ConsurrentDictionary并发字典知多少?
Posted coderayu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ConsurrentDictionary并发字典知多少?相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景
在上一篇文章你真的了解字典吗?一文中我介绍了Hash Function和字典的工作的基本原理.
有网友在文章底部评论,说我的Remove和Add方法没有考虑线程安全问题.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.collections.generic.dictionary-2?redirectedfrom=MSDN&view=netframework-4.7.2
查阅相关资料后,发现字典.net中Dictionary本身时不支持线程安全的,如果要想使用支持线程安全的字典,那么我们就要使用ConcurrentDictionary了.
在研究ConcurrentDictionary的源码后,我觉得在ConcurrentDictionary的线程安全的解决思路很有意思,其对线程安全的处理对对我们项目中的其他高并发场景也有一定的参考价值,在这里再次分享我的一些学习心得和体会,希望对大家有所帮助.
Concurrent
ConcurrentDictionary是Dictionary的线程安全版本,位于System.Collections.Concurrent的命名空间下,该命名空间下除了有ConcurrentDictionary,还有以下Class都是我们常用的那些类库的线程安全版本.
BlockingCollection
ConcurrentBag
ConcurrentQueue
如果读过我上一篇文章你真的了解字典吗?的小伙伴,对这个ConcurrentDictionary的工作原理应该也不难理解,它是简简单单地在读写方法加个lock吗?
工作原理
Dictionary
如下图所示,在字典中,数组entries用来存储数据,buckets作为桥梁,每次通过hash function获取了key的哈希值后,对这个哈希值进行取余,即hashResult%bucketsLength=bucketIndex,余数作为buckets的index,而buckets的value就是这个key对应的entry所在entries中的索引,所以最终我们就可以通过这个索引在entries中拿到我们想要的数据,整个过程不需要对所有数据进行遍历,的时间复杂度为1.
ConcurrentDictionary
ConcurrentDictionary的数据存储类似,只是buckets有个更多的职责,它除了有dictionary中的buckets的桥梁的作用外,负责了数据存储.
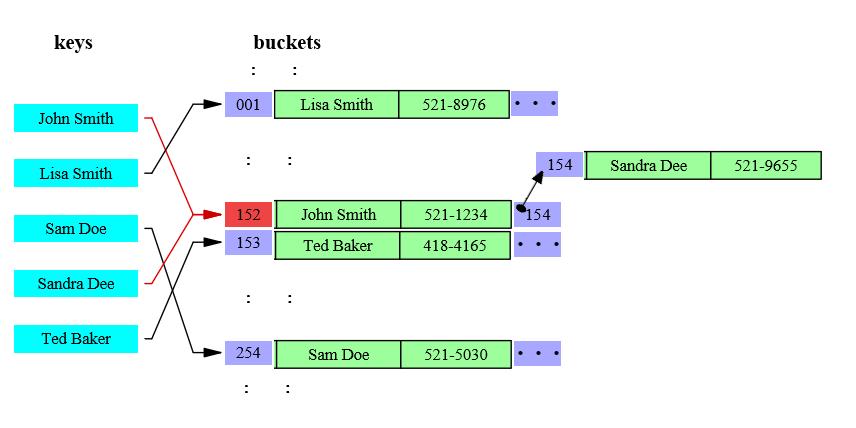
key的哈希值与buckets的length取余后hashResult%bucketsLength=bucketIndex,余数作为buckets的索引就能找到我们要的数据所存储的块,当出现两个key指向同一个块时,即上图中的John Smith和Sandra Dee他同时指向152怎么办呢?存储节点Node具有Next属性执行下个Node,上图中,node 152的Next为154,即我们从152开始找Sandra Dee,发现不是我们想要的,再到154找,即可取到所需数据.
