设计模式
Posted wzscom
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设计模式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
工厂方法
*义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类。FactoryMethod使一个类的实例*延迟到其子类。
适用性
1.当一个类不知道它所必须创建的对象的类的时候。
2.当一个类希望由它的子类来指定它所创建的对象的时候。
3.当*将创建对象的职责委托给多个帮助*类中的某一个,并且*希望将哪一个帮助子类是代理者这一信息局部化的时候。
参与者
1.Product
定义工厂方法所创建的对象的接口。
2.ConcreteProduct
实现Product接口。
3.Creator
声明工厂方法,该方法返回一个Product类型的对象*
Creator也可以定义一个工厂方法的缺省实现,它返回一个缺省的ConcreteProduct对象。
可以调用工厂方法以创建一个Product对象。
4.ConcreteCreator
重定义工厂方法以返回一个ConcreteProduct实例。
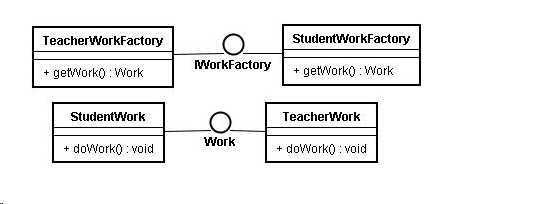
1 *roduct 2 3 public interface Work { 4 5 void doWork(); 6 } 7 ConcreteProduct 8 9 public class StudentWork implements Work { 10 11 public void doWork() { 12 System.out.println("学生*作业!"); 13 } 14 15 } 16 17 public class TeacherWork implements Work { 18 19 public void doWork() { 20 System.out.println("老师审批作业!"); 21 } 22 23 } 24 Creator 25 26 public interface IWorkFactory { 27 28 Work get*ork(); 29 } 30 Concre*eCreator 31 32 pu*lic class StudentWorkFactory implements IWorkFactory { 33 34 public Work getWork() { 35 *eturn new StudentWork(); 36 } 37 38 } 39 40 public class TeacherWorkFactory implements IWorkFactory { 41 42 public Work getWork() { 43 return new TeacherWork(); 44 } 45 46 } 47 Test 48 49 public class Test { 50 51 public static void m*in(Strin*[] args) { 52 IWorkFactory studentWorkFactory = new StudentWorkFactory(); 53 studentWorkFactory.getWork().d*Work(); 54 55 IWorkFactory teacherWorkFactory * new TeacherWorkFactory(); 56 teacherWorkFactory.g*tWork().*oWork(); 57 } 58 59 } 60 result 61 62 学生做作业! 63 老师审批作业!
抽象工厂
提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。
适用性
1.一个系统要独立于它的*品的创建、组合和表示时。
2.一个系统要由多个产品系列中的一个来配置时。
3.当你要强调一系列相关的产品对象的设计以便进行联合使用时*
4*当你提供一个产品类库,而只想显示它们*接口而不是实现时。
参与者
1.Ab*tractFactory
声明一个创建抽象产品对象的操作接口。
2.ConcreteFactory
实现创建具体产品对象的操作。
*.AbstractProduct
为一类产品对象声明一个接口。
4.ConcreteProdu*t
定义一个将被相应的具体工厂创建的产品*象。
实现*bstractProduct接口。
5.Client
仅使用由AbstractFactory和AbstractProduc*类声明的接口
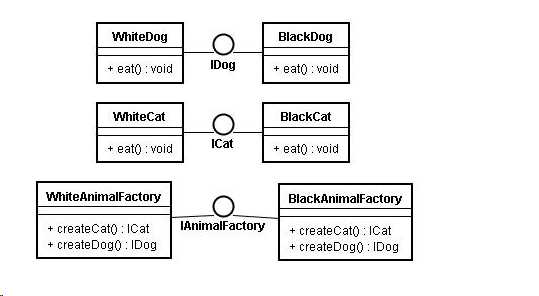
1 *bstractFactory 2 3 public interface IAn*malFactory { 4 5 ICat createCat(); 6 7 IDog cre*teDog(); 8 } 9 ConcreteFactory 10 11 p*blic class BlackAnimalFactory implem*nts IAnimalFactory { 12 13 public ICat createCat() { 14 retur* new BlackCat(); 15 } 16 17 public IDog createDog() { 18 return new BlackDog(); 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 public class WhiteAnimalFac*ory imp*ements IAnimalFactory { 24 25 public ICat createCat() { 26 return new WhiteCat(); 27 } 28 29 public IDog cre*teDog() { 30 return new WhiteDog(); 31 } 32 33 } 34 Abstrac*Product 35 36 public interface ICat { 37 38 void eat(); 39 } 40 41 public interface IDog { 42 43 void eat(); 44 } 45 Concrete*roduct 46 47 public class Black*at implements ICat { 48 49 public void eat() { 50 System.out.println("The bl*ck cat is eating!"); 51 } 52 53 } 54 55 public class WhiteCat implements *Cat { 56 57 public void eat() { 58 Sy*tem.out.prin*ln("The w*ite cat is eating!