机器学习算法,机器让我学习
Posted bai2018
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习算法,机器让我学习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这个小段的内容主要是朴素贝叶斯、支持向量机、决策树和集成学习的代码,看不懂..........后面的更是看不懂..................
朴素贝叶斯:


scikit-learn提供了伯努利,多项式,高斯三个变体。伯努利是一个二项分布,多项式是离散分布,高斯是连续分布。用在不同的场景里:
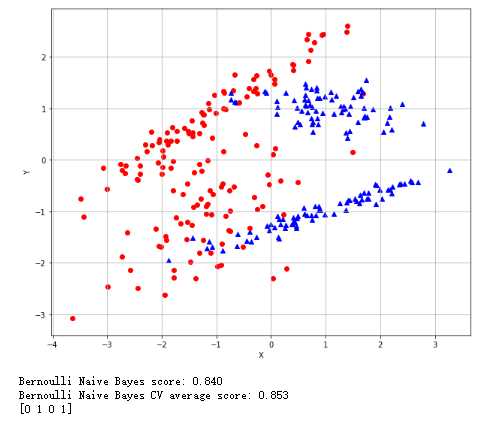
伯努利朴素贝叶斯:验证测试点的分布:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification 5 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score 6 from sklearn.naive_bayes import BernoulliNB 7 # For reproducibility 8 np.random.seed(1000) 9 nb_samples = 300 10 def show_dataset(X, Y): 11 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8)) 12 ax.grid() 13 ax.set_xlabel(‘X‘) 14 ax.set_ylabel(‘Y‘) 15 for i in range(nb_samples): 16 if Y[i] == 0: 17 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘o‘, color=‘r‘) 18 else: 19 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘^‘, color=‘b‘) 20 plt.show() 21 22 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 23 # Create dataset 24 X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0) 25 # Show dataset 26 show_dataset(X, Y) 27 # Split dataset 28 X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.25) 29 # Create and train Bernoulli Naive Bayes classifier 30 bnb = BernoulliNB(binarize=0.0) 31 bnb.fit(X_train, Y_train) 32 print(‘Bernoulli Naive Bayes score: %.3f‘ % bnb.score(X_test, Y_test)) 33 # Compute CV score 34 bnb_scores = cross_val_score(bnb, X, Y, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10) 35 print(‘Bernoulli Naive Bayes CV average score: %.3f‘ % bnb_scores.mean()) 36 # Predict some values 37 data = np.array([[0, 0], [1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 1]]) 38 Yp = bnb.predict(data) 39 print(Yp)
多项式朴素贝叶斯:根据数据预测城市还是农村:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer 4 from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB 5 # For reproducibility 6 np.random.seed(1000) 7 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 8 # Prepare a dummy dataset 9 data = [ 10 {‘house‘: 100, ‘street‘: 50, ‘shop‘: 25, ‘car‘: 100, ‘tree‘: 20}, 11 {‘house‘: 5, ‘street‘: 5, ‘shop‘: 0, ‘car‘: 10, ‘tree‘: 500, ‘river‘: 1} 12 ] 13 # Create and train a dictionary vectorizer 14 dv = DictVectorizer(sparse=False) 15 X = dv.fit_transform(data) 16 Y = np.array([1, 0]) 17 print(X) 18 # Create and train a Multinomial Naive Bayes classifier 19 mnb = MultinomialNB() 20 mnb.fit(X, Y) 21 22 # Create dummy test data 23 test_data = data = [ 24 {‘house‘: 80, ‘street‘: 20, ‘shop‘: 15, ‘car‘: 50, ‘tree‘: 20, ‘river‘: 1}, 25 {‘house‘: 10, ‘street‘: 5, ‘shop‘: 1, ‘car‘: 8, ‘tree‘: 300, ‘river‘: 0} 26 ] 27 #测试城市还是农村 28 Yp = mnb.predict(dv.fit_transform(test_data)) 29 print(Yp)

