暖*墟#网络流# 最大权闭合子图
Posted floraloveryuuji
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了暖*墟#网络流# 最大权闭合子图相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【相关概念详解】
闭合图:有向图的一个点集,且这个点集的所有出边仍然指向该点集。
最大权闭合图:(每一个点有一个权值)在所有的合法闭合图中,点权之和最大的图。
处理问题:权值有正有负,重复选只算一次,选择有相互关联性 的问题。
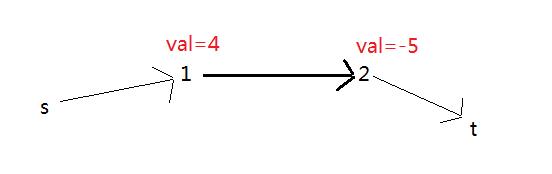
首先有一个有向连通图(闭合图),每个点带有一个权值,例如:
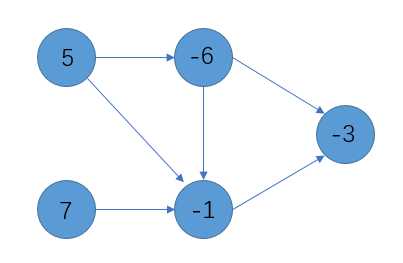
造出一个超级源点S和一个超级汇点T,把S连边到所有带有正权的点上,每条边的容量是这个点的权;
把所有带负权的点连边到T,每条边的容量是这个点的权的相反数(正值)。原来的边的容量设成无限大。
所有的点按权值的正负连接到s和t上,转换成一个边权值有向图。
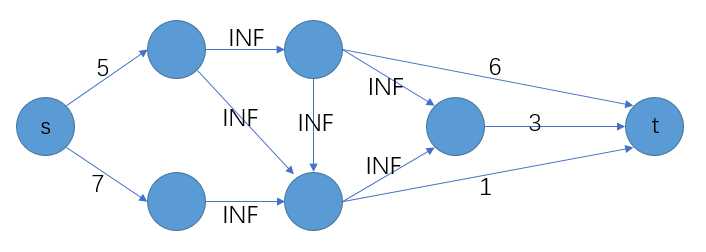
最大权闭合图的最大权 = 所有正权值之和 — 最小割容量(最大流的值) 。
步骤归纳:1. 建立超级源点s,超级汇点t。
2. 所有点权为正数的点i,建边 s->i,容量为(正)点权。
3. 所有点权为负数的点i,建边i->t,容量为(负)点权绝对值。
4. 原图建图后,(互相关联影响的)边容量设为正无穷。
5.最大权闭合图的权值 = 正权点之和 - (s->t)最大流。
建图方法的推导
源点s可以理解为最大可获得的权值(即正权点之和)。
汇点t可以理解为最大的会损失的权值(负权点之和)。
我们现在要尽量的获得s,而避免t。
想选出最大权闭合图,则如果选定一个点,这个点的所有后继子孙点都必须选择。
因此,想拿正数,就不可避免的要取负数子孙后继点。
所以:要尽量选择正权点为起点,才有可能增大闭合图点集的权值和。
因此,我们从源点s向正权点连边(即只以正权点为起点)。
至于过程中遇到的负权点,我们让其流向t,即建立边 负权点->t的意图。
好,现在我们尽量去取正数点(直接从源点s起始),过程中遇到的负权点流向t。
现在就变成了:s->t的流量就是我们的损失。
即:我们希望流向t的流量flow尽量少,而从s流出的流量sum尽量多,
从s流出而没有流入t的流量(sum-flow)就是闭合图的最大权。
可能有种情况很懵逼:
若要选点,选2吧,权为-5;选1和2吧,权为-1;不如选空集,权为0。明显最后的选择是对的。
但按照上面的思路,从s流出4,所以损失最多为4,sum-flow=0。
所以对该图就产生这么一种结论:
选择1号点,和不选1号点,结果是相同的,我选的时候他会被损失完,效果等同于不选。
那不妨我一开始就把所有的正权点都给选了(满足从s流出的最多),让他们往后代流,
大不了被负权子孙点损失完,而那些没有被损失完的,就是我们统计下来的结果。
那个损失,就是s->t的最大流。于是得证:闭合图最大权 = 正权和sum - 最大流flow。
【例题1】【p4174】最大获利

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<map> #include<vector> #include<cmath> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; /*【p4174】最大获利 n个中转站,第i个的建立成本为pi。M个用户:ai与bi通讯,获利ci。 ---> 求净获利最大。(净获利=获益之和–投入成本之和)*/ //【标签】网络流 + 最大权闭合子图 /*【分析】注意,‘用户’和‘中转站’是两种东西,不能混淆。*/ void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int fx=1;x=0;char ch_=getchar(); while(ch_<‘0‘||ch_>‘9‘){if(ch_==‘-‘)fx=-1;ch_=getchar();} while(ch_>=‘0‘&&ch_<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch_-‘0‘;ch_=getchar();} x*=fx; //正负号 } const int N=1000019,inf=0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m,s,t,tot=-1,head[N],dep[N],sum=0; struct node{ int nextt,ver,w; }e[N]; void add(int x,int y,int z) //正向边权值为1,反向边权值为0 { e[++tot].ver=y,e[tot].nextt=head[x],e[tot].w=z,head[x]=tot; e[++tot].ver=x,e[tot].nextt=head[y],e[tot].w=0,head[y]=tot; } int bfs(){ memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep)); //dep记录深度 queue<int> q; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); dep[s]=1; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ int u=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].nextt) if((e[i].w>0)&&(dep[e[i].ver]==0)) //分层 dep[e[i].ver]=dep[u]+1,q.push(e[i].ver); } if(dep[t]!