算法进阶面试题05——树形dp解决步骤返回最大搜索二叉子树的大小二叉树最远两节点的距离晚会最大活跃度手撕缓存结构LRU
Posted xieyupeng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了算法进阶面试题05——树形dp解决步骤返回最大搜索二叉子树的大小二叉树最远两节点的距离晚会最大活跃度手撕缓存结构LRU相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
接着第四课的内容,加入部分第五课的内容,主要介绍树形dp和LRU
第一题:
给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,请返回最大搜索二叉子树的大小
二叉树的套路
统一处理逻辑:假设以每个节点为头的这棵树,他的最大搜索二叉子树是什么。答案一定在其中
第一步,列出可能性(最难部分)
1、可能来自左子树上的某课子树
2、可能来自右子树上的某课子树
3、整颗都是(左右子树都是搜索二叉树并且左子树最大小于该节点,右子树最小大于该节点)
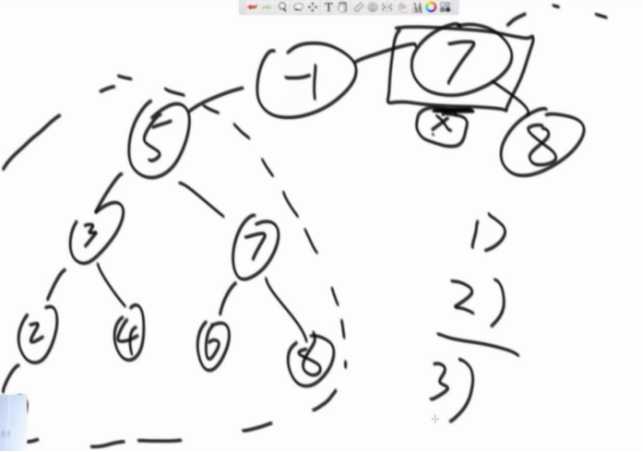
第二步,收集信息:
1、左树最大搜索子树大小
2、右树最大搜索子树大小
3、左树最大二叉搜索子树的头部(通过查看这个头部是否等于节点的左孩子,来判断整个左子树是否都是二叉搜索树)
4、右树最大二叉搜索子树的头部
5、左树最大值
6、右树最小值
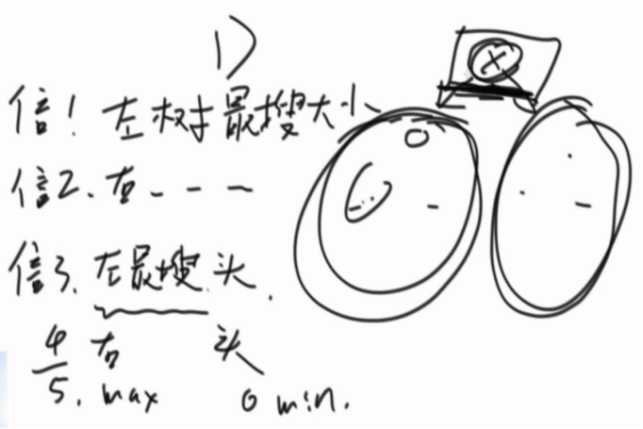
化简为一个信息体:
1、左/右搜大小
2、左/右搜头
3、左max
4、右min
不管左树还是右树都存储
1、最大搜索子树大小
2、最大搜索子树的头部
3、这棵树上的最大值和最小值
如果不理解可以看引子题(很简单的)
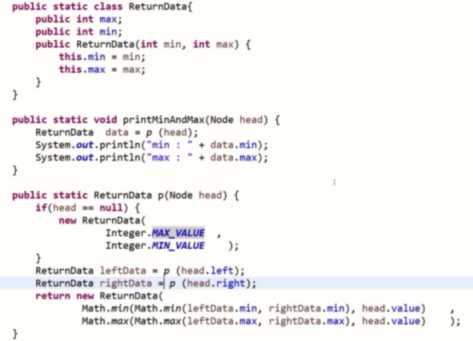
一棵树中找最大最小
第三步,改递归(比较复杂)
先假设左和右都给我这样的信息了,然后怎么利用左边和右边的信息,组出来我该返回的信息。最后baseKey填什么,搞定!