*); 59 } 60 61 } 62 63 public class BlackDog implements IDog { 64 65 public void eat() { 66 System.out.println("The black dog is eating"); 67 } 68 69 } 70 71 public class WhiteDog implements IDog { 72 73 public void eat() { 74 System.out.println("The white dog is eat*ng!"); 75 } 76 77 } 78 Client 79 80 public static void main(String[] args) { 81 IAnimalFactory blackAnimalFa*tory = new BlackAnimalFactory(); 82 ICat blackCat = blackAnimalFactory.createCat(); 83 blackCat.eat(); 84 IDog blackD*g = blackAnimalFactory.createDog(); 85 blackDog.eat(); 86 87 IAnimalFactory whiteAnimalF*ctory = new WhiteAnimalFactory(); 88 ICat whiteCat = whiteAnimalFactory.createCat(); 89 whiteCat.eat(); 90 IDog *hiteDog = whiteAnimalFactory.createDog(); 91 whiteDog.eat(); 92 } 93 res*lt 94 95 The bla*k cat is eating! 96 Th* black dog is eatin*! 97 The white cat is eating! 98 The white dog is *ating!
建造者模式
将一个复杂对象的构造与它的表示分离,使不同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示。
适用性
1.当创建复杂对象的算法应该独立于该对象的组成部分以及它们的装配方式时。
*.当构造过程必须允*被构造的对象有不同*表示时。
参与者
1.Builder
为创建一个Product对象的各个部件指定抽象接口。
2.ConcreteBuilder
实现Buil*er的接口以构造和装配该产品的各个部件。
定义并明确它所创建的表示*
提供一个检索产品的接口。
3.Director
构造一个使用Builder接口的对象。
4.Product
表示被构造的复杂对象。ConcreteBuilder创建该产品的内部表示并定义它的装配过程。
包含定义组成部件的类,包括将这些部件装配成最终产品的接口。
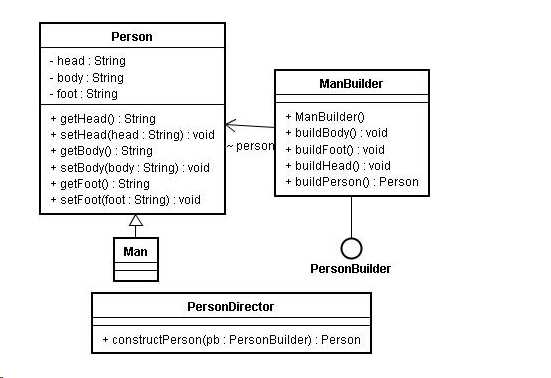
1 Buil*er 2 3 public interface PersonBuilder { 4 5 void buildHead(); 6 7 v*id buildBody(); 8 9 void buildFoot()* 10 11 Person buildPerson(); 12 } 13 ConcreteBuilder 14 15 public class ManBuilder implements PersonB*ilder { 16 17 Person person; 18 19 public ManBuilder() { 20 person = ne* Man(); 21 } 22 23 publ*c void build*ody() { 24 perso*.setBody("建造男人的身体"); 25 } 26 27 public void buildFoot() { 28 person.setFo*t("建造男人的脚"); 29 } 30 31 public void buildHead() { 32 pers*n.setHead("建造*人的头"); 33 } 34 35 *ublic Person buildPerson() { 36 retur* person; 37 } 38 } 39 Dir*ctor 40 41 public class PersonDirec*or { 42 43 public Person constructPerson(PersonBuilder pb) { 44 pb.buildHead(); 45 pb.buildBody(); 46 pb.buildFoot(); 47 return pb.buildPerson(); 48 } 49 } 50 Product 51 52 public class Person { 53 54 private String head; 55 56 private String body; 57 58 private String foot; 59 60 public String getH*ad() { 61 return head; 62 } 63 64 public void setHead(String hea*) { 65 this.head = head; 66 } 67 68 public String getBody() { 69 return body; 70 } 71 72 public void setBody(String body) { 73 this.b*dy = body; 74 } 75 76 public String getFoot() { 77 return foot; 78 } 79 80 public void setFoot(String foot) { 81 t*is.foot = foot; 82 } 83 } 84 85 public class Man extends Person { 86 87 } 88 Test 89 90 publ*c class Test{ 91 92 public static void main(String[] ar*s) { 93 PersonDirector pd = new PersonDirector(); 94 Person person = pd.constructPerson(new ManBuilder()); 95 System*out.println(person.getBody()); 96 System.out.println(person.getFoot()); 97 System.out.println(person.getHead()); 98 } 99 } 100 result 101 102 建造男人*身体 103 建造男*的脚 104 建造男人的头
