《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15
Posted ky027wh-sx
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
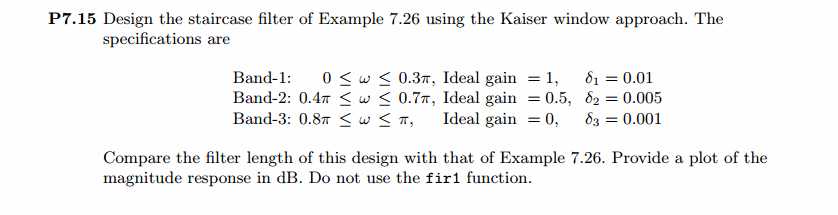
用Kaiser窗方法设计一个台阶状滤波器。
代码:
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output Info about this m-file fprintf(‘ *********************************************************** ‘); fprintf(‘ <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 7.15 ‘); banner(); %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ % staircase bandpass 3-Band w1 = 0; w2 = 0.3*pi; delta1 = 0.01; w3 = 0.4*pi; w4 = 0.7*pi; delta2 = 0.005; w5 = 0.8*pi; w6 = pi; delta3 = 0.001; tr_width = min(w3-w2, w5-w3); f = [0 w2 w3 w4 w5 w6]/pi; m = [1 1 0.5 0.5 0 0]; [Rp1, As1] = delta2db(delta1, delta3); [Rp2, As2] = delta2db(delta2, delta3); As = min(As1, As2) M = ceil((As-7.95)/(2.285*tr_width)) + 1; % Kaiser Window Length if As > 21 || As < 50 beta = 0.5842*(As-21)^0.4 + 0.07886*(As-21); else beta = 0.1102*(As-8.7); end fprintf(‘ Kaiser Window method, Filter Length: M = %d. beta = %.4f ‘, M, beta); n = [0:1:M-1]; wc1 = (w2+w3)/2; wc2 = (w4+w5)/2; %wc = (ws + wp)/2, % ideal LPF cutoff frequency hd = ideal_lp(wc1, M) + 0.5*(ideal_lp(wc2, M) - ideal_lp(wc1, M)); w_kai = (kaiser(M, beta))‘; h = hd .* w_kai; [db, mag, pha, grd, w] = freqz_m(h, [1]); delta_w = 2*pi/1000; [Hr,ww,P,L] = ampl_res(h); Rp1 = -(min(db(1 :1: w2/delta_w+1))); % Actual Passband Ripple fprintf(‘ Actual Passband Ripple1 is %.4f dB. ‘, Rp1); Rp2 = -(min(db(w3/delta_w+1 :1: w4/delta_w+1))); % Actual Passband Ripple fprintf(‘ Actual Passband Ripple2 is %.4f dB. ‘, Rp2); As = -round(max(db(floor(w5/delta_w)+1 : 1 : floor(w6/delta_w)+1 ))); % Min Stopband attenuation fprintf(‘ Min Stopband attenuation is %.4f dB. ‘, As); [delta1, delta3] = db2delta(Rp1, As) [delta2, delta3] = db2delta(Rp2, As) % Plot figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 7.15 ideal_lp Method‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,‘white‘); subplot(2,2,1); stem(n, hd); axis([0 M-1 -0.3 0.5]); grid on; xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘hd(n)‘); title(‘Ideal Impulse Response‘); subplot(2,2,2); stem(n, w_kai); axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); grid on; xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘w(n)‘); title(‘Kaiser Window‘); subplot(2,2,3); stem(n, h); axis([0 M-1 -0.3 0.5]); grid on; xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘h(n)‘); title(‘Actual Impulse Response‘); subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, db); axis([0 1 -120 10]); grid on; set(gca,‘YTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTick‘,[-90,-65,-6,0]); set(gca,‘YTickLabelMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTickLabel‘,[‘90‘;‘65‘;‘ 6‘;‘ 0‘]); set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[f]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Decibels‘); title(‘Magnitude Response in dB‘); figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 7.15 h(n) ideal_lp Method‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,‘white‘); subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi, db); grid on; axis([0 2 -120 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Decibels‘); title(‘Magnitude Response in dB‘); set(gca,‘YTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTick‘,[-90,-65,-6,0]) set(gca,‘YTickLabelMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTickLabel‘,[‘90‘;‘65‘;‘ 6‘;‘ 0‘]); set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[f,1+f(2:6)]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, mag); grid on; %axis([0 2 -100 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Absolute‘); title(‘Magnitude Response in absolute‘); set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[f,1+f(2:6)]); set(gca,‘YTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTick‘,[0,0.5, 1]) subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi, pha); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Rad‘); title(‘Phase Response in Radians‘); subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, grd*pi/180); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Rad‘); title(‘Group