public class Code_04_BiggestSubBSTInTree { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static Node biggestSubBST(Node head) { int[] record = new int[3]; // 0->size, 1->min, 2->max return posOrder(head, record); } public static class ReturnType{ public int size; public Node head; public int min; public int max; public ReturnType(int a, Node b,int c,int d) { this.size =a; this.head = b; this.min = c; this.max = d; } } public static ReturnType process(Node head) { if(head == null) { //设置系统最大最小为了不干扰判断最大最小的决策 return new ReturnType(0,null,Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE); } Node left = head.left; ReturnType leftSubTressInfo = process(left);//当成一个黑盒 Node right = head.right; ReturnType rightSubTressInfo = process(right); int includeItSelf = 0; if(leftSubTressInfo.head == left &&rightSubTressInfo.head == right && head.value > leftSubTressInfo.max && head.value < rightSubTressInfo.min ) { includeItSelf = leftSubTressInfo.size + 1 + rightSubTressInfo.size; } int p1 = leftSubTressInfo.size; int p2 = rightSubTressInfo.size; //解黑盒的过程 int maxSize = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), includeItSelf); Node maxHead = p1 > p2 ? leftSubTressInfo.head : rightSubTressInfo.head; if(maxSize == includeItSelf) { maxHead = head; } return new ReturnType(maxSize, maxHead, Math.min(Math.min(leftSubTressInfo.min,rightSubTressInfo.min),head.value), Math.max(Math.max(leftSubTressInfo.max,rightSubTressInfo.max),head.value)); } //数组实现版本 public static Node posOrder(Node head, int[] record) { if (head == null) { record[0] = 0; record[1] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; record[2] = Integer.MIN_VALUE; return null; } int value = head.value; Node left = head.left; Node right = head.right; Node lBST = posOrder(left, record); int lSize = record[0]; int lMin = record[1]; int lMax = record[2]; Node rBST = posOrder(right, record); int rSize = record[0]; int rMin = record[1]; int rMax = record[2]; record[1] = Math.min(rMin, Math.min(lMin, value)); // lmin, value, rmin -> min record[2] = Math.max(lMax, Math.max(rMax, value)); // lmax, value, rmax -> max if (left == lBST && right == rBST && lMax < value && value < rMin) { record[0] = lSize + rSize + 1; return head; } record[0] = Math.max(lSize, rSize); return lSize > rSize ? lBST : rBST; } // for test -- print tree public static void printTree(Node head) { System.out.println("Binary Tree:"); printInOrder(head, 0, "H", 17); System.out.println(); } public static void printInOrder(Node head, int height, String to, int len) { if (head == null) { return; } printInOrder(head.right, height + 1, "v", len); String val = to + head.value + to; int lenM = val.length(); int lenL = (len - lenM) / 2; int lenR = len - lenM - lenL; val = getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR); System.out.println(getSpace(height * len) + val); printInOrder(head.left, height + 1, "^", len); } public static String getSpace(int num) { String space = " "; StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer(""); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { buf.append(space); } return buf.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(6); head.left = new Node(1); head.left.left = new Node(0); head.left.right = new Node(3); head.right = new Node(12); head.right.left = new Node(10); head.right.left.left = new Node(4); head.right.left.left.left = new Node(2); head.right.left.left.right = new Node(5); head.right.left.right = new Node(14); head.right.left.right.left = new Node(11); head.right.left.right.right = new Node(15); head.right.right = new Node(13); head.right.right.left = new Node(20); head.right.right.right = new Node(16); printTree(head); Node bst = biggestSubBST(head); printTree(bst); } }
第二题,继续套路:
二叉树中,一个节点可以往上走和往下走,那么从节点A总能走到节点B。
节点A走到节点B的距离为:A走到B最短路径上的节点个数。
求一棵二叉树上的最远距离
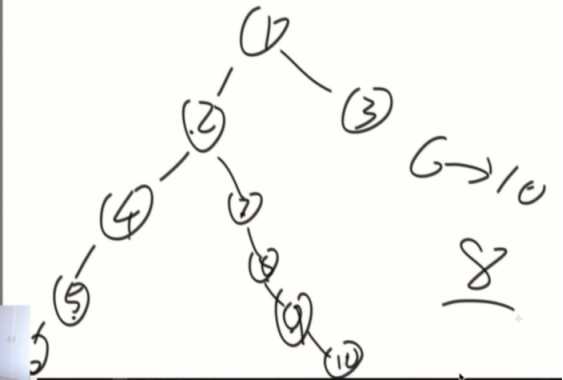
列可能性:
1、来自左子树最长距离
2、来自右子树最长距离
3、经过X的情况下的最远距离,左树最深+右树最深+1
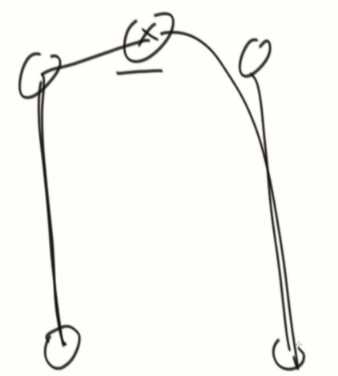
收集信息:
1、最长距离
2、深度
public class Code_03_MaxDistanceInTree { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static int maxDistance(Node head) { int[] record = new int[1]; return posOrder(head, record); } public static class ReturnType{ public int maxDistance; public int h; public ReturnType(int m, int h) { this.maxDistance = m; this.h = h; } } public static ReturnType process(Node head) { if(head == null) { return new ReturnType(0,0); } ReturnType leftReturnType = process(head.left); ReturnType rightReturnType = process(head.right); int includeHeadDistance = leftReturnType.h + 1 + rightReturnType.h; int p1 = leftReturnType.maxDistance; int p2 = rightReturnType.maxDistance; int resultDistance = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), includeHeadDistance); int hitSelf = Math.max(leftReturnType.h, leftReturnType.h) + 1; return new ReturnType(resultDistance, hitSelf); } public static int posOrder(Node head, int[] record) { if (head == null) { record[0] = 0; return 0; } int lMax = posOrder(head.left, record); int maxFromLeft = record[0]; int rMax = posOrder(head.right, record); int maxFromRight = record[0]; int curNodeMax = maxFromLeft + maxFromRight + 1; record[0] = Math.max(maxFromLeft, maxFromRight) + 1; return Math.max(Math.max(lMax, rMax), curNodeMax); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head1 = new Node(1); head1.left = new Node(2); head1.right = new Node(3); head1.left.left = new Node(4); head1.left.right = new Node(5); head1.right.left = new Node(6); head1.right.right = new Node(7); head1.left.left.left = new Node(8); head1.right.left.right = new Node(9); System.out.println(maxDistance(head1)); Node head2 = new Node(1); head2.left = new Node(2); head2.right = new Node(3); head2.right.left = new Node(4); head2.right.right = new Node(5); head2.right.left.left = new Node(6); head2.right.right.right = new Node(7); head2.right.left.left.left = new Node(8); head2.right.right.right.right = new Node(9); System.out.println(maxDistance(head2)); } }
扩充:如果是计算两个固定节点a~b的距离,需要找出他们的最近公共祖先,然后计算a~公共祖先+b~公共祖先。
第三题
一个公司的上下节关系是一棵多叉树,这个公司要举办晚会,你作为组织者已经摸清了大家的心理:一个员工的直接上级如果到场,这个员工肯定不会来。每个员工都有一个活跃度的值,决定谁来你会给这个员工发邀请函,怎么让舞会的气氛最活跃?返回最大的活跃值。
举例:
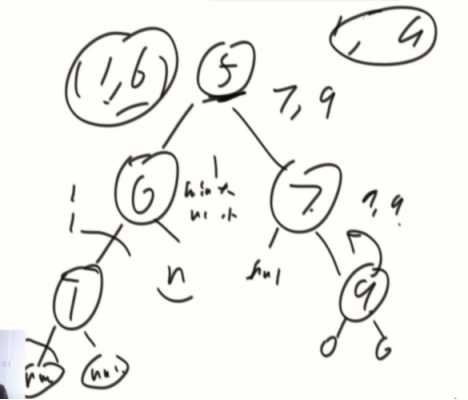
给定一个矩阵来表述这种关系
matrix =
{
1,6
1,5
1,4
}
这个矩阵的含义是:
matrix[0] = {1 , 6},表示0这个员工的直接上级为1,0这个员工自己的活跃度为6
matrix[1] = {1 , 5},表示1这个员工的直接上级为1(他自己是这个公司的最大boss),1这个员工自己的活跃度为5
matrix[2] = {1 , 4},表示2这个员工的直接上级为1,2这个员工自己的活跃度为4
为了让晚会活跃度最大,应该让1不来,0和2来。最后返回活跃度为10
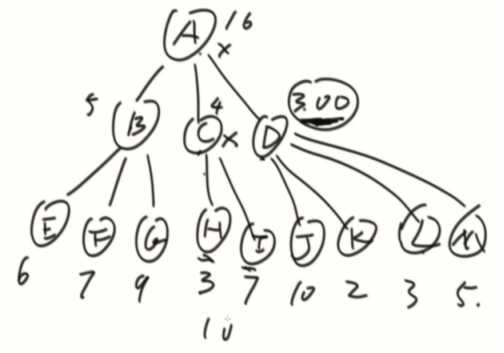
可能性
1、X来,活跃度就是x活跃度+x1不来+x2不来+x3不来的总和。
2、X不来,活跃度就是x1/x2/x3来和不来中选最大的总和。
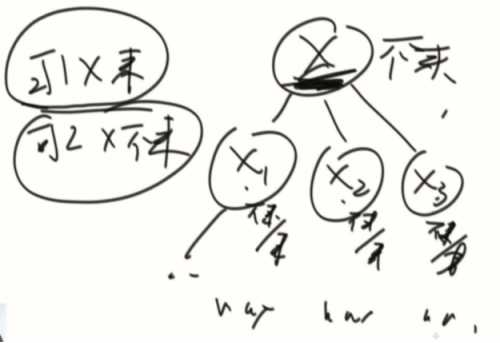
收集信息:
1、一棵树在头结点来的活跃度
2、一棵树在头结点不来的活跃度
public class Code_04_MaxHappy { public static class Node{ public int happy; public ArrayList<Node> nexts; public Node(int happy){ this.happy = happy; nexts = new ArrayList<Node>(); } } public static class ReturnData{ public int comeHappy; public int notComeHappy; public ReturnData(int c,int nc){ comeHappy = c; notComeHappy = nc; } } public static ReturnData process(Node head){ int comeHappy = head.happy; int notComeHappy = 0; for (int i = 0;i!=head.nexts.size();i++){ ReturnData data = process(head.nexts.get(i)); comeHappy += data.notComeHappy; notComeHappy += Math.max(data.notComeHappy,data.comeHappy); } return new ReturnData(comeHappy,notComeHappy); } public static int calcMaxHappy(Node head){ ReturnData data = process(head); return Math.max(data.comeHappy, data.notComeHappy); } //下面是用数组结构去求 public static int maxHappy(int[][] matrix) { int[][] dp = new int[matrix.length][2]; boolean[] visited = new boolean[matrix.length]; int root = 0; for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) { if (i == matrix[i][0]) { root = i; } } process(matrix, dp, visited, root); return Math.max(dp[root][0], dp[root][1]); } public static void process(int[][] matrix, int[][] dp, boolean[] visited, int root) { visited[root] = true; dp[root][1] = matrix[root][1]; for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) { if (matrix[i][0] == root && !visited[i]) { process(matrix, dp, visited, i); dp[root][1] += dp[i][0]; dp[root][0] += Math.max(dp[i][1], dp[i][0]); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] matrix = { { 1, 8 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 10 } }; System.out.println(maxHappy(matrix)); } }