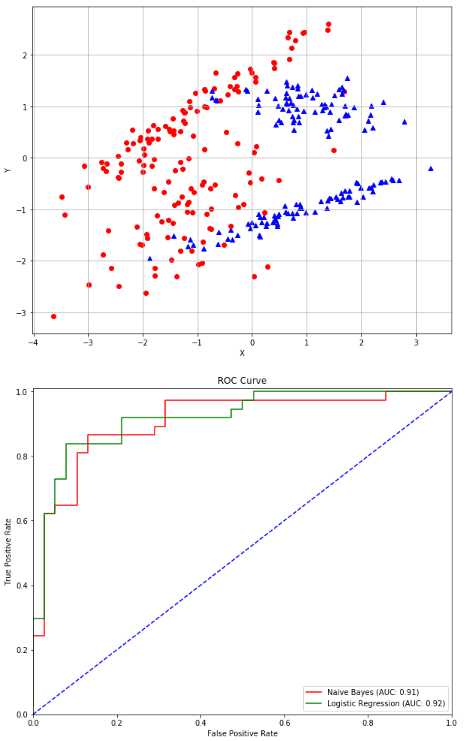
高斯朴素贝叶斯:验证点并通过ROC曲线比较结果

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification 5 from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB 6 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 7 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 8 from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc 9 # For reproducibility 10 np.random.seed(1000) 11 nb_samples = 300 12 def show_dataset(X, Y): 13 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8)) 14 15 ax.grid() 16 ax.set_xlabel(‘X‘) 17 ax.set_ylabel(‘Y‘) 18 19 for i in range(nb_samples): 20 if Y[i] == 0: 21 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘o‘, color=‘r‘) 22 else: 23 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘^‘, color=‘b‘) 24 25 plt.show() 26 27 28 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 29 # Create dataset 30 X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0) 31 32 # Show dataset 33 show_dataset(X, Y) 34 35 # Split dataset 36 X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.25) 37 38 # Create and train Gaussian Naive Bayes classifier 39 gnb = GaussianNB() 40 gnb.fit(X_train, Y_train) 41 42 # Create and train a Logistic regressor (for comparison) 43 lr = LogisticRegression() 44 lr.fit(X_train, Y_train) 45 46 # Compute ROC Curve 47 Y_gnb_score = gnb.predict_proba(X_test) 48 Y_lr_score = lr.decision_function(X_test) 49 50 fpr_gnb, tpr_gnb, thresholds_gnb = roc_curve(Y_test, Y_gnb_score[:, 1]) 51 fpr_lr, tpr_lr, thresholds_lr = roc_curve(Y_test, Y_lr_score) 52 53 # Plot ROC Curve 54 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 55 56 plt.plot(fpr_gnb, tpr_gnb, color=‘red‘, label=‘Naive Bayes (AUC: %.2f)‘ % auc(fpr_gnb, tpr_gnb)) 57 plt.plot(fpr_lr, tpr_lr, color=‘green‘, label=‘Logistic Regression (AUC: %.2f)‘ % auc(fpr_lr, tpr_lr)) 58 plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color=‘blue‘, linestyle=‘--‘) 59 plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0]) 60 plt.ylim([0.0, 1.01]) 61 plt.title(‘ROC Curve‘) 62 plt.xlabel(‘False Positive Rate‘) 63 plt.ylabel(‘True Positive Rate‘) 64 plt.legend(loc="lower right") 65 66 plt.show()
对比高斯朴素贝叶斯和多项式朴素贝叶斯在MNIST上的性能:
1 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 2 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 3 digits = load_digits() 4 gnb = GaussianNB() 5 mnb = MultinomialNB() 6 print(cross_val_score(gnb, digits.data, digits.target, scoring = ‘accuracy‘, cv = 10).mean()) 7 print(cross_val_score(mnb, digits.data, digits.target, scoring = ‘accuracy‘, cv = 10).mean())
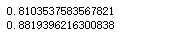
