xml文件读取与xml文件数据保存(使用YOLO算法的辅助函数)
Posted tangjunjun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了xml文件读取与xml文件数据保存(使用YOLO算法的辅助函数)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目前使用yolo系列算法较多,特别是今年yolo4的出现,是我们异常兴奋,但鉴于某些数据集使用xml标注的数据,未能转换成train.txt文件,为此,我写了一份xml文件读取,并将其转换为yolo等训练所需要的格式。希望对读者有些帮助与启示。本博客仅展示代码与结果图片。
代码如下:
def read_xml(path_xml):
‘‘‘
:param path_xml: 输入处理xml文件的绝对路径
:return: 返回xml的label与box,其中label是一维的,并与box一一对应。
‘‘‘
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
with open( path_xml) as f:
root = ET.parse(f).getroot()
boxes = [] # 每张图片的所有box保存在这里boxes,并重新读取图片将重新开始 # We‘ll store all boxes for this image here.
labels = [] #每张图片的所有box对应的label保存在这里
objects = root.findall(‘object‘) # Get a list of all objects in this image.
# Parse the data for each object.
for obj in objects:
class_name = obj.find(‘name‘).text
# Check whether this class is supposed to be included in the dataset.
# Get the bounding box coordinates.
bndbox = obj.find(‘bndbox‘)
xmin = int(bndbox.find(‘xmin‘).text) # bndbox.find(‘xmin‘).text
ymin = int(bndbox.find(‘ymin‘).text)
xmax = int(bndbox.find(‘xmax‘).text)
ymax = int(bndbox.find(‘ymax‘).text)
item_dict = { # ‘folder‘: ‘‘,#folder,
‘class_name‘: class_name,
‘xmin‘: xmin,
‘ymin‘: ymin,
‘xmax‘: xmax,
‘ymax‘: ymax
}
box = []
box.append(item_dict[‘xmin‘])
box.append(item_dict[‘ymin‘])
box.append(item_dict[‘xmax‘])
box.append(item_dict[‘ymax‘])
labels.append(item_dict[‘class_name‘])
boxes.append(box)
result=[]
result.append(labels)
result.append(boxes)
return result
def result2txt(data,f):
labels=data[0]
boxes=data[1]
print(labels)
print(boxes)
num=len(list(labels))
for i in range(num):
s=str(boxes[i][0])+ ‘,‘+str(boxes[i][1])+ ‘,‘+str(boxes[i][2])+ ‘,‘+str(boxes[i][3])+ ‘,‘+str(labels[i])+‘ ‘
f.write(s)
def readtotxt(write_file,path_xml,img_path=None):
‘‘‘
:param write_file: 将结果写入的文件夹路径,后缀为.txt
:param path_xml: xml文件夹的路径
:param img_path: 将给出图像所在文件夹路径,便于图像读取
‘‘‘
f = open(write_file, ‘w‘) # 写入txt文件
import os
for name in os.listdir(path_xml):
path = os.path.join(path_xml, name)
result = read_xml(path)
labels = result[0]
boxes = result[1]
num = len(list(labels))
for i in range(num):
if img_path is not None:
if i == 0:
img, _ = os.path.splitext(name)
img_str = str(img_path + ‘/‘ + img + ‘.jpg‘)
s = img_str + ‘ ‘ + str(boxes[i][0]) + ‘,‘ + str(boxes[i][1]) + ‘,‘ + str(
boxes[i][2]) + ‘,‘ + str(
boxes[i][3]) + ‘,‘ + str(
labels[i]) + ‘ ‘
else:
s = str(boxes[i][0]) + ‘,‘ + str(boxes[i][1]) + ‘,‘ + str(
boxes[i][2]) + ‘,‘ + str(
boxes[i][3]) + ‘,‘ + str(
labels[i]) + ‘ ‘
else:
s = str(boxes[i][0]) + ‘,‘ + str(boxes[i][1]) + ‘,‘ + str(
boxes[i][2]) + ‘,‘ + str(
boxes[i][3]) + ‘,‘ + str(
labels[i]) + ‘ ‘
f.write(s)
f.write(‘ ‘)
f.close() # 关闭文件
if __name__ == "__main__":
path1 = r‘C:Users51102Desktop123‘ # 读取文件路径
path = "./yol22o_anchors.txt"
readtotxt(path, path1,path)
读取与写入结果如下:
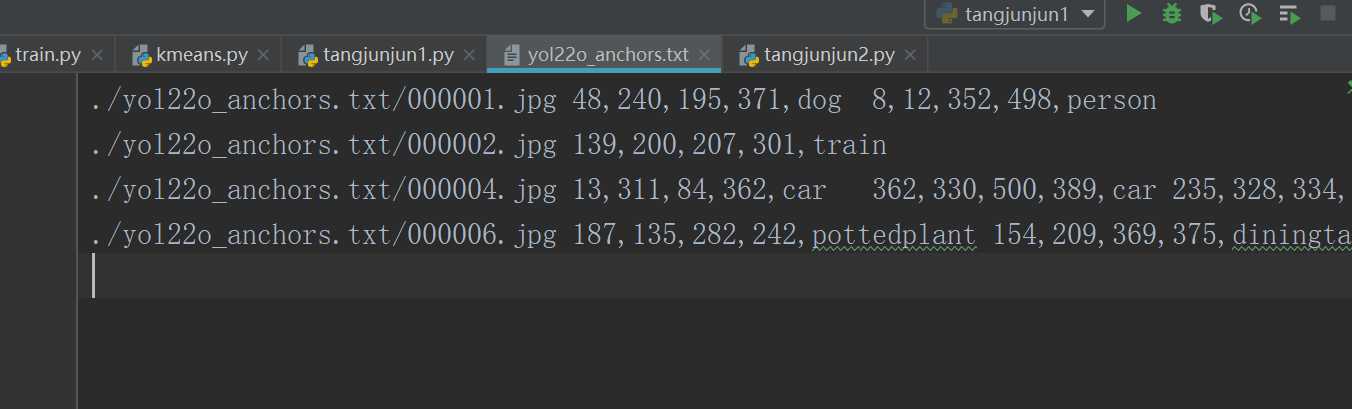
以上是关于xml文件读取与xml文件数据保存(使用YOLO算法的辅助函数)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章