由于官方原版的源码较为复杂,理解起来有所难度,我对官方源码做了一些精简,下文将围绕这个精简版的ConcurrentDictionary展开叙述.
https://github.com/liuzhenyulive/DictionaryMini
数据结构
Node
ConcurrentDictionary中的每个数据存储在一个Node中,它除了存储value信息,还存储key信息,以及key对应的hashcode
private class Node
{
internal TKey m_key; //数据的key
internal TValue m_value; //数据值
internal volatile Node m_next; //当前Node的下级节点
internal int m_hashcode; //key的hashcode
//构造函数
internal Node(TKey key, TValue value, int hashcode, Node next)
{
m_key = key;
m_value = value;
m_next = next;
m_hashcode = hashcode;
}
}Table
而整个ConcurrentDictionary的数据存储在这样的一个Table中,其中m_buckets的Index负责映射key,m_locks是线程锁,下文中会有详细介绍,m_countPerLock存储每个lock锁负责的node数量.
private class Tables
{
internal readonly Node[] m_buckets; //上文中提到的buckets
internal readonly object[] m_locks; //线程锁
internal volatile int[] m_countPerLock; //索格锁所管理的数据数量
internal readonly IEqualityComparer<TKey> m_comparer; //当前key对应的type的比较器
//构造函数
internal Tables(Node[] buckets, object[] locks, int[] countPerlock, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer)
{
m_buckets = buckets;
m_locks = locks;
m_countPerLock = countPerlock;
m_comparer = comparer;
}
}
ConcurrentDictionary会在构造函数中创建Table,这里我对原有的构造函数进行了简化,通过默认值进行创建,其中DefaultConcurrencyLevel默认并发级别为当前计算机处理器的线程数.
//构造函数
public ConcurrentDictionaryMini() : this(DefaultConcurrencyLevel, DEFAULT_CAPACITY, true,
EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default)
{
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="concurrencyLevel">并发等级,默认为CPU的线程数</param>
/// <param name="capacity">默认容量,31,超过31后会自动扩容</param>
/// <param name="growLockArray">时否动态扩充锁的数量</param>
/// <param name="comparer">key的比较器</param>
internal ConcurrentDictionaryMini(int concurrencyLevel, int capacity, bool growLockArray, IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer)
{
if (concurrencyLevel < 1)
{
throw new Exception("concurrencyLevel 必须为正数");
}
if (capacity < 0)
{
throw new Exception("capacity 不能为负数.");
}
if (capacity < concurrencyLevel)
{
capacity = concurrencyLevel;
}
object[] locks = new object[concurrencyLevel];
for (int i = 0; i < locks.Length; i++)
{
locks[i] = new object();
}
int[] countPerLock = new int[locks.Length];
Node[] buckets = new Node[capacity];
m_tables = new Tables(buckets, locks, countPerLock, comparer);
m_growLockArray = growLockArray;
m_budget = buckets.Length / locks.Length;
}
方法
ConcurrentDictionary中较为基础重点的方法分别位Add,Get,Remove,Grow Table方法,其他方法基本上是建立在这四个方法的基础上进行的扩充.
Add
向Table中添加元素有以下亮点值得我们关注.
开始操作前会声明一个tables变量来存储操作开始前的m_tables,在正式开始操作后(进入lock)的时候,会检查tables在准备工作阶段是否别的线程改变,如果改变了,则重新开始准备工作并从新开始.
通过GetBucketAndLockNo方法获取bucket索引以及lock索引,其内部就是取余操作.
private void GetBucketAndLockNo(
int hashcode, out int bucketNo, out int lockNo, int bucketCount, int lockCount)
{
//0x7FFFFFFF 是long int的最大值 与它按位与数据小于等于这个最大值
bucketNo = (hashcode & 0x7fffffff) % bucketCount;
lockNo = bucketNo % lockCount;
}对数据进行操作前会从m_locks取出第lockNo个对象最为lock,操作完成后释放该lock.多个lock一定程度上减少了阻塞的可能性.
在对数据进行更新时,如果该Value的Type为允许原子性写入的,则直接更新该Value,否则创建一个新的node进行覆盖.
/// <summary>
/// Determines whether type TValue can be written atomically
/// </summary>
private static bool IsValueWriteAtomic()
{
Type valueType = typeof(TValue);
//
// Section 12.6.6 of ECMA CLI explains which types can be read and written atomically without
// the risk of tearing.