支持向量机:
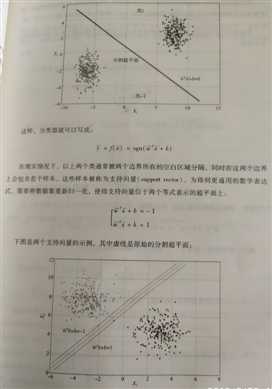


线性分类:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification 5 from sklearn.svm import SVC 6 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 7 # For reproducibility 8 np.random.seed(1000) 9 nb_samples = 500 10 def show_dataset(X, Y): 11 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8)) 12 ax.grid() 13 ax.set_xlabel(‘X‘) 14 ax.set_ylabel(‘Y‘) 15 for i in range(nb_samples): 16 if Y[i] == 0: 17 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘o‘, color=‘r‘) 18 else: 19 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘^‘, color=‘b‘) 20 plt.show() 21 22 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 23 # Create dataset 24 X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, 25 n_clusters_per_class=1) 26 # Show dataset 27 show_dataset(X, Y) 28 # Create a SVM with linear kernel 29 svc = SVC(kernel=‘linear‘) 30 # Compute CV score 31 svc_scores = cross_val_score(svc, X, Y, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10) 32 print(‘Linear SVM CV average score: %.3f‘ % svc_scores.mean())
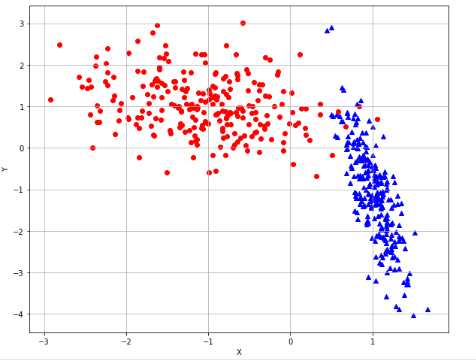
基于内核的分类:径向基核(Radial Basis Function),多项式核(Ploymomial kernel),sigmoid核,自定义核:
非线性例子:找到最好的内核并得到测试结果

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import multiprocessing 5 from sklearn.datasets import make_circles 6 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 7 from sklearn.svm import SVC 8 # For reproducibility 9 np.random.seed(1000) 10 nb_samples = 500 11 12 def show_dataset(X, Y): 13 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8)) 14 ax.grid() 15 ax.set_xlabel(‘X‘) 16 ax.set_ylabel(‘Y‘) 17 for i in range(nb_samples): 18 if Y[i] == 0: 19 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘o‘, color=‘r‘) 20 else: 21 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘^‘, color=‘b‘) 22 plt.show() 23 24 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 25 # Create datasets 26 X, Y = make_circles(n_samples=nb_samples, noise=0.1) 27 # Show dataset 28 show_dataset(X, Y) 29 # Define a param grid 30 param_grid = [ 31 { 32 ‘kernel‘: [‘linear‘, ‘rbf‘, ‘poly‘, ‘sigmoid‘], 33 ‘C‘: [0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 1.8, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0] 34 } 35 ] 36 # Create a train grid search on SVM classifier 37 gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=SVC(), param_grid=param_grid, 38 scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10, n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count()) 39 gs.fit(X, Y) 40 print(gs.best_estimator_) 41 print(‘Kernel SVM score: %.3f‘ % gs.best_score_) 42 43 #线性回归的分类效果 44 lr = LogisticRegression() 45 print(cross_val_score(lr,X,Y,scoring=‘accuracy‘,cv=10).mean())
