[图解算法] 线性时间选择——//递归与分治策略//图解才是最直观
Posted cc1997
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[图解算法] 线性时间选择——//递归与分治策略//图解才是最直观相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

1 #include <ctime> 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 template <class Type> 6 void Swap(Type &x,Type &y); 7 8 inline int Random(int x, int y); 9 10 template <class Type> 11 void BubbleSort(Type a[],int p,int r); 12 13 template <class Type> 14 int Partition(Type a[],int p,int r,Type x); 15 16 template <class Type> 17 Type Select(Type a[],int p,int r,int k); 18 19 void main() 20 { 21 //初始化数组 22 int a[100]; 23 24 //必须放在循环体外面 25 srand((unsigned)time(0)); 26 27 for(int i=0; i<100; i++) 28 { 29 a[i] = Random(0,100); 30 cout<<"a["<<i<<"]:"<<a[i]<<" "; 31 } 32 cout<<endl; 33 34 cout<<"第23小元素是"<<Select(a,0,99,23)<<endl; 35 36 37 //重新排序,对比结果 38 BubbleSort(a,0,99); 39 for(i=0; i<100; i++) 40 { 41 cout<<"a["<<i<<"]:"<<a[i]<<" "; 42 } 43 cout<<endl; 44 } 45 46 template <class Type> 47 void Swap(Type &x,Type &y) 48 { 49 Type temp = x; 50 x = y; 51 y = temp; 52 } 53 54 inline int Random(int x, int y) 55 { 56 int ran_num = rand() % (y - x) + x; 57 return ran_num; 58 } 59 60 //冒泡排序 61 template <class Type> 62 void BubbleSort(Type a[],int p,int r) 63 { 64 //记录一次遍历中是否有元素的交换 65 bool exchange; 66 for(int i=p; i<r;i++) 67 { 68 exchange = false ; 69 for(int j=0; j<=r-i; j++) 70 { 71 if(a[j]<a[j-1]) 72 { 73 Swap(a[j],a[j-1]); 74 exchange = true; 75 } 76 } 77 //如果这次遍历没有元素的交换,那么排序结束 78 if(false == exchange) 79 { 80 break ; 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 85 template <class Type> 86 int Partition(Type a[],int p,int r,Type x) 87 { 88 int i = p-1,j = r + 1; 89 90 while(true) 91 { 92 while(a[++i]<x && i<r); 93 while(a[--j]>x); 94 if(i>=j) 95 { 96 break; 97 } 98 Swap(a[i],a[j]); 99 } 100 return j; 101 } 102 103 104 template <class Type> 105 Type Select(Type a[],int p,int r,int k) 106 { 107 if(r-p<75) 