类定义20175320
Posted nameless-student
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了类定义20175320相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
类定义
一、设计思路
(一)定义一个Book类,包含书名,作者,出版社和出版日期。
新建一个类Book,在类中定义String型变量Name、Author、Press、Date分别用来表示“书名”、“作者”、“出版社”以及“出版日期”
(二)定义三个构造方法,接收并初始化数据
三个构造方法分别可以实现不同的初始化方式。
- 1、将Book类对象的所有字符串变量初始化为“unknown”。
- 2、分别对Book类对象的所有字符串变量进行初始化。
- 3、将Book类对象的所有字符串变量初始化为同一字符串。
构造方法代码如下:
Book(){
Name="Unknown";
Author="Unknown";
Press="Unknown";
Date="Unknown";
}
Book(String a,String b,String c,String d) {
Name=a;
Author=b;
Press=c;
Date=d;
}
Book(String e){
Name=e;
Author=e;
Press=e;
Date=e;
}(三)定义getter和setter
我将getter分为四个get方法,分别用于返回代表对象的书名、作者、出版社以及出版日期的信息,将setter设置为setMessage这一方法,将参数中的数据写入对象的字符串变量中。代码如下:
public void setMessage(String a,String b,String c,String d) {
this.Name=a;
this.Author=b;
this.Press=c;
this.Date=d;
}(四)覆盖toString以及equals方法
在进行这部分的设计之前,我上网搜索了重写toString以及equals方法的作用,了解到了toString()是一种自我描述方法,equals方法可用于比较两个变量的地址以及值是否相等,同时我注意到重写equals方法的同时需要重写hashcode方法。代码如下:
public boolean equals(Object one) {
Book two = (Book)one;
if(one==null) return false;
if(one==this) return true;
if(!(one instanceof Book)) return false;
if(two.Name==this.Name&&two.Author==this.Author&&two.Press==this.Press&&two.Date==this.Date) return true;
else return false;
}
public String toString() {
return ("书名:"+this.Name+'
'+"作者:"+this.Author+'
'+"出版社:"+this.Press+'
'+"出版日期:"+this.Date+'
');
}
public int hashCode() {
int result=1;
result=31*result+((Name==null)?0:Name.hashCode());
result=31*result+((Author==null)?0:Author.hashCode());
result=31*result+((Press==null)?0:Press.hashCode());
result=31*result+((Date==null)?0:Date.hashCode());
return result;
}(五)创建一个测试类Bookshelf
我在Bookshelf类中设计了两种初始化Book类的方式,并需要手动输入书本的各项信息,使用第一种构造方法时,Book类的对象在初始化后再进行信息录入,而第二种构造方法在初始化的同时将输入的数据给对象的变量。Bookshelf类种还使用对象调用了toString方法返回书的描述信息。关键代码如下:
System.out.println("是否在构造时初始化,输入1为[yes]:");
answer=scanner.nextInt();
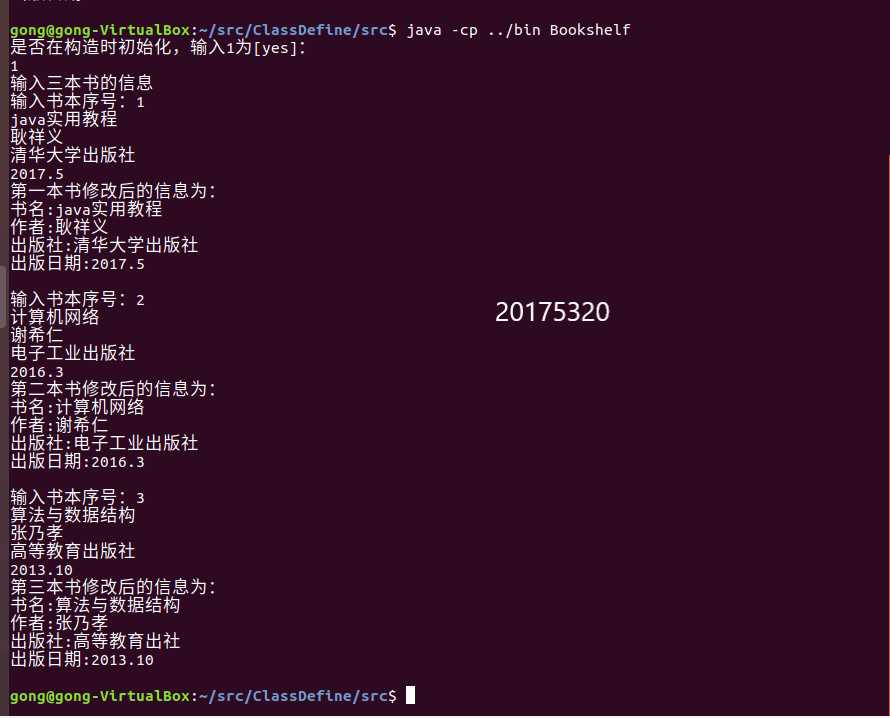
if(answer==1){ //使用将Book类对象的所有字符串变量初始化为同一字符串的构造方法
