设计模式-工厂模式
Posted yanshw
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设计模式-工厂模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
工厂模式是最常用的设计模式之一,属于创造型模式,提供了创建对象的最佳方式。
工厂模式分为简单工厂模式,工厂模式,抽象工厂模式,什么意思,先上代码
简单工厂模式
class ShapeFactory(object): ‘‘‘工厂类‘‘‘ def getShape(self): return self.shape_name class Circle(ShapeFactory): def __init__(self): self.shape_name = "Circle" def draw(self): print(‘draw circle‘) class Rectangle(ShapeFactory): def __init__(self): self.shape_name = "Retangle" def draw(self): print(‘draw Rectangle‘) class Shape(object): ‘‘‘接口类,负责决定创建哪个ShapeFactory的子类‘‘‘ def create(self, shape): if shape == ‘Circle‘: return Circle() elif shape == ‘Rectangle‘: return Rectangle() else: return None fac = Shape() obj = fac.create(‘Circle‘) obj.draw() print obj.getShape()
图形解释
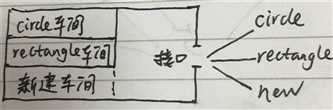
工厂模式
class AbstractSchool(object): def enroll(self,name,course): pass def info(self): pass class AbstractCourse(object): def __init__(self,name,time_range,study_type,fee): pass def enroll_test(self): print("课程[%s]测试中..." % self.name) def print_course_outline(self): pass class LinuxOPSCourse(AbstractCourse): def print_course_outline(self): pass def enroll_test(self): print("不用测试,是个人就能学...") class PythonCourse(AbstractCourse): def print_course_outline(self): pass def enroll_test(self): print("-------python入学测试-------") class BJSchool(AbstractSchool): name = "老男孩北京校区" def create_course(self,course_type): if course_type == ‘py_ops‘: course = PythonCourse("Python自动化开发", 7,‘面授‘,11000) elif course_type == ‘linux‘: course = LinuxOPSCourse("Linux运维课程", 5,‘面授‘,12800) return course def enroll(self,name,course): course.enroll_test() def info(self): print("------[%s]-----"%self.name) class SHSchool(AbstractSchool): name = "老男孩上海分校" def create_course(self,course_type): if course_type == ‘py_ops‘: course = PythonCourse("Python自动化开发", 8,‘在线‘,6500) elif course_type == ‘linux‘: course = LinuxOPSCourse("Linux运维课程", 6,‘在线‘,8000) return course def enroll(self,name,course): pass def info(self): print("--------[%s]-----" % self.name ) school1 = BJSchool() school2 = SHSchool() school1.info() c1=school1.create_course("py_ops") school1.enroll("张三",c1) school2.info() c2=school1.create_course("py_ops") school2.enroll("李四",c2)
图形解释
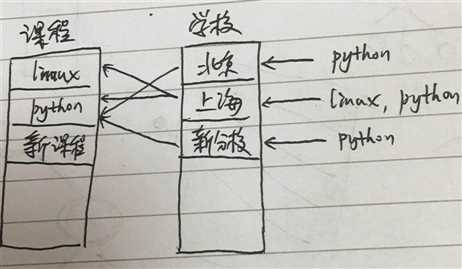
抽象工厂模式