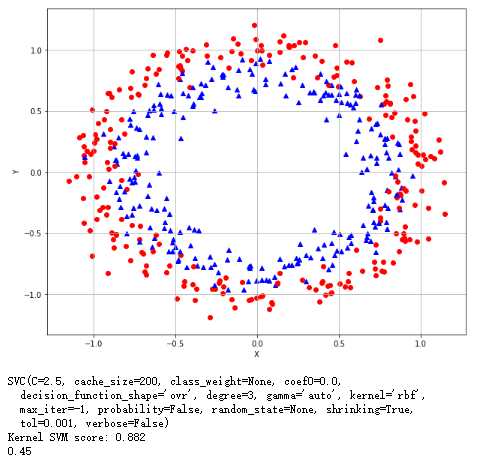
对MNIST使用支持向量机找到最好的内核:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import multiprocessing 4 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 5 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 6 from sklearn.svm import SVC 7 # For reproducibility 8 np.random.seed(1000) 9 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 10 # Load dataset 11 digits = load_digits() 12 # Define a param grid 13 param_grid = [ 14 { 15 ‘kernel‘: [‘linear‘, ‘rbf‘, ‘poly‘, ‘sigmoid‘], 16 ‘C‘: [0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 1.8, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0] 17 } 18 ] 19 # Create a train grid search on SVM classifier 20 gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=SVC(), param_grid=param_grid, 21 scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10, n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count()) 22 print(gs.fit(digits.data, digits.target)) 23 print(gs.best_estimator_)#最好的内核 24 print(‘Kernel SVM score: %.3f‘ % gs.best_score_)

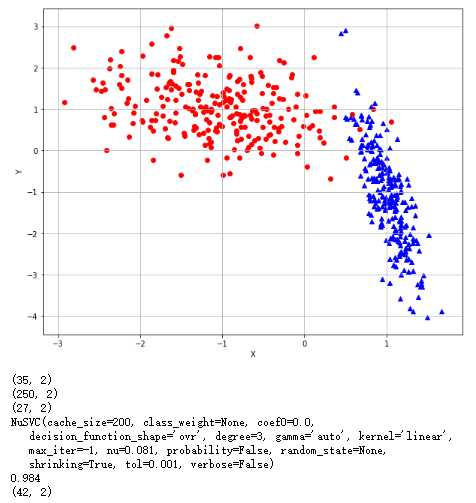
受控支持向量机:并通过网格寻找最佳选择

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification 5 from sklearn.svm import SVC, NuSVC 6 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 7 import multiprocessing 8 # For reproducibility 9 np.random.seed(1000) 10 nb_samples = 500 11 def show_dataset(X, Y): 12 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8)) 13 ax.grid() 14 ax.set_xlabel(‘X‘) 15 ax.set_ylabel(‘Y‘) 16 for i in range(nb_samples): 17 if Y[i] == 0: 18 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘o‘, color=‘r‘) 19 else: 20 ax.scatter(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], marker=‘^‘, color=‘b‘) 21 plt.show() 22 23 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 24 # Create dataset 25 X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, 26 n_clusters_per_class=1) 27 # Show dataset 28 show_dataset(X, Y) 29 # Create and train a linear SVM 30 svc = SVC(kernel=‘linear‘) 31 svc.fit(X, Y) 32 print(svc.support_vectors_.shape) 33 # Create and train a Nu-SVM classifier 34 nusvc = NuSVC(kernel=‘linear‘, nu=0.5) 35 nusvc.fit(X, Y) 36 print(nusvc.support_vectors_.shape) 37 nusvc = NuSVC(kernel=‘linear‘, nu=0.05) 38 nusvc.fit(X, Y) 39 print(nusvc.support_vectors_.shape) 40 41 param_grid = [ 42 { 43 ‘nu‘ : np.arange(0.081,1.0,0.5) 44 } 45 ] 46 gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=NuSVC(kernel=‘linear‘),param_grid = param_grid , scoring=‘accuracy‘,cv=10,n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count()) 47 gs.fit(X,Y) 48 print(gs.best_estimator_) 49 print(gs.best_score_) 50 print(gs.best_estimator_.support_vectors_.shape)
