy < cluster->busy_down_thres[thres_idx]) c->is_busy = false; trace_core_ctl_set_busy(c->cpu, c->busy, old_is_busy, c->is_busy); need_cpus += c->is_busy; } need_cpus = apply_task_need(cluster, need_cpus); //根据task需要,计算need_cpus } new_need = apply_limits(cluster, need_cpus); //限制need_cpus范围:cluster->min_cpus <= need_cpus <= clusterr->max_cpus need_flag = adjustment_possible(cluster, new_need); //(*)enable boost时:判断是否需要unisolate cpu; disable boost时:判断need_cpus < active_cpus是否成立 last_need = cluster->need_cpus; now = ktime_to_ms(ktime_get()); if (new_need > cluster->active_cpus) { ret = 1; //enable boost } else { /* * When there is no change in need and there are no more * active CPUs than currently needed, just update the * need time stamp and return. //当需要的cpu没有变化时,只需要更新时间戳,然后return */ if (new_need == last_need && new_need == cluster->active_cpus) { cluster->need_ts = now; spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, flags); return 0; } elapsed = now - cluster->need_ts; ret = elapsed >= cluster->offline_delay_ms; //修改need_cpus的时间要大于delay时间,才认为有必要进行更改 } if (ret) { cluster->need_ts = now; //更新时间戳,need_cpus cluster->need_cpus = new_need; } trace_core_ctl_eval_need(cluster->first_cpu, last_need, new_need, ret && need_flag); spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, flags); return ret && need_flag; }
满足更新要求的条件后,就会唤醒core control thread
static void wake_up_core_ctl_thread(struct cluster_data *cluster) { unsigned long flags; spin_lock_irqsave(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); cluster->pending = true; spin_unlock_irqrestore(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); wake_up_process(cluster->core_ctl_thread); }
static int __ref try_core_ctl(void *data) { struct cluster_data *cluster = data; unsigned long flags; while (1) { set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); spin_lock_irqsave(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); if (!cluster->pending) { spin_unlock_irqrestore(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); schedule(); if (kthread_should_stop()) break; spin_lock_irqsave(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); } set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); cluster->pending = false; spin_unlock_irqrestore(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); do_core_ctl(cluster); } return 0; }
(2)freq aggregation
(待补完)
Conservative
(待补完)
Restrained
(待补完)
以上是关于Sched_Boost小结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章