hdu 4942
Posted microcodes
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了hdu 4942相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Game on S♂play
Time Limit: 16000/8000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 942 Accepted Submission(s):
208
Problem Description
Uncle Fang is learning Splay. When he heard about the
rotate operation, he would like to play a game with Captain Chen. There is a
tree with n nodes initially, and the node 1 is the root. The i-th nodes gets a
weight of wi, and an attribute of interesting value defined as the sum of the
weight of it’s descendants. Following are two operations in this
tree:
1.do a rotation on a node x. The rotation is the common rotation in splay tree, it can be right-rotation or left-rotation, as demonstrated in the following picture.If it‘s impossible to rotate, just ignore it!
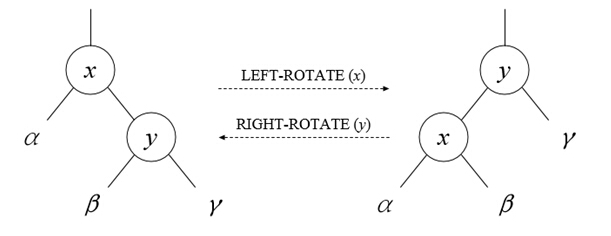
2.ask Captain Chen the product of interesting values of the nodes in a subtree rooted at node x.
1.do a rotation on a node x. The rotation is the common rotation in splay tree, it can be right-rotation or left-rotation, as demonstrated in the following picture.If it‘s impossible to rotate, just ignore it!

2.ask Captain Chen the product of interesting values of the nodes in a subtree rooted at node x.
Input
There are several cases.The first line of the input
contains a single integer T (T <= 30) which is the number of test cases.Then
comes the T test cases .
For each case, the first line contains two integer numbers n and m(1<=n, m<=100000).
The following n lines describe the tree. In the i-th line, there was three number wi, xi, yi,(0<=w<=100000, 0<=x, y<=n) indicate the weight of node i, the left child of node i, and the right child of node i. If xi or yi equals to 0, it means node i has no such child.
And the following m lines describe the operations. There are two numbers p x in each line. If p is 0, it means do right-rotation on node x; If p is 1, it means do left-rotation on node x; if p is 2, it means ask the product of interesting values of the nodes in a subtree rooted at node x.
For each case, the first line contains two integer numbers n and m(1<=n, m<=100000).
The following n lines describe the tree. In the i-th line, there was three number wi, xi, yi,(0<=w<=100000, 0<=x, y<=n) indicate the weight of node i, the left child of node i, and the right child of node i. If xi or yi equals to 0, it means node i has no such child.
And the following m lines describe the operations. There are two numbers p x in each line. If p is 0, it means do right-rotation on node x; If p is 1, it means do left-rotation on node x; if p is 2, it means ask the product of interesting values of the nodes in a subtree rooted at node x.
Output
For the k-th test case, first output “Case #k:” in a
separate line.Then for each query,output a single num in each line after mod
1000000007.
Sample Input
1
3 4
1 2 3
1 0 0
1 0 0
2 1
0 1
2 2
2 1
Sample Output
Case #1:
3
6
2
析:给一颗n个节点的树,每个节点附带一个权值wi,而每个节点拥有兴趣值为其所有子树权值之和,要求支持三种操作:
1.对节点x右旋
2.对节点x左旋
3.查询指定节点所有子树兴趣值之积
说到左右旋,首先可以想到平衡树,可知平衡树左右旋仍满足中序遍历序列不变,每个节点与子树处于同一段连续序列中,故每次左右旋仅改变两个节点,其他节点不受影响,可以预处理每个节点的兴趣值以及兴趣值之积,
并依次按中序遍历顺序指定每个节点的序号,以及每个点的子树边界区间,然后用线段树维护改变的两个点上的路径即可,注意维护子树左右边界值
注意:模运算后,子树权值和即节点兴趣值可能为负数,故需要加上模值后再取模

#pragma comment (linker,"/STACK:102400000,102400000") #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define ll long long #define mod 1000000007 using namespace std; const int N = 101015; int t, n, m, ans; int l[N], r[N], L[N], R[N], C[N], f[N]; ll w[N], s[N], sum[N], prd[N<<2]; inline void Maintain(int rt){ L[rt] = R[rt] = C[rt]; if(l[rt]){ L[rt] = min(L[rt], L[l[rt]]); R[rt] = max(R[rt], R[l[rt]]); } if(r[rt]){ L[rt] = min(L[rt], L[r[rt]]); R[rt] = max(R[rt], R[r[rt]]); } } inline ll dfs(int cur){ s[cur] = w[cur]; if(l[cur]){ s[cur] += dfs(l[cur])%mod; } L[cur] = R[cur] = C[cur] = ans++; if(r[cur]){ s[cur] += dfs(r[cur])%mod; } Maintain(cur); return sum[C[cur]] = s[cur]; } inline void Build(int rt, int l, int r){ if(l == r){ prd[rt] = sum[l]; return; } int m = (l+r)>>1; Build(rt<<1, l, m); Build(rt<<1|1, m+1, r); prd[rt] = prd[rt<<1]*prd[rt<<1|1]%mod; } inline void Modify(int rt, int l, int r, int pos, ll val){ if(l == r){ prd[rt] = val; return; } int m = (l+r)>>1; if(pos <= m) Modify(rt<<1, l, m, pos, val); else Modify(rt<<1|1, m+1, r, pos, val); prd[rt] = prd[rt<<1]*prd[rt<<1|1]%mod; } inline ll Query(int rt, int l, int r, int L, int R){ if(L <= l && r <= R) return prd[rt]; ll res = 1; int m = (l+r)>>1; if(L <= m) res = res*Query(rt<<1, l, m, L, R)%mod; if(R > m) res = res*Query(rt<<1|1, m+1, r, L, R)%mod; return res; } int main(){ scanf("%d", &t); for (int i = 1; i <= t; i ++) { printf("Case #%d: ", i); f[0] = f[1] = 0; //wa点,必须置零 scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%lld%d%d", &w[i], &l[i], &r[i]); f[l[i]] = i; f[r[i]] = i; } int x, y, Q; ans = 1, dfs(1); Build(1, 1, n); for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &Q, &x); if(!Q){ y = l[x]; if(!y) continue; s[x] = (s[x]+s[r[y]]-s[y]+mod)%mod; //wa点,可能出现负数 s[y] = (s[y]+s[x]-s[r[y]]+mod)%mod; Modify(1, 1, n, C[x], s[x]); Modify(1, 1, n, C[y], s[y]); if(x == l[f[x]]){ l[f[x]] = y; }else{ r[f[x]] = y; } f[y] = f[x], l[x] = r[y], f[r[y]] = x; r[y] = x, f[x] = y; Maintain(x); Maintain(y); }else if(Q == 1){ y = r[x]; if(!y) continue; s[x] = (s[x]+s[l[y]]-s[y]+mod)%mod; //wa点,可能出现负数 s[y] = (s[y]+s[x]-s[l[y]]+mod)%mod; Modify(1, 1, n, C[x], s[x]); Modify(1, 1, n, C[y], s[y]); if (x == l[f[x]]){ l[f[x]] = y; }else{ r[f[x]] = y; } f[y] = f[x], r[x] = l[y], f[l[y]] = x; l[y] = x; f[x] = y; Maintain(x); Maintain(y); }else { printf("%lld ", Query(1, 1, n, L[x], R[x])); } } } }
以上是关于hdu 4942的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