Delay‘); figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 7.15 Amp Res of h(n)‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,‘white‘); plot(ww/pi, Hr); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Hr‘); title(‘Amplitude Response‘); set(gca,‘YTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTick‘,[-delta3,0,delta3,0.5-0.005, 0.5+0.005,1-delta1,1,1+delta1]) %set(gca,‘YTickLabelMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTickLabel‘,[‘90‘;‘45‘;‘ 0‘]); set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[f,2]); %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% fir2 function method %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ f = [w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6]/pi; m = [1 1 0.5 0.5 0 0]; ripple = [0.01 0.005 0.001]; fprintf(‘ --------- use fir2 function --------- ‘); h_check = fir2(M-1, f, m, kaiser(M, beta)); [db, mag, pha, grd, w] = freqz_m(h_check, [1]); %[Hr,ww,P,L] = ampl_res(h_check); [Hr,ww,P,L] = Hr_Type2(h_check); %% ------------------------------------------- %% plot %% ------------------------------------------- figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 7.15 fir2 Method‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,‘white‘); subplot(2,2,1); stem(n, hd); axis([0 M-1 -0.3 0.5]); grid on; xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘hd(n)‘); title(‘Ideal Impulse Response‘); subplot(2,2,2); stem(n, w_kai); axis([0 M-1 0 1.1]); grid on; xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘w(n)‘); title(‘Kaiser Window‘); subplot(2,2,3); stem([0:M-1], h_check); axis([0 M -0.3 0.5]); grid on; set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[0 M/2 M]); xlabel(‘n‘); ylabel(‘h\\_check(n)‘); title(‘Actual Impulse Response‘); subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, db); axis([0 1 -120 10]); grid on; set(gca,‘YTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTick‘,[-90,-65,-6,0]); set(gca,‘YTickLabelMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTickLabel‘,[‘90‘;‘65‘;‘ 6‘;‘ 