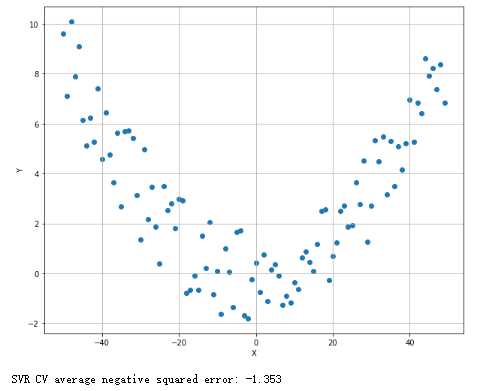
支持向量回归:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 from sklearn.svm import SVR 5 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 6 # For reproducibility 7 np.random.seed(1000) 8 nb_samples = 50 9 def show_dataset(X, Y): 10 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8)) 11 ax.grid() 12 ax.set_xlabel(‘X‘) 13 ax.set_ylabel(‘Y‘) 14 ax.scatter(X, Y) 15 plt.show() 16 17 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 18 # Create dataset 19 X = np.arange(-nb_samples, nb_samples, 1) 20 Y = np.zeros(shape=(2 * nb_samples,)) 21 for x in X: 22 Y[int(x) + nb_samples] = np.power(x * 6, 2.0) / 1e4 + np.random.uniform(-2, 2) 23 # Show dataset 24 #show_dataset(X, Y) 25 # Create and train a Support Vector regressor 26 svr = SVR(kernel=‘poly‘, degree=2, C=1.5, epsilon=0.5) 27 svr_scores = cross_val_score(svr, X.reshape((nb_samples*2, 1)), Y, scoring=‘neg_mean_squared_error‘, cv=10) 28 print(‘SVR CV average negative squared error: %.3f‘ % svr_scores.mean())
决策树和集成学习:
二元决策:
不纯度的衡量:基尼不纯度指数、交叉熵不纯度指数、误分类不纯度指数
特征重要度:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification 6 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, export_graphviz 7 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 8 9 10 # For reproducibility 11 np.random.seed(1000) 12 13 nb_samples = 500 14 15 # Set a folder to store the graph in 16 graph_folder = ‘‘ 17 18 19 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 20 # Create dataset 21 X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=3, n_informative=3, n_redundant=0, n_classes=3, 22 n_clusters_per_class=1) 23 24 # Create a Decision tree classifier 25 dt = DecisionTreeClassifier() 26 dt_scores = cross_val_score(dt, X, Y, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10) 27 print(‘Decision tree score: %.3f‘ % dt_scores.mean()) 28 29 # Save in Graphviz format 30 dt.fit(X, Y) 31 32 with open(‘dt.dot‘, ‘w‘) as df: 33 df = export_graphviz(dt, out_file=df, 34 feature_names=[‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘], 35 class_names=[‘C1‘, ‘C2‘, ‘C3‘])
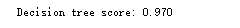
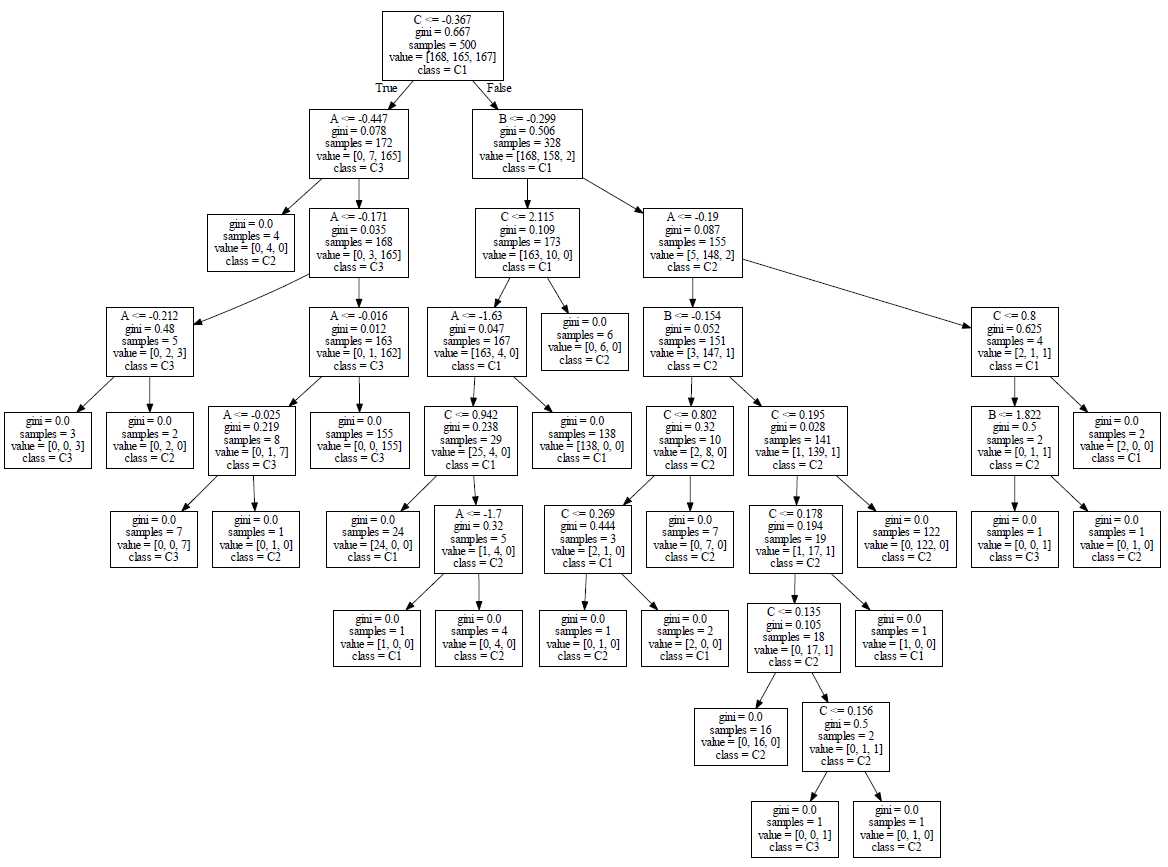