上述所有题目都叫树形dp。(列可能性)
思路:小树计算完,再算父亲树。
summary(总结)
1、分析可能性(先计算小树,再计算大树)
2、列信息全集,定下返回值结构。
3、编写代码的时候,默认每颗子树都给你这样的信息,然后看拿到这些子树信息后怎么加工出父的信息。
4、basekey要单独考虑一下,作为最简单的情况,要给父返回啥,不至于让他干扰。
第四题:(基础班讲过)
判断一棵树是否是平衡二叉树
public class c04_04IsBalancedTree { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } public static class ReturnData{ public boolean isBalance; public int level; public ReturnData(boolean isBalance, int level) { this.isBalance = isBalance; this.level = level; } } public static ReturnData process(Node head){ if(head == null){ return new ReturnData(true,0); } //如果左子树或者右子树返回了他们不是平衡的,那总体也不会是平衡的 ReturnData lRData = process(head.left); if(!lRData.isBalance){ return new ReturnData(true,0); } ReturnData rRData = process(head.right); if(!rRData.isBalance){ return new ReturnData(true,0); } if(Math.abs(lRData.level - rRData.level) > 1){ return new ReturnData(true,0); } return new ReturnData(true,Math.max(lRData.level,rRData.level)+1); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(1); head.left = new Node(2); head.right = new Node(3); head.left.left = new Node(4); head.left.right = new Node(5); head.right.left = new Node(6); head.right.right = new Node(7); System.out.println(process(head).isBalance); } }
第五题:
数据结构设计题(LeetCode中等难度)难在code上
设计可以变更的缓存结构(LRU)(经常使用的留下)
【题目】
设计一种缓存结构,该结构在构造时确定大小,假设大小为K,并有两个功能:
set(key,value):将记录(key,value)插入该结构。
get(key):返回key对应的value值。
【要求】
1.set和get方法的时间复杂度为O(1)。
2.某个key的set或get操作一旦发生,认为这个key的记录成了最经常使用的。
3.当缓存的大小超过K时,移除最不经常使用的记录,即set或get最久远的。
【举例】
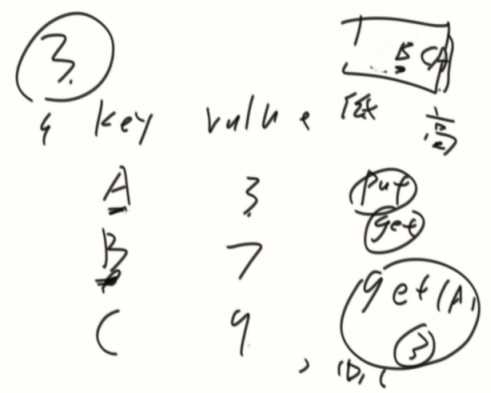
假设缓存结构的实例是cache,大小为3,并依次发生如下行为:
1.cache.set("A",1)。最经常使用的记录为("A",1)。
2.cache.set("B",2)。最经常使用的记录为("B",2),("A",1)变为最不经常的。
3.cache.set("C",3)。最经常使用的记录为("C",2),("A",1)还是最不经常的。
4.cache.get("A")。最经常使用的记录为("A",1),("B",2)变为最不经常的。
5.cache.set("D",4)。大小超过了3,所以移除此时最不经常使用的记录("B",2),加入记录 ("D",4),并且为最经常使用的记录,然后("C",2)变为最不经常使用的记录
思路:hash表(key,Node<key,value>内存地址)+定制的双向链表(尾加头出)
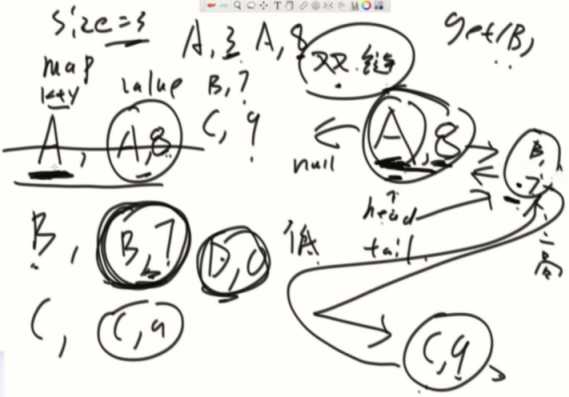
加入的时候先把节点从环境分离,挂到最后,再重连其他节点。
有一个size记录大小,在删的时候可以通过head指针把优先级最低的删除,再根据key到hash里面寻找并彻底删除。