//
// See http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/files/ECMA-ST/ECMA-335.pdf
//
if (valueType.IsClass)
{
return true;
}
switch (Type.GetTypeCode(valueType))
{
case TypeCode.Boolean:
case TypeCode.Byte:
case TypeCode.Char:
case TypeCode.Int16:
case TypeCode.Int32:
case TypeCode.SByte:
case TypeCode.Single:
case TypeCode.UInt16:
case TypeCode.UInt32:
return true;
case TypeCode.Int64:
case TypeCode.Double:
case TypeCode.UInt64:
return IntPtr.Size == 8;
default:
return false;
}
}该方法依据CLI规范进行编写,简单来说,32位的计算机,对32字节以下的数据类型写入时可以一次写入的而不需要移动内存指针,64位计算机对64位以下的数据可一次性写入,不需要移动内存指针.保证了写入的安全.
详见12.6.6 http://www.ecma-international.org/publications/files/ECMA-ST/ECMA-335.pdf
private bool TryAddInternal(TKey key, TValue value, bool updateIfExists, bool acquireLock, out TValue resultingValue)
{
while (true)
{
int bucketNo, lockNo;
int hashcode;
//https://www.cnblogs.com/blurhkh/p/10357576.html
//需要了解一下值传递和引用传递
Tables tables = m_tables;
IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer = tables.m_comparer;
hashcode = comparer.GetHashCode(key);
GetBucketAndLockNo(hashcode, out bucketNo, out lockNo, tables.m_buckets.Length, tables.m_locks.Length);
bool resizeDesired = false;
bool lockTaken = false;
try
{
if (acquireLock)
Monitor.Enter(tables.m_locks[lockNo], ref lockTaken);
//如果表刚刚调整了大小,我们可能没有持有正确的锁,必须重试。
//当然这种情况很少见
if (tables != m_tables)
continue;
Node prev = null;
for (Node node = tables.m_buckets[bucketNo]; node != null; node = node.m_next)
{
if (comparer.Equals(node.m_key, key))
{
//key在字典里找到了。如果允许更新,则更新该key的值。
//我们需要为更新创建一个node,以支持不能以原子方式写入的TValue类型,因为free-lock 读取可能同时发生。
if (updateIfExists)
{
if (s_isValueWriteAtomic)
{
node.m_value = value;
}
else
{
Node newNode = new Node(node.m_key, value, hashcode, node.m_next);
if (prev == null)
{
tables.m_buckets[bucketNo] = newNode;
}
else
{
prev.m_next = newNode;
}
}
resultingValue = value;
}
else
{
resultingValue = node.m_value;
}
return false;
}
prev = node;
}
//key没有在bucket中找到,则插入该数据
Volatile.Write(ref tables.m_buckets[bucketNo], new Node(key, value, hashcode, tables.m_buckets[bucketNo]));
//当m_countPerLock超过Int Max时会抛出OverflowException
checked
{
tables.m_countPerLock[lockNo]++;
}
//
// 如果m_countPerLock[lockNo] > m_budget,则需要调整buckets的大小。
// GrowTable也可能会增加m_budget,但不会调整bucket table的大小。.
// 如果发现bucket table利用率很低,也会发生这种情况。
//
if (tables.m_countPerLock[lockNo] > m_budget)
{
resizeDesired = true;
}
}
finally
{
if (lockTaken)
Monitor.Exit(tables.m_locks[lockNo]);
}
if (resizeDesired)
{
GrowTable(tables, tables.m_comparer, false, m_keyRehashCount);
}
resultingValue = value;
return true;
}
}
Get
从Table中获取元素的的流程与前文介绍ConcurrentDictionary工作原理时一致,但有以下亮点值得关注.
- 读取bucket[i]在Volatile.Read()方法中进行,该方法会自动对读取出来的数据加锁,避免在读取的过程中,数据被其他线程remove了.
- Volatile读取指定字段时,在读取的内存中插入一个内存屏障,阻止处理器重新排序内存操作,如果在代码中此方法之后出现读取或写入,则处理器无法在此方法之前移动它。
public bool TryGetValue(TKey key, out TValue value)
{
if (key == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
// We must capture the m_buckets field in a local variable. It is set to a new table on each table resize.
Tables tables = m_tables;
IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer = tables.m_comparer;
GetBucketAndLockNo(comparer.GetHashCode(key), out var bucketNo, out _, tables.m_buckets.Length, tables.m_locks.Length);
// We can get away w/out a lock here.
// The Volatile.Read ensures that the load of the fields of 'n' doesn't move before the load from buckets[i].