Graphviz下载后,windows安装后,找到目录下的:bin下的:dot,加入环境变量path,然后在cmd中输入:dot -Tpdf dt.dot dt.pdf,将dt.dot转化为dt.pdf,可视化图:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 import numpy as np 3 import multiprocessing 4 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 5 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 6 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 7 # For reproducibility 8 np.random.seed(1000) 9 10 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 11 # Load dataset 12 digits = load_digits() 13 # Define a param grid 14 param_grid = [ 15 { 16 ‘criterion‘: [‘gini‘, ‘entropy‘], 17 ‘max_features‘: [‘auto‘, ‘log2‘, None], 18 ‘min_samples_split‘: [2, 10, 25, 100, 200], 19 ‘max_depth‘: [5, 10, 15, None] 20 } 21 ] 22 # Create and train a grid searh 23 gs = GridSearchCV(estimator=DecisionTreeClassifier(), param_grid=param_grid, 24 scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10, n_jobs=multiprocessing.cpu_count()) 25 gs.fit(digits.data, digits.target) 26 print(gs.best_estimator_) 27 print(‘Decision tree score: %.3f‘ % gs.best_score_)

随机森林:

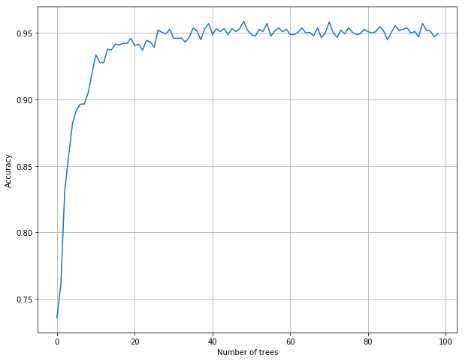
1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 7 from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier 8 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 9 10 11 # For reproducibility 12 np.random.seed(1000) 13 14 nb_classifications = 100 15 16 17 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 18 # Load dataset 19 digits = load_digits() 20 21 # Collect accuracies 22 rf_accuracy = [] 23 24 for i in range(1, nb_classifications): 25 a = cross_val_score(RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=i), digits.data, digits.target, scoring=‘accuracy‘, 26 cv=10).mean() 27 rf_accuracy.append(a) 28 29 # Show results 30 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 31 plt.xlabel(‘Number of trees‘) 32 plt.ylabel(‘Accuracy‘) 33 plt.grid(True) 34 plt.plot(rf_accuracy) 35 plt.show()

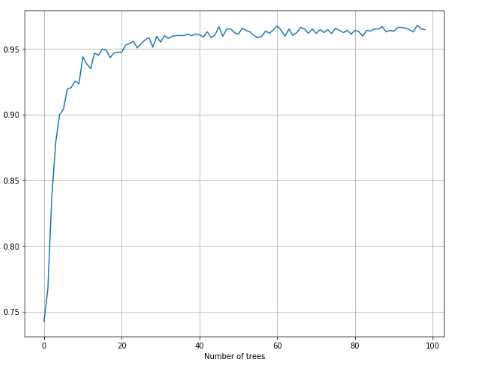
1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 7 from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier 8 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 9 10 11 # For reproducibility 12 np.random.seed(1000) 13 14 nb_classifications = 100 15 16 17 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 18 # Load dataset 19 digits = load_digits() 20 21 # Collect accuracies 22 et_accuracy = [] 23 24 for i in range(1, nb_classifications): 25 a = cross_val_score(ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators=i), digits.data, digits.target, scoring=‘accuracy‘, 26 cv=10).mean() 27 et_accuracy.append(a) 28 29 # Show results 30 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 31 plt.xlabel(‘Number of trees‘) 32 plt.ylabel(‘Accuracy‘) 33 plt.grid(True) 34 plt.plot(et_accuracy) 35 plt.show()