=0) return 1; else return 0; //此时不存在分层图也不存在增广路 } int dfs(int u,int lastt){ int ans=0; if(u==t) return lastt; //lastt:此点还剩余的流量 for(int i=head[u];i!=-1&&ans<lastt;i=e[i].nextt) if((dep[e[i].ver]==dep[u]+1)&&(e[i].w!=0)){ int f=dfs(e[i].ver,min(lastt-ans,e[i].w)); if(f>0){ e[i].w-=f,e[i^1].w+=f,ans+=f; } } if(ans<lastt) dep[u]=-1; return ans; } int dinic(){ int ans=0; while(bfs()) ans+=dfs(s,1<<30); return ans; } int main(){ reads(n),reads(m); s=0,t=n+m+1; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(int i=1,pi;i<=n;i++) reads(pi),add(i+m,t,pi); //编号点---T(相当于负权点) for(int i=1,ai,bi,ci;i<=m;i++){ reads(ai),reads(bi),reads(ci); sum+=ci; add(s,i,ci),add(i,ai+m,inf),add(i,bi+m,inf); } printf("%d ",sum-dinic()); return 0; //↑↑把每个用户与两个中转站相连 }
【例题2】【p3749】寿司餐厅

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<map> #include<vector> #include<cmath> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; /*【p3749】寿司餐厅 */ //【标签】网络流 + 最大权闭合子图 + 读题/细节处理 /* 1. n<=2,种数只有 {不选}{1}{2}{1,2}{1;2} 10pts。 2. 60%数据m=0,即支出=∑每个代号吃了的种类数*代号。 */ /*【分析】感觉有点像网络流但我不会写0.0 最大权闭合子图。 日常%GXZ https://www.cnblogs.com/GXZlegend/p/6795784.html 对于每个点(i,j)(j>i),如果它被选择,那么点(i,j-1)和点(i+1,j)也一定被选择。 由此建点权图。对于点(i,j)(j>i),点权为d[i][j],并向点(i,j-1)和点(i+1,j)连边。 对于点(i,i),点权为d[i][i]-a[i](收益减去费用),并向编号a[i]连边。 对于编号p,点权为-m*p*p。所求为最大权闭合图,所以转化为网络流最小割来求。 最后的答案 : 闭合图最大权 = 正权和sum - 最大流flow。*/ void reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int fx=1;x=0;char ch_=getchar(); while(ch_<‘0‘||ch_>‘9‘){if(ch_==‘-‘)fx=-1;ch_=getchar();} while(ch_>=‘0‘&&ch_<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch_-‘0‘;ch_=getchar();} x*=fx; //正负号 } const int N=50019,inf=0x3f3f3f3f; int a[N],d[110][110],id[110][110],cnt_; int s,t,tot=-1,n1,n2,n3,head[N],dep[N]; //s为源点,t为汇点 struct node{ int nextt,ver,w; }e[N]; void add(int x,int y,int z) //正向边权值为1,反向边权值为0 { e[++tot].ver=y,e[tot].nextt=head[x],e[tot].w=z,head[x]=tot; e[++tot].ver=x,e[tot].nextt=head[y],e[tot].w=0,head[y]=tot; } int bfs(){ memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep)); //dep记录深度 queue<int> q; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); dep[s]=1; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ int u=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].nextt) if((e[i].w>0)&&(dep[e[i].ver]==0)) //分层 dep[e[i].ver]=dep[u]+1,q.push(e[i].ver); } if(dep[t]!=0) return 1; else return 0; //此时不存在分层图也不存在增广路 } int dfs(int u,int lastt){ int ans=0; if(u==t) return lastt; //lastt:此点还剩余的流量 for(int i=head[u];i!