Node n = Volatile.Read(ref tables.m_buckets[bucketNo]);
while (n != null)
{
if (comparer.Equals(n.m_key, key))
{
value = n.m_value;
return true;
}
n = n.m_next;
}
value = default(TValue);
return false;
}
Remove
Remove方法实现其实也并不复杂,类似我们链表操作中移除某个Node.移除节点的同时,还要对前后节点进行链接,相信一块小伙伴们肯定很好理解.
private bool TryRemoveInternal(TKey key, out TValue value, bool matchValue, TValue oldValue)
{
while (true)
{
Tables tables = m_tables;
IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer = tables.m_comparer;
int bucketNo, lockNo;
GetBucketAndLockNo(comparer.GetHashCode(key), out bucketNo, out lockNo, tables.m_buckets.Length, tables.m_locks.Length);
lock (tables.m_locks[lockNo])
{
if (tables != m_tables)
continue;
Node prev = null;
for (Node curr = tables.m_buckets[bucketNo]; curr != null; curr = curr.m_next)
{
if (comparer.Equals(curr.m_key, key))
{
if (matchValue)
{
bool valuesMatch = EqualityComparer<TValue>.Default.Equals(oldValue, curr.m_value);
if (!valuesMatch)
{
value = default(TValue);
return false;
}
}
if (prev == null)
Volatile.Write(ref tables.m_buckets[bucketNo], curr.m_next);
else
{
prev.m_next = curr.m_next;
}
value = curr.m_value;
tables.m_countPerLock[lockNo]--;
return true;
}
prev = curr;
}
}
value = default(TValue);
return false;
}
}Grow table
当table中任何一个m_countPerLock的数量超过了设定的阈值后,会触发此操作对Table进行扩容.
private void GrowTable(Tables tables, IEqualityComparer<TKey> newComparer, bool regenerateHashKeys,
int rehashCount)
{
int locksAcquired = 0;
try
{
//首先锁住第一个lock进行resize操作.
AcquireLocks(0, 1, ref locksAcquired);
if (regenerateHashKeys && rehashCount == m_keyRehashCount)
{
tables = m_tables;
}
else
{
if (tables != m_tables)
return;
long approxCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tables.m_countPerLock.Length; i++)
{
approxCount += tables.m_countPerLock[i];
}
//如果bucket数组太空,则将预算加倍,而不是调整表的大小
if (approxCount < tables.m_buckets.Length / 4)
{
m_budget = 2 * m_budget;
if (m_budget < 0)
{
m_budget = int.MaxValue;
}
return;
}
}
int newLength = 0;
bool maximizeTableSize = false;
try
{
checked
{
newLength = tables.m_buckets.Length * 2 + 1;
while (newLength % 3 == 0 || newLength % 5 == 0 || newLength % 7 == 0)
{
newLength += 2;
}
}
}
catch (OverflowException)
{
maximizeTableSize = true;
}
if (maximizeTableSize)
{
newLength = int.MaxValue;
m_budget = int.MaxValue;
}
AcquireLocks(1, tables.m_locks.Length, ref locksAcquired);
object[] newLocks = tables.m_locks;
//Add more locks
if (m_growLockArray && tables.m_locks.Length < MAX_LOCK_NUMBER)
{
newLocks = new object[tables.m_locks.Length * 2];
Array.Copy(tables.m_locks, newLocks, tables.m_locks.Length);
for (int i = tables.m_locks.Length; i < newLocks.Length; i++)
{
newLocks[i] = new object();
}
}
Node[] newBuckets = new Node[newLength];