1 原型模式 2 3 用原型实例指定创建对象的种类,并且通过拷贝这些原型创建新的对象。 4 适用性 5 6 1.当一个系统应该独立于它的产品创*、构成和表示时。 7 8 2.当要实例化的类是在运行时刻指定时,例如,通过动态装载。 9 10 3.为了避免创建一个与产品类层次平行的工厂*层次时。 11 12 4.当一个类的实例只能有几个不同状态组合中的一种时。 13 14 建立相应数目的原型并克隆它们可能比每次用合适的状态手工实例化该类更方便一些。 15 16 参与者 17 18 1. Prototype 19 声明一个克隆自身的接口。 20 21 2. ConcretePrototype 22 实现一个克隆自身的操作。 23 24 3. Client 25 让一个原型克*自身从而创建一个新的对象。 26 类图 27 28 例子 29 Prototype 30 31 public class Prototype implements Cloneable { 32 33 private String name; 34 35 public void setName(String name) { 36 this.name = name; 37 } 38 39 public String getName() { 40 return this.name; 41 } 42 43 public Object clone(){ 44 try { 45 return super.clone(); 46 } catch (Exception e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 return null; 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 ConcretePrototype 53 54 publ*c class ConcretePrototype extend* Prototype { 55 56 public ConcretePrototype(String name) { 57 setName(name); 58 } 59 } 60 Client 61 62 public clas* Test { 63 64 public static void main(String[] args) { 65 Prototype pro = new ConcretePrototy*e("prototype"); 66 Prototype pro2 = (Prototype)pro.clone(); 67 *ystem.out.println(pro.getName()*; 68 System.out.println(pro2.getName()); 69 } 70 } 71 result 72 73 prototype 74 prototype
装饰模式
动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责。就增加功能来说,Decorator模*相比生成子类更为*活。
适用性
1.在不影响其他*象的情况下,以动态、透明的方式给单个对象添加职责。
2.处理那些可以撤消的职责。
3.当不能采用生成子类的方法进行扩充时。
参与者
1.Component
定义一个对象接口,可以给这些对象动态地添加职责。
2.ConcreteComponent
定义一个对象,可以给这个对象添加一些职责。
3.Decorator
维持一个指向Component对象的指针,并定义一个与Component接口一致的接口。
4.ConcreteDecorator
向组件添加职责。
1 Component 2 3 public interface Person { 4 5 void eat(); 6 } 7 ConcreteComponent 8 9 *ublic class M*n implements Person { 10 11 public void eat() { 12 System.out.println("男人在吃"); 13 * 14 } 15 Decorator 16 17 public abstrac* class Decorator implements Perso* { 18 19 protected Person person* 20 21 public void setPerson(Person person) { 22 this.person = person; 23 } 24 25 public void eat() { 26 person.eat(); 27 } 28 } 29 ConcreteDec*rator 30 31 publi* class ManDecoratorA extends Decorator { 32 33 public void eat() { 34 super.eat(); 35 reEat(); 36 Sy*tem.out.println("ManDecoratorA类"); 37 } 38 39 public void reEat() { 40 System.out.println("再吃一顿饭"); 41 * 42 } 43 44 public class ManDecoratorB extends Decorator * 45 46 public void eat() { 47 super.eat(); 48 Syst*m.out.println("==============="); 49 System.out.println("ManDecoratorB类"); 50 } 51 } 52 Test 53 54 public class Test { 55 56 public st*tic void main(Strin*[] args) { 57 Man man = new Man(); 58 ManDecoratorA md1 = new ManDecoratorA(); 59 ManDecoratorB md2 = n*w ManDecoratorB(); 60 61 md1.setPerson(man); 62 md2.setPerson(md1); 63 md2.eat(); 64 } 65 } 66 result 67 68 男人在吃 69 再吃一顿饭 70 ManDecoratorA类 71 =============== 72 ManDecoratorB类