System.out.println("输入三本书的信息");
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.print("输入书本序号:");
dir=scanner.nextInt();
switch(dir)
{
case 1: {
scanner.nextLine();
a=scanner.nextLine();
b=scanner.nextLine();
c=scanner.nextLine();
d=scanner.nextLine();
numa=new Book(a,b,c,d);
System.out.println("第一本书修改后的信息为:");
System.out.println(numa.toString());//输出书的描述信息
break;
}
case 2: {
scanner.nextLine();
a=scanner.nextLine();
b=scanner.nextLine();
c=scanner.nextLine();
d=scanner.nextLine();
numb=new Book(a,b,c,d);
System.out.println("第二本书修改后的信息为:");
System.out.println(numb.toString());
break;
}
case 3: {
scanner.nextLine();
a=scanner.nextLine();
b=scanner.nextLine();
c=scanner.nextLine();
d=scanner.nextLine();
numc=new Book(a,b,c,d);
System.out.println("第三本书修改后的信息为:");
System.out.println(numc.toString());
break;
}
}
}
}
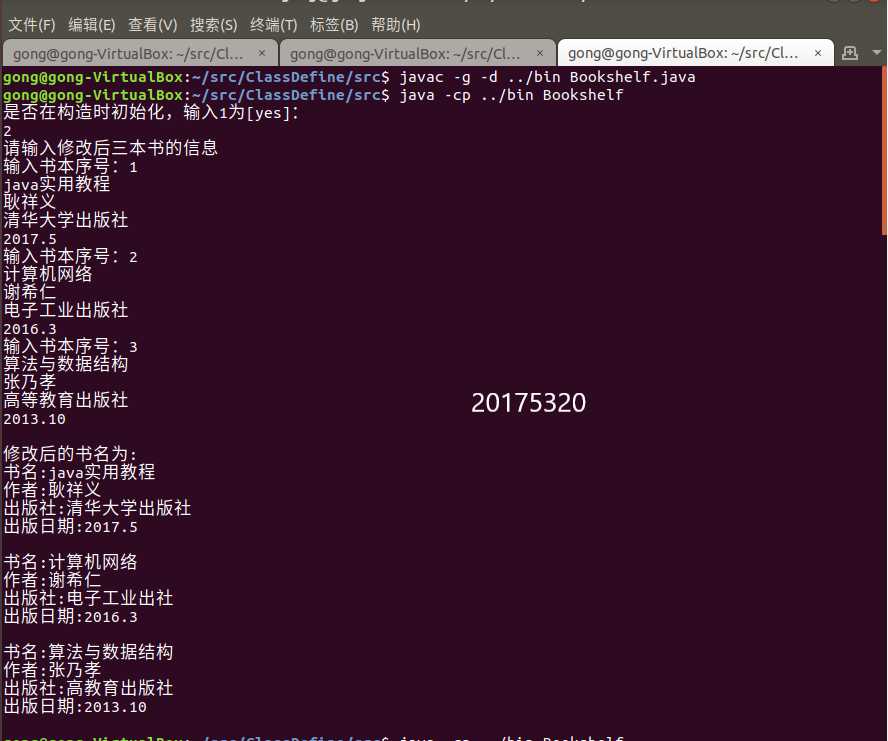
else {//使用将Book类对象的所有字符串变量初始化为“unknown”的构造方法
numa=new Book();
numb=new Book();
numc=new Book();
System.out.println("请输入修改后三本书的信息");
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.print("输入书本序号:");
dir=scanner.nextInt();
switch(dir)
{
case 1: {
scanner.nextLine();
a=scanner.nextLine();
b=scanner.nextLine();
c=scanner.nextLine();
d=scanner.nextLine();
numa.setMessage(a,b,c,d);//调用setMessage方法设置对象的各项信息
break;
}
case 2: {
scanner.nextLine();
a=scanner.nextLine();
b=scanner.nextLine();
c=scanner.nextLine();
d=scanner.nextLine();
numb.setMessage(a,b,c,d);
break;
}
case 3: {
scanner.nextLine();
a=scanner.nextLine();
b=scanner.nextLine();
c=scanner.nextLine();
d=scanner.nextLine();
numc.setMessage(a,b,c,d);
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println(numa.toString());//输出书的描述信息
System.out.println(numb.toString());
System.out.println(numc.toString());二、测试代码
由于使用集成开发环境进行编程,一些小问题在编写代码时就已被开发工具标示出来,测试时没有遇到问题,而较为复杂的问题我写在了第五部分。
三、运行结果
四、码云代码
五、遇到的问题
- 问题1:在使用第一种构造方法时出现初始化后对象无法调用方法。
- 问题1解决方法:经尝试后发现初始化语句在括号内,调用方法语句在括号外时会发生此种错误,于是将两部分语句放到一个括号内。
六、参考资料
以上是关于类定义20175320的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章