int[] newCountPerLock = new int[newLocks.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < tables.m_buckets.Length; i++)
{
Node current = tables.m_buckets[i];
while (current != null)
{
Node next = current.m_next;
int newBucketNo, newLockNo;
int nodeHashCode = current.m_hashcode;
if (regenerateHashKeys)
{
//Recompute the hash from the key
nodeHashCode = newComparer.GetHashCode(current.m_key);
}
GetBucketAndLockNo(nodeHashCode, out newBucketNo, out newLockNo, newBuckets.Length,
newLocks.Length);
newBuckets[newBucketNo] = new Node(current.m_key, current.m_value, nodeHashCode,
newBuckets[newBucketNo]);
checked
{
newCountPerLock[newLockNo]++;
}
current = next;
}
}
if (regenerateHashKeys)
{
unchecked
{
m_keyRehashCount++;
}
}
m_budget = Math.Max(1, newBuckets.Length / newLocks.Length);
m_tables = new Tables(newBuckets, newLocks, newCountPerLock, newComparer);
}
finally
{
ReleaseLocks(0, locksAcquired);
}
}
学习感悟
lock[]:在以往的线程安全上,我们对数据的保护往往是对数据的修改写入等地方加上lock,这个lock经常上整个上下文中唯一的,这样的设计下就可能会出现多个线程,写入的根本不是一块数据,却要等待前一个线程写入完成下一个线程才能继续操作.在ConcurrentDictionary中,通过哈希算法,从数组lock[]中找出key的准确lock,如果不同的key,使用的不是同一个lock,那么这多个线程的写入时互不影响的.写入要考虑线程安全,读取呢?不可否认,在大部分场景下,读取不必去考虑线程安全,但是在我们这样的链式读取中,需要自上而下地查找,是不是有种可能在查找个过程中,链路被修改了呢?所以ConcurrentDictionary中使用Volatile.Read来读取出数据,该方法从指定字段读取对象引用,在需要它的系统上,插入一个内存屏障,阻止处理器重新排序内存操作,如果在代码中此方法之后出现读取或写入,则处理器无法在此方法之前移动它。
在ConcurrentDictionary的更新方法中,对数据进行更新时,会判断该数据是否可以原子写入,如果时可以原子写入的,那么就直接更新数据,如果不是,那么会创建一个新的node覆盖原有node,起初看到这里时候,我百思不得其解,不知道这么操作的目的,后面在jeo duffy的博客中Thread-safety, torn reads, and the like中找到了答案,这样操作时为了防止torn reads(撕裂读取),什么叫撕裂读取呢?通俗地说,就是有的数据类型写入时,要分多次写入,写一次,移动一次指针,那么就有可能写了一半,这个结果被另外一个线程读取走了.比如说我把
刘振宇三个字改成周杰伦的过程中,我先改把刘改成周了,正在我准备去把振改成杰的时候,另外一个线程过来读取结果了,读到的数据是周振宇,这显然是不对的.所以对这种,更安全的做法是先把周杰伦三个字写好在一张纸条上,然后直接替换掉刘振宇.更多信息在CLI规范12.6.6有详细介绍.checked和unckecked关键字.非常量的运算(non-constant)运算在编译阶段和运行时下不会做溢出检查,如下这样的代码时不会抛出异常的,算错了也不会报错。
int ten = 10;
int i2 = 2147483647 + ten;但是我们知道,int的最大值是2147483647,如果我们将上面这样的代码嵌套在checked就会做溢出检查了.
checked
{
int ten = 10;
int i2 = 2147483647 + ten;
}相反,对于常量,编译时是会做溢出检查的,下面这样的代码在编译时就会报错的,如果我们使用unckeck标签进行标记,则在编译阶段不会做移除检查.
int a = int.MaxValue * 2;那么问题来了,我们当然知道checked很有用,那么uncheck呢?如果我们只是需要那么一个数而已,至于溢出不溢出的关系不大,比如说生成一个对象的HashCode,比如说根据一个算法计算出一个相对随机数,这都是不需要准确结果的,ConcurrentDictionary中对于m_keyRehashCount++这个运算就使用了unchecked,就是因为m_keyRehashCount是用来生成哈希值的,我们并不关心它有没有溢出.
volatile关键字,表示一个字段可能是由在同一时间执行多个线程进行修改。出于性能原因,编译器运行时系统甚至硬件可以重新排列对存储器位置的读取和写入。声明的字段volatile不受这些优化的约束。添加volatile修饰符可确保所有线程都能按照执行顺序由任何其他线程执行的易失性写入,易失性写入是一件疯狂的事情的事情:普通玩家慎用.
本博客锁涉及的代码都保存在github中,Take it easy to enjoy it!
https://github.com/liuzhenyulive/DictionaryMini/blob/master/DictionaryMini/DictionaryMini/ConcurrentDictionaryMini.cs
以上是关于ConsurrentDictionary并发字典知多少?的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章