=-1&&ans<lastt;i=e[i].nextt) if((dep[e[i].ver]==dep[u]+1)&&(e[i].w!=0)){ int f=dfs(e[i].ver,min(lastt-ans,e[i].w)); if(f>0){ e[i].w-=f,e[i^1].w+=f,ans+=f; } } if(ans<lastt) dep[u]=-1; return ans; } int main(){ int n,m,k=0,sum=0; reads(n),reads(m); memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); //死也会忘记的... for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) reads(a[i]),k=max(k,a[i]); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=i;j<=n;j++) reads(d[i][j]),id[i][j]=++cnt_; s=0,t=cnt_+k+1; //cnt_个d(i,j),k种编号 for(int i=1;i<=k;i++) add(cnt_+i,t,m*i*i); //↑↑k种编号向汇点连边(便于处理最后的m*x^2) 利用线性的‘互相影响’关系 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) add(id[i][i],cnt_+a[i],inf), d[i][i]-=a[i]; //点权-a[i](费用),向编号点a[i]连边 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) for(int j=i;j<=n;j++){ //最大全闭合子图的建边 if(d[i][j]>0) add(s,id[i][j],d[i][j]),sum+=d[i][j]; //正权 if(d[i][j]<0) add(id[i][j],t,-d[i][j]); //负权,向T建立全值为绝对值的边 if(j>i) add(id[i][j],id[i][j-1],inf),add(id[i][j],id[i+1][j],inf); } //↑↑处理相关联有影响的性质:(i,j) -> (i,j-1)、(i+1,j) while(bfs()) sum-=dfs(s,inf); printf("%d ",sum); }
【例题3】【p2762】太空飞行问题

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<map> #include<vector> #include<cmath> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; //【p2762】太空飞行问题 // 网络流 + 最大权闭合子图 + 读入方式 /*【分析】S - m个实验 - n个仪器 - T */ const int N=1000019,inf=0x3f3f3f3f; int n,m,s,t,tot=-1,head[N],dep[N],sum=0,flag=0; int reads(int &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) int fx=1;x=0;char ch_=getchar(); while(ch_<‘0‘||ch_>‘9‘){if(ch_==‘-‘)fx=-1;ch_=getchar();} while(ch_>=‘0‘&&ch_<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch_-‘0‘;ch_=getchar();} x*=fx; return ch_==‘ ‘||ch_==‘ ‘?0:1; //十分厉害的读入... } struct node{ int nextt,ver,w; }e[N]; void add(int x,int y,int z) //正向边权值为1,反向边权值为0 { e[++tot].ver=y,e[tot].nextt=head[x],e[tot].w=z,head[x]=tot; e[++tot].ver=x,e[tot].nextt=head[y],e[tot].w=0,head[y]=tot; } int bfs(){ memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep)); //dep记录深度 queue<int> q; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); dep[s]=1; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ int u=q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].nextt) if((e[i].w>0)&&(dep[e[i].ver]==0)) //分层 dep[e[i].ver]=dep[u]+1,q.push(e[i].ver); } if(dep[t]!=0) return 1; else return 0; //此时不存在分层图也不存在增广路 } int dfs(int u,int lastt){ int ans=0; if(u==t) return lastt; //lastt:此点还剩余的流量 for(int i=head[u];i!