0‘]); set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[f]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Decibels‘); title(‘Magnitude Response in dB‘); figure(‘NumberTitle‘, ‘off‘, ‘Name‘, ‘Problem 7.15 h_check(n) fir2 Method‘) set(gcf,‘Color‘,‘white‘); subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi, db); grid on; axis([0 2 -120 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Decibels‘); title(‘Magnitude Response in dB‘); set(gca,‘YTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTick‘,[-90,-65,-6,0]) set(gca,‘YTickLabelMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTickLabel‘,[‘90‘;‘65‘;‘ 6‘;‘ 0‘]); set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[f,1+f(2:6)]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, mag); grid on; %axis([0 2 -100 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Absolute‘); title(‘Magnitude Response in absolute‘); set(gca,‘XTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘XTick‘,[f,1+f(2:6)]); set(gca,‘YTickMode‘,‘manual‘,‘YTick‘,[0,0.5, 1]) subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi, pha); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Rad‘); title(‘Phase Response in Radians‘); subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, grd*pi/180); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]); xlabel(‘frequency in pi units‘); ylabel(‘Rad‘); title(‘Group Delay‘);
运行结果:
Kaiser窗长M=74,两个通带衰减分别为0.0079dB和6.0345dB,阻带最小衰减65dB>60dB,满足设计要求。
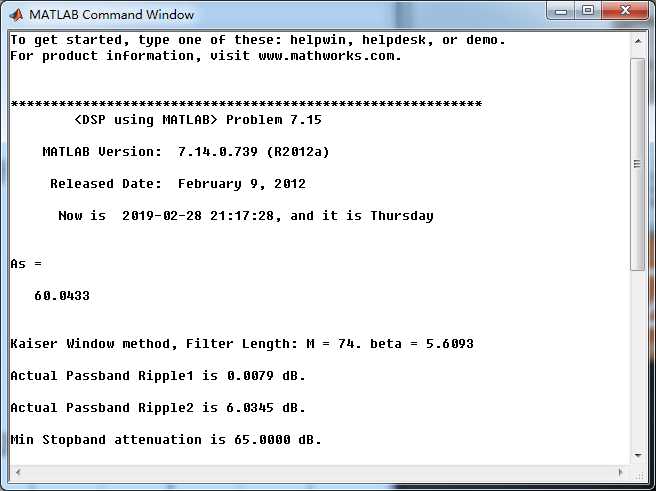
用理想低通滤波方法设计的结果,实际脉冲响应、幅度谱(dB单位)
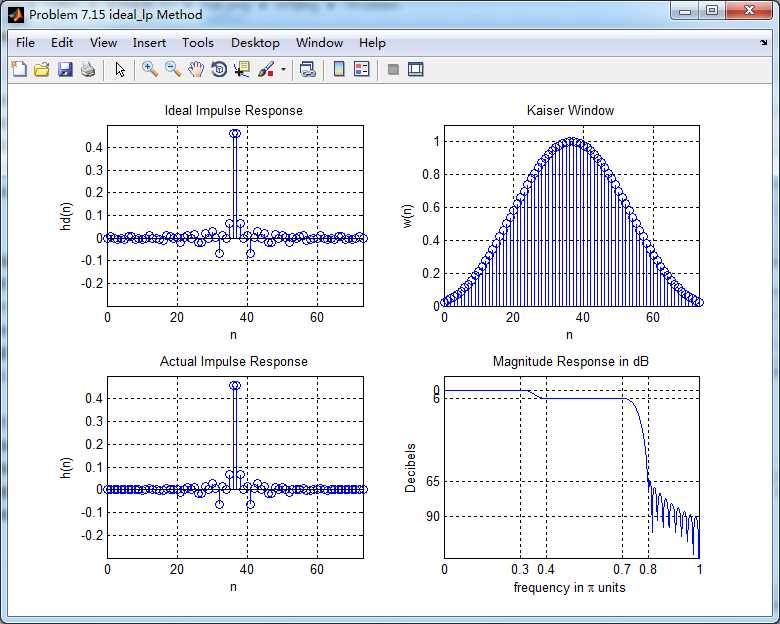
幅度谱(dB和绝对单位)、相位谱和群延迟响应
振幅响应(台阶状)
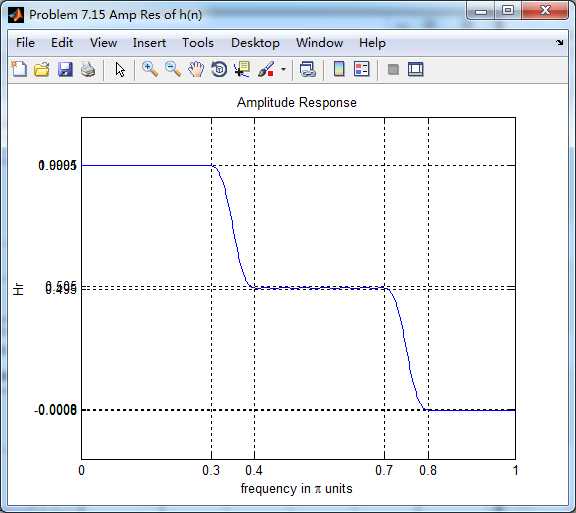
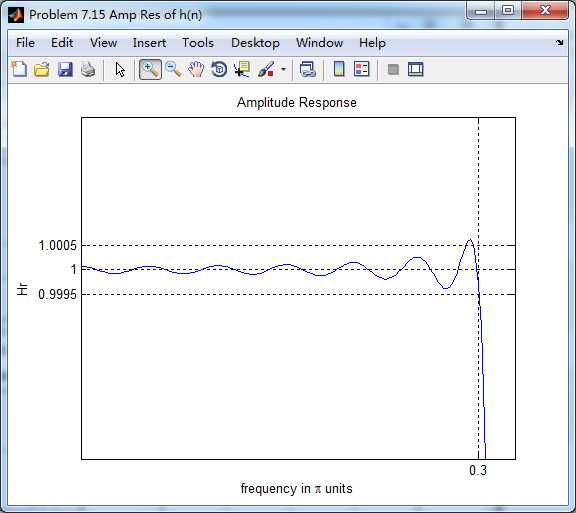
第一个台阶(通带)
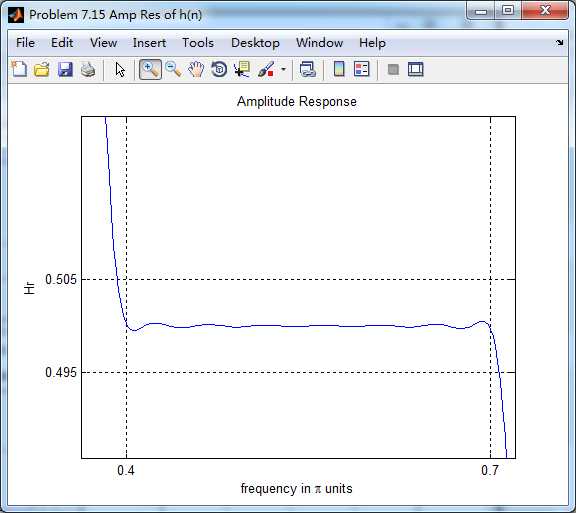
第二个台阶(通带)
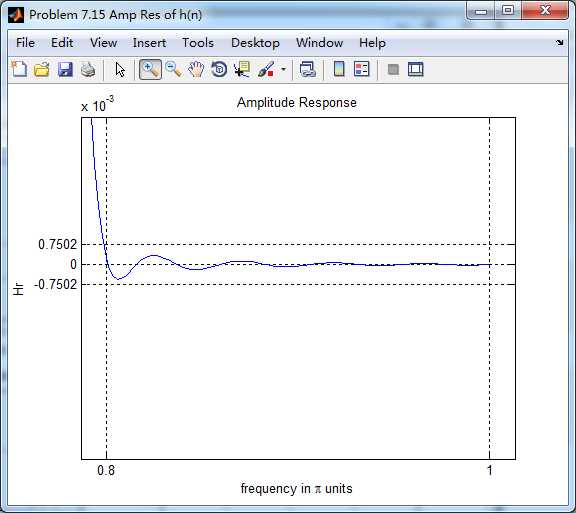
阻带
题目中暗示可以用fir1函数,但查了帮助和网上资料还是不会,只好用fir2函数的方法来设计,结果如下:
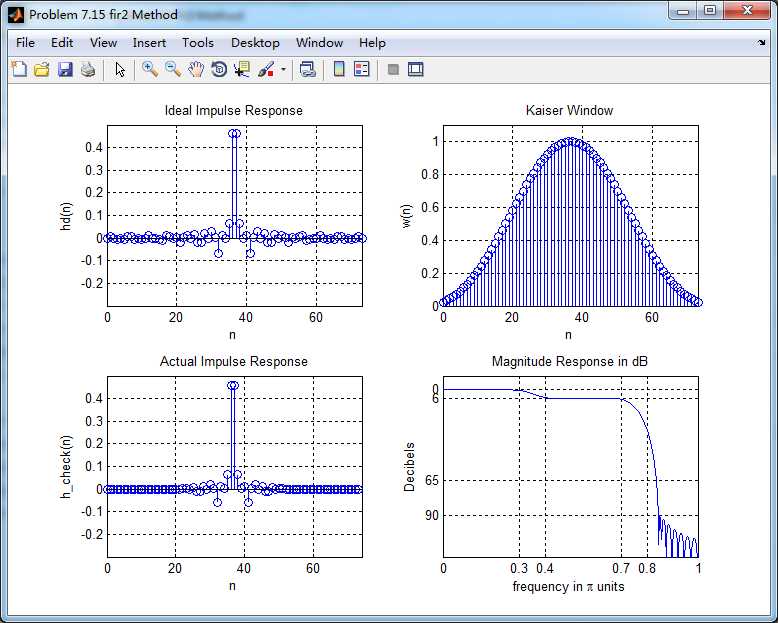
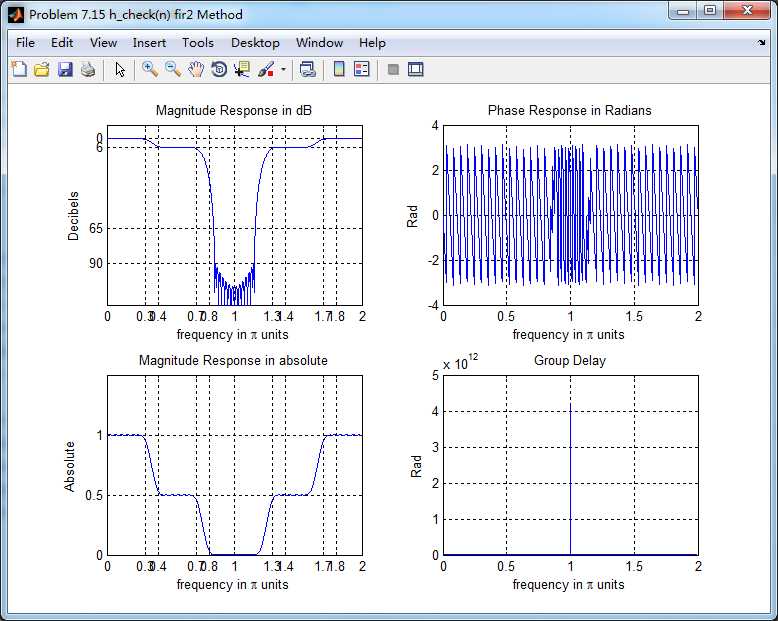
群延迟不是严格的常数了,非线性相位滤波器。
以上是关于《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.15的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章