108 { 109 BubbleSort(a,p,r); 110 return a[p+k-1]; 111 } 112 //(r-p-4)/5相当于n-5 113 for(int i=0; i<=(r-p-4)/5; i++) 114 { 115 //将元素每5个分成一组,分别排序,并将该组中位数与a[p+i]交换位置 116 //使所有中位数都排列在数组最左侧,以便进一步查找中位数的中位数 117 BubbleSort(a,p+5*i,p+5*i+4); 118 Swap(a[p+5*i+2],a[p+i]); 119 } 120 //找中位数的中位数 121 Type x = Select(a,p,p+(r-p-4)/5,(r-p-4)/10); 122 i = Partition(a,p,r,x); 123 int j = i-p+1; 124 if(k<=j) 125 { 126 return Select(a,p,i,k); 127 } 128 else 129 { 130 return Select(a,i+1,r,k-j); 131 } 132 }
提醒:此篇需要先理解快速排序。
[图解+例子]
一、建立随机数组

(共27个数)(代码中为100个数,为了放得下举的例子改为27个)
二、给线性时间选择函数Select()传参
Type a[] 数组a
int p 起始位置
int r 结束位置
int k 查找第k小
三、判断
元素个数<75 不需要线性选择--》直接进行冒泡排序返回a[p+k-1](第k小元素)
元素个数>75 进行线性选择 --》进行下一步
四、线性时间选择
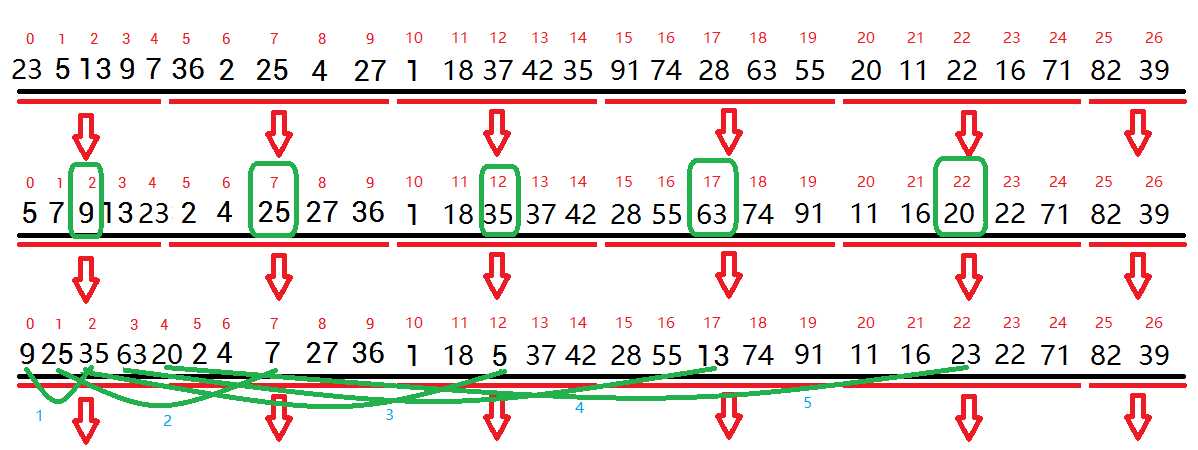
1- 分组并取各组中位数 (将元素每5个分成一组,分别排序,并将该组中位数与a[p+i]交换位置 )【图中绿线12345表示要交换的一对对数据】
for(int i=0; i<=(r-p-4)/5; i++)
{
BubbleSort(a,p+5*i,p+5*i+4);
Swap(a[p+5*i+2],a[p+i]);
}
目的:使所有组的中位数都排列在数组最左侧,以便进一步查找中位数的中位数
2- 查找中位数的中位数
Type x = Select(a , p , p+(r-p-4)/5 , (r-p-4)/10 );
p到p+(r-p-4)/5为中位数的范围,p+(r-p-4)/5 ÷ 2 = (r-p-4)/10-->中位数的中位数
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
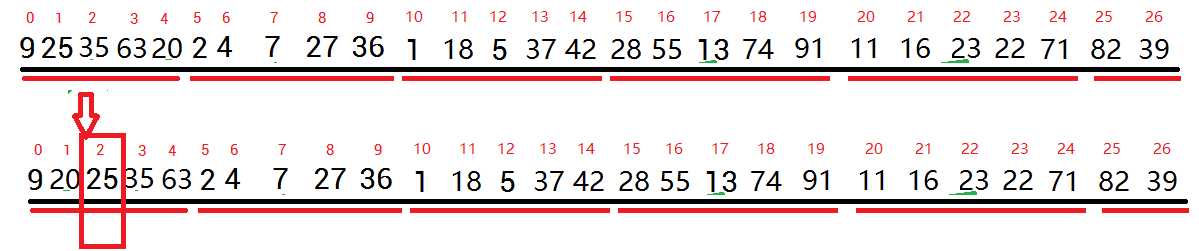
3-用找到的中位数的中位数做为快速排序的标准进行一趟快速排序(前面有篇讲的快速排序为了方便直接用第一个做标准,也有用随机数做标准的)
i = Partition(a,p,r,x);
排序结束后,标准元素将数组分为三部分:左,标准元素,右。
快排讲过啦,这里快速排序省略图解啦 !想看点这里 快速排序
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4-判断
快速排序后看成三部分:左,标准元素,右。
左都比标准元素小,右都比它大;(此时左右还是乱序,只有标准元素找到了它最终应该排的位置,这里不清晰先看快速排序那篇文章)
所以判断下我们要找的第k小是比它大(在右)还是比它小(在左);
int j = i-p+1;
if(k<=j)
{
return Select(a,p,i,k);
}
else
{
return Select(a,i+1,r,k-j);
}
i为快速排序返回值,j = i - 起始位置 + 1;
小于或者等于,对左半段重复上述操作(递归);
反之,对右半段。
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[特例]
有空更新。。。
[总结]
线性时间选择其实就是————>>快速排序的加强版,
快速排序中的标准元素变为————>>分组后取得的各组中位数的中位数。
所以多了一步取中位数的操作而已。
本人保留解析著作权。
算法引用自 王晓东. 计算机算法设计与分析[M]. 电子工业出版社, 2012.
以上是关于[图解算法] 线性时间选择——//递归与分治策略//图解才是最直观的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