=-1&&ans<lastt;i=e[i].nextt) if((dep[e[i].ver]==dep[u]+1)&&(e[i].w!=0)){ int f=dfs(e[i].ver,min(lastt-ans,e[i].w)); if(f>0){ e[i].w-=f,e[i^1].w+=f,ans+=f; } } if(ans<lastt) dep[u]=-1; return ans; } int dinic(){ int ans=0; while(bfs()) ans+=dfs(s,1<<30); return ans; } int main(){ reads(m),reads(n); s=0,t=n+m+1; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(int i=1,pi,ai;i<=m;i++){ flag=reads(pi),sum+=pi,add(s,i,pi); while(flag) flag=reads(ai),add(i,ai+m,inf); } for(int i=1,ci;i<=n;i++) reads(ci),add(i+m,t,ci); //费用点---T int ans=sum-dinic(); //最大权闭合子图的最大权 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) if(dep[i]>0) cout<<i<<" "; printf(" "); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(dep[i+m]>0) cout<<i<<" "; printf(" "); printf("%d ",ans); //最大权闭合子图的最大权 }
【例题4】【poj2987】Fireing

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<map> #include<vector> #include<cmath> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; //【poj2987】Firing // 网络流 + 最大权闭合子图 /* 炒掉一个人能够获得b收益(b可以<0),但必须炒掉他的下属。求最大收益和此时最小裁员。 */ //【分析】把u是v的上司变成u—>v,运行最大权闭合子图 const ll N=1000019,inf=0x3f3f3f3f; ll n,m,s,t,tot=-1,head[N],dep[N]; ll sum=0; void reads(ll &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) ll fx=1;x=0;char ch_=getchar(); while(ch_<‘0‘||ch_>‘9‘){if(ch_==‘-‘)fx=-1;ch_=getchar();} while(ch_>=‘0‘&&ch_<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch_-‘0‘;ch_=getchar();} x*=fx; //正负号 } struct node{ ll nextt,ver,w; }e[N]; void add(ll x,ll y,ll z) //正向边权值为1,反向边权值为0 { e[++tot].ver=y,e[tot].nextt=head[x],e[tot].w=z,head[x]=tot; e[++tot].ver=x,e[tot].nextt=head[y],e[tot].w=0,head[y]=tot; } ll bfs(){ memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep)); //dep记录深度 queue<ll> q; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); dep[s]=1; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ ll u=q.front(); q.pop(); for(ll i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].nextt) if((e[i].w>0)&&(dep[e[i].ver]==0)) //分层 dep[e[i].ver]=dep[u]+1,q.push(e[i].ver); } if(dep[t]!=0) return 1; else return 0; //此时不存在分层图也不存在增广路 } ll dfs(ll u,ll lastt){ ll ans=0; if(u==t) return lastt; //lastt:此点还剩余的流量 for(ll i=head[u];i!=-1&&ans<lastt;i=e[i].nextt) if((dep[e[i].ver]==dep[u]+1)&&(e[i].w!