public class Code_02_LRU { public static class Node<K,V> { public K key; public V value; public Node<K,V> last; public Node<K,V> next; public Node(K key,V value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; } } //定制的双向链表 public static class NodeDoubleLinkedList<K,V> { private Node<K,V> head; private Node<K,V> tail; public NodeDoubleLinkedList() { this.head = null; this.tail = null; } public void addNode(Node<K,V> newNode) { if (newNode == null) { return; } if (this.head == null) { this.head = newNode; this.tail = newNode; } else {//最新的添加到尾部 this.tail.next = newNode; newNode.last = this.tail;//新节点的前一个是之前的尾部 this.tail = newNode; } } //操作节点后把结点调整在尾部 public void moveNodeToTail(Node<K,V> node) { if (this.tail == node) { return; } //先把节点从环境分离 if (this.head == node) { this.head = node.next; this.head.last = null; } else {//中间的普遍节点 node.last.next = node.next; node.next.last = node.last; } node.last = this.tail; node.next = null; this.tail.next = node; this.tail = node; } //容量满了删除最不经常操作的数 public Node<K,V> removeHead() { if (this.head == null) { return null; } Node<K,V> res = this.head; if (this.head == this.tail) {//只有一个节点 this.head = null; this.tail = null; } else { this.head = res.next; res.next = null; this.head.last = null; } return res; } } public static class MyCache<K, V> { //通过key可以找到Node private HashMap<K, Node<K,V>> keyNodeMap; private NodeDoubleLinkedList<K,V> nodeList; private int capacity; public MyCache(int capacity) { if (capacity < 1) { throw new RuntimeException("should be more than 0."); } this.keyNodeMap = new HashMap<K, Node<K,V>>(); this.nodeList = new NodeDoubleLinkedList<K,V>(); this.capacity = capacity; } public V get(K key) { if (this.keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) { Node<K,V> res = this.keyNodeMap.get(key); this.nodeList.moveNodeToTail(res); return res.value; } return null; } public void set(K key, V value) { if (this.keyNodeMap.containsKey(key)) { Node<K,V> node = this.keyNodeMap.get(key); node.value = value; this.nodeList.moveNodeToTail(node); } else {//没有就新增 Node<K,V> newNode = new Node<K,V>(key,value); this.keyNodeMap.put(key, newNode); this.nodeList.addNode(newNode); if (this.keyNodeMap.size() == this.capacity + 1) { this.removeMostUnusedCache(); } } } private void removeMostUnusedCache() { Node<K,V> removeNode = this.nodeList.removeHead();//取出优先级最低的 K removeKey = removeNode.key; this.keyNodeMap.remove(removeKey); } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyCache<String, Integer> testCache = new MyCache<String, Integer>(3); testCache.set("A", 1); testCache.set("B", 2); testCache.set("C", 3); System.out.println(testCache.get("B")); System.out.println(testCache.get("A")); testCache.set("D", 4); System.out.println(testCache.get("D")); System.out.println(testCache.get("C")); } }
就是有限的几个结构组成出来。(链表、hash)
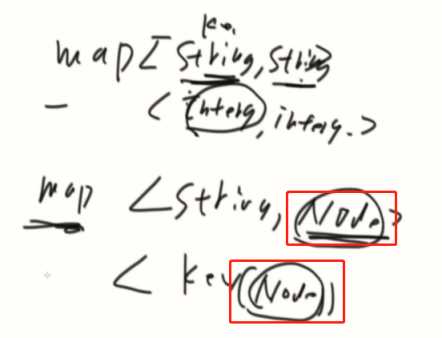
自定义的Node,Map会存内存地址(8字节)。
回去看一下LFU。
以上是关于算法进阶面试题05——树形dp解决步骤返回最大搜索二叉子树的大小二叉树最远两节点的距离晚会最大活跃度手撕缓存结构LRU的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章