AdaBoost:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.datasets import load_digits 7 from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier 8 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 9 10 11 # For reproducibility 12 np.random.seed(1000) 13 14 nb_classifications = 100 15 16 17 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 18 # Load dataset 19 digits = load_digits() 20 21 # Collect accuracies 22 ab_accuracy = [] 23 24 for i in range(1, nb_classifications): 25 a = cross_val_score(AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=i), digits.data, digits.target, scoring=‘accuracy‘, 26 cv=10).mean() 27 ab_accuracy.append(a) 28 29 # Show results 30 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 31 plt.xlabel(‘Number of trees‘) 32 plt.ylabel(‘Accuracy‘) 33 plt.grid(True) 34 plt.plot(ab_accuracy) 35 plt.show()
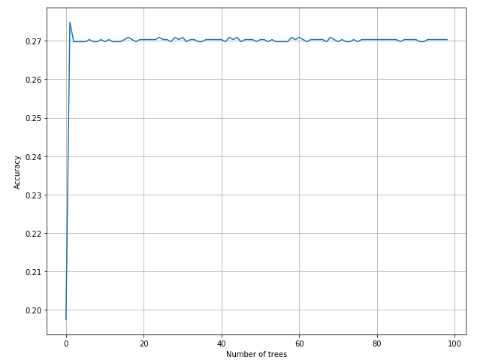

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 from sklearn.datasets import load_iris 6 from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier 7 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 8 9 10 # For reproducibility 11 np.random.seed(1000) 12 13 14 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 15 # Load dataset 16 iris = load_iris() 17 18 # Create and train an AdaBoost classifier 19 ada = AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=100, learning_rate=1.0) 20 ada_scores = cross_val_score(ada, iris.data, iris.target, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10) 21 print(‘AdaBoost score: %.3f‘ % ada_scores.mean())
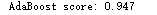
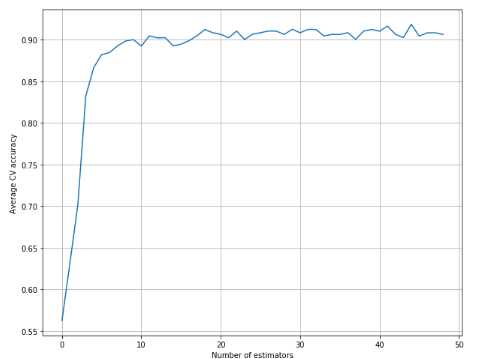
梯度树提升:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification 7 from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier 8 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 9 10 # For reproducibility 11 np.random.seed(1000) 12 13 nb_samples = 500 14 15 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 16 # Create the dataset 17 X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=4, n_informative=3, n_redundant=1, n_classes=3) 18 19 # Collect the scores for n_estimators in (1, 50) 20 a = [] 21 max_estimators = 50 22 23 for i in range(1, max_estimators): 24 score = cross_val_score(GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=i, learning_rate=10.0 / float(i)), X, Y, 25 cv=10, scoring=‘accuracy‘).mean() 26 a.append(score) 27 28 # Plot the results 29 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) 30 plt.xlabel(‘Number of estimators‘) 31 plt.ylabel(‘Average CV accuracy‘) 32 plt.grid(True) 33 plt.plot(a) 34 plt.show()
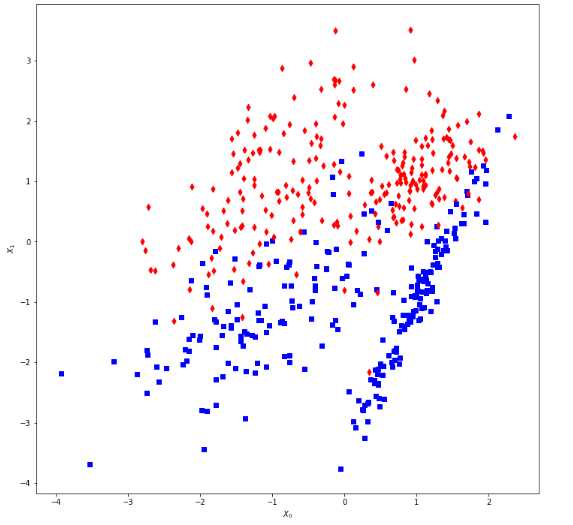
投票分类器:

1 from __future__ import print_function 2 3 import numpy as np 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 5 6 from sklearn.datasets import make_classification 7 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 8 from sklearn.svm import SVC 9 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 10 from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier 11 from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score 12 13 # For reproducibility 14 np.random.seed(1000) 15 16 nb_samples = 500 17 18 19 def compute_accuracies(lr, dt, svc, vc, X, Y): 20 accuracies = [] 21 22 accuracies.append(cross_val_score(lr, X, Y, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10).mean()) 23 accuracies.append(cross_val_score(dt, X, Y, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10).mean()) 24 accuracies.append(cross_val_score(svc, X, Y, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10).mean()) 25 accuracies.append(cross_val_score(vc, X, Y, scoring=‘accuracy‘, cv=10).mean()) 26 27 print(‘Accuracies:‘) 28 print(np.array(accuracies)) 29 30 return accuracies 31 32 33 def plot_accuracies(accuracies): 34 fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8)) 35 positions = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3]) 36 37 ax.bar(positions, accuracies, 0.5) 38 ax.set_ylabel(‘Accuracy‘) 39 ax.set_xticklabels((‘Logistic Regression‘, ‘Decision Tree‘, ‘SVM‘, ‘Ensemble‘)) 40 ax.set_xticks(positions + (5.0 / 20)) 41 plt.ylim([0.80, 0.93]) 42 plt.show() 43 44 45 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 46 # Create the dataset 47 X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=2, n_redundant=0, n_classes=2) 48 49 # Show the dataset 50 fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 12)) 51 52 for i, x in enumerate(X): 53 if Y[i] == 0: 54 ax.scatter(x[0], x[1], marker=‘s‘, color=‘blue‘) 55 else: 56 ax.scatter(x[0], x[1], marker=‘d‘, color=‘red‘) 57 58 ax.set_xlabel(r‘$X_0$‘) 59 ax.set_ylabel(r‘$X_1$‘) 60 plt.show() 61 62 # Create the classifiers 63 lr = LogisticRegression() 64 svc = SVC(kernel=‘poly‘, probability=True) 65 dt = DecisionTreeClassifier() 66 67 classifiers = [(‘lr‘, lr), 68 (‘dt‘, dt), 69 (‘svc‘, svc)] 70 71 # Hard voting 72 vc = VotingClassifier(estimators=classifiers, voting=‘hard‘) 73 74 # Compute and plot accuracies 75 hard_accuracies = compute_accuracies(lr, dt, svc, vc, X, Y) 76 plot_accuracies(hard_accuracies) 77 78 # Soft weighted voting 79 weights = [1.5, 0.5, 0.75] 80 81 vc = VotingClassifier(estimators=classifiers, weights=weights, voting=‘soft‘) 82 83 # Compute and plot accuracies 84 soft_accuracies = compute_accuracies(lr, dt, svc, vc, X, Y) 85 plot_accuracies(soft_accuracies)
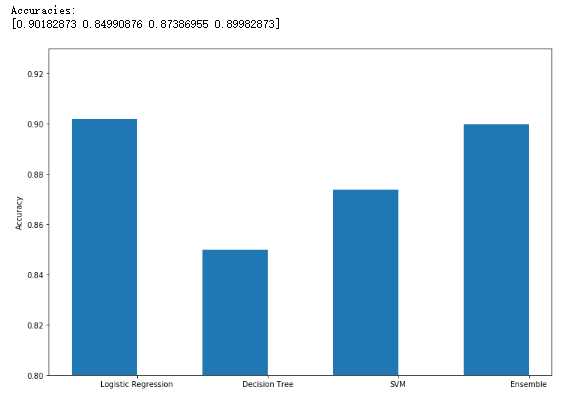
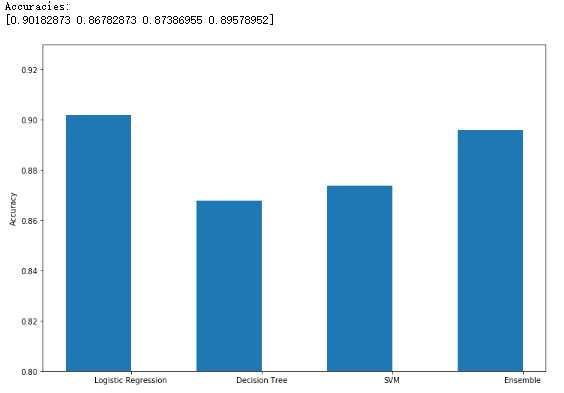
看不懂也看不进去,希望以后还有的话,再看看吧.....
以上是关于机器学习算法,机器让我学习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