class AbstractFactory(object): computer_name = ‘‘ def createCpu(self): pass def createMainboard(self): pass class IntelFactory(AbstractFactory): computer_name = ‘Intel I7-series computer ‘ def createCpu(self): return IntelCpu(‘I7-6500‘) def createMainboard(self): return IntelMainBoard(‘Intel-6000‘) class AmdFactory(AbstractFactory): computer_name = ‘Amd 4 computer ‘ def createCpu(self): return AmdCpu(‘amd444‘) def createMainboard(self): return AmdMainBoard(‘AMD-4000‘) ############# cpu工厂 class AbstractCpu(object): series_name = ‘‘ instructions = ‘‘ arch=‘‘ class IntelCpu(AbstractCpu): def __init__(self,series): self.series_name = series class AmdCpu(AbstractCpu): def __init__(self,series): self.series_name = series ############# 主板工厂 class AbstractMainboard(object): series_name = ‘‘ class IntelMainBoard(AbstractMainboard): def __init__(self,series): self.series_name = series class AmdMainBoard(AbstractMainboard): def __init__(self,series): self.series_name = series ############# 客户端 class ComputerEngineer(object): def makeComputer(self,computer_obj): self.prepareHardwares(computer_obj) def prepareHardwares(self,computer_obj): self.cpu = computer_obj.createCpu() self.mainboard = computer_obj.createMainboard() info = ‘‘‘------- computer [%s] info: cpu: %s mainboard: %s -------- End -------- ‘‘‘% (computer_obj.computer_name,self.cpu.series_name,self.mainboard.series_name) print(info) if __name__ == "__main__": engineer = ComputerEngineer() computer_factory = IntelFactory() engineer.makeComputer(computer_factory) computer_factory2 = AmdFactory() engineer.makeComputer(computer_factory2)
图形解释
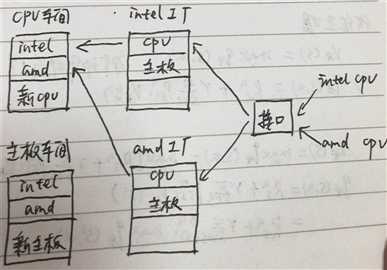
是不是觉得越来越复杂,但是还是云里雾里?往下看。
对比分析传统方法
首先我们来思考一下,如果传统方法实现上面这张图(就近,方便看),是不是这样,写个函数,函数里一堆参数,函数里一堆if ,是的,完全可以实现,而且可能更简单,
但是我们思考一下,如果有其他cpu呢?传统方法在一堆代码里,找if,然后加个if,而上图,只需改变cpu车间,再加个工厂,
继续,如果cpu生产要求输出生产报告,传统方法又开始找了,在每个cpu出加代码,这里是2个cpu,那如果是几万个呢?你要找几万次,改几万次,还没累死吗?而这里只需改一处,就是cpu工厂父类里加上输出报告的方法,几万个cpu瞬间搞定。
是不是觉得很方便?
总结
1. 在工厂模式中,对象的创建逻辑被封装,客户端只需要接口即可。
2. 创建对象采用继承方式,公共属性被统一定义,子类决定产品特色。
3. 代码可读性强,可维护性高
网上还有各种说法,鄙人觉得没什么鸟用,只是炫技,记住上面3点即可。
那为什么还分3种工厂模式呢?当然各自有优缺点了
简单工厂模式
优点:客户端不需要修改代码
缺点:如果增加产品,不仅需要新建车间,还需要修改接口,当然如果你把接口写在工厂类里,就是要修改工厂类。产品工厂都得改,大动作

一个工厂,多个产品,一个接口
工厂模式
优点:如果增加产品,只需修改产品类和相应工厂类
缺点:增加产品时,需要修改客户端代码

抽象工厂模式
优点
1.分离接口和实现
客户端使用抽象工厂来创建需要的对象,而客户端根本就不知道具体的实现是谁,客户端只是面向产品的接口编程而已。也就是说,客户端从具体的产品实现中解耦。
2.使切换产品族变得容易
因为一个具体的工厂实现代表的是一个产品族,比如上面例子的从Intel系列到AMD系列只需要切换一下具体工厂。
缺点
不太容易扩展新的产品如果需要给整个产品族添加一个新的产品,那么就需要修改抽象工厂,这样就会导致修改所有的工厂实现类。

以上的优缺点分析部分是有说服力的,也有一部分是为了迎合网上的说法,说的天花乱坠,云里雾里的,很有炫技嫌疑,
鄙人觉得,设计模式只是一种设计思路,具体执行过程中,可以天马行空,自己设定,无招胜有招,创新,柔和才是真正的应用,
记住一条即可:让所有人都方便,而且最好别让客户麻烦
参考资料:
http://www.cnblogs.com/yangxiaolan/p/5977465.html
以上是关于设计模式-工厂模式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章