=0)){ ll f=dfs(e[i].ver,min(lastt-ans,e[i].w)); if(f>0){ e[i].w-=f,e[i^1].w+=f,ans+=f; } } if(ans<lastt) dep[u]=-1; return ans; } ll dinic(){ ll ans=0; while(bfs()) ans+=dfs(s,1<<30); return ans; } bool vis[N]; ll get_(ll u){ ll ans=1; vis[u]=1; //要删去的所有人:e[i].w>0 for(ll i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].nextt) { ll v=e[i].ver; if(e[i].w>0&&!vis[v]) ans+=get_(v); } return ans; } int main(){ reads(n),reads(m); s=0,t=n+1; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(ll i=1,bi;i<=n;i++){ reads(bi); if(bi>0) sum+=bi,add(s,i,bi); else add(i,t,-bi); } for(ll i=1,a,b;i<=m;i++) reads(a),reads(b),add(a,b,inf); //限制关系 ll ans=sum-dinic(); //最大权闭合子图的最大权 printf("%lld %lld ",get_(s)-1,ans); //最大权闭合子图的最大权 }

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<queue> #include<map> #include<vector> #include<cmath> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; //【poj2987】Firing // 网络流 + 最大权闭合子图 /* 炒掉一个人能够获得b收益(b可以<0),但必须炒掉他的下属。求最大收益和此时最小裁员。 */ //【分析】把u是v的上司变成u—>v,运行最大权闭合子图 const ll N=1000019,inf=0x3f3f3f3f; ll n,m,s,t,tot=-1,head[N],dep[N]; ll sum=0; void reads(ll &x){ //读入优化(正负整数) ll fx=1;x=0;char ch_=getchar(); while(ch_<‘0‘||ch_>‘9‘){if(ch_==‘-‘)fx=-1;ch_=getchar();} while(ch_>=‘0‘&&ch_<=‘9‘){x=x*10+ch_-‘0‘;ch_=getchar();} x*=fx; //正负号 } struct node{ ll nextt,ver,w; }e[N]; void add(ll x,ll y,ll z) //正向边权值为1,反向边权值为0 { e[++tot].ver=y,e[tot].nextt=head[x],e[tot].w=z,head[x]=tot; e[++tot].ver=x,e[tot].nextt=head[y],e[tot].w=0,head[y]=tot; } ll bfs(){ memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep)); //dep记录深度 queue<ll> q; while(!q.empty()) q.pop(); dep[s]=1; q.push(s); while(!q.empty()){ ll u=q.front(); q.pop(); for(ll i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].nextt) if((e[i].w>0)&&(dep[e[i].ver]==0)) //分层 dep[e[i].ver]=dep[u]+1,q.push(e[i].ver); } if(dep[t]!=0) return 1; else return 0; //此时不存在分层图也不存在增广路 } ll dfs(ll u,ll lastt){ ll ans=0; if(u==t) return lastt; //lastt:此点还剩余的流量 for(ll i=head[u];i!=-1&&ans<lastt;i=e[i].nextt) if((dep[e[i].ver]==dep[u]+1)&&(e[i].w!=0)){ ll f=dfs(e[i].ver,min(lastt-ans,e[i].w)); if(f>0){ e[i].w-=f,e[i^1].w+=f,ans+=f; } } if(ans<lastt) dep[u]=-1; return ans; } ll dinic(){ ll ans=0; while(bfs()) ans+=dfs(s,1<<30); return ans; } int main(){ reads(n),reads(m); s=0,t=n+1; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); for(ll i=1,bi;i<=n;i++){ reads(bi); if(bi>0) sum+=bi,add(s,i,bi); else add(i,t,-bi); } for(ll i=1,a,b;i<=m;i++) reads(a),reads(b),add(a,b,inf); //限制关系 ll ans=sum-dinic(),ans_=0; //最大权闭合子图的最大权 for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++) if(dep[i]>0) ans_++; printf("%lld %lld ",ans_,ans); //最大权闭合子图的最大权 }
相关资料补充:https://www.cnblogs.com/dilthey/p/7565206.html
——时间划过风的轨迹,那个少年,还在等你。
以上是关于暖*墟#网络流# 最大权闭合子图的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章