IO流的输入输出
Posted liuzeyu12a
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了IO流的输入输出相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Java IO 体系
字节流操作类和字符流操作类组成了Java IO体系。
看下面一张图
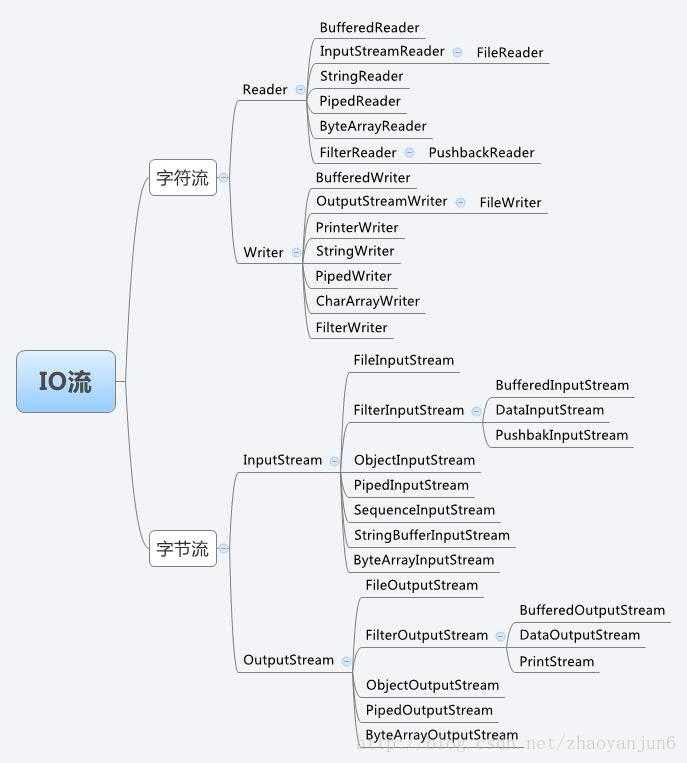
从上图可以看到,整个Java IO体系都是基于字符流(InputStream/OutputStream) 和 字节流(Reader/Writer)作为基类,它们是IO操作的四大抽象类,根据不同的数据载体或功能派生出来的。
流的概念和作用
流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象。即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输,根据数据传输特性将流抽象为各种类,方便更直观的进行数据操作。
字符流和字节流
字符流的由来: 因为数据编码的不同,而有了对字符进行高效操作的流对象。本质其实就是基于字节流读取时,去查了指定的码表。 字节流和字符流的区别:
- 读写单位不同:字节流以字节(8bit)为单位,字符流以字符为单位,根据码表映射字符,一次可能读多个字节。
-
处理对象不同:字节流能处理所有类型的数据(如图片、avi等),而字符流只能处理字符类型的数据。
- 字节流:一次读入或读出是8位二进制。
-
字符流:一次读入或读出是16位二进制。
设备上的数据无论是图片或者视频,文字,它们都以二进制存储的。二进制的最终都是以一个8位为数据单元进行体现,所以计算机中的最小数据单元就是字节。意味着,字节流可以处理设备上的所有数据,所以字节流一样可以处理字符数据。
结论:只要是处理纯文本数据,就优先考虑使用字符流。 除此之外都使用字节流。
****************************************************************************
操作IO的基本步骤
* 1、创建数据源
* 2、选择流:字符流/字节流
* 3、操作
* 4、关闭数据缓冲
***********************************************************
1、输入流字节流 InputStream
InputStream是所有的输入字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。ByteArrayInputStream、StringBufferInputStream、FileInputStream是三种基本的介质流,它们分别从Byte 数组、StringBuffer、和本地文件中读取数据。PipedInputStream是从与其它线程共用的管道中读取数据,与Piped 相关的知识后续单独介绍。ObjectInputStream和所有FilterInputStream的子类都是装饰流(装饰器模式的主角)。
2、输出字节流 OutputStream
OutputStream是所有的输出字节流的父类,它是一个抽象类。ByteArrayOutputStream、FileOutputStream是两种基本的介质流,它们分别向Byte 数组、和本地文件中写入数据。PipedOutputStream是向与其它线程共用的管道中写入数据。ObjectOutputStream和所有FilterOutputStream的子类都是装饰流。
- 文件流:FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
这四个类是专门操作文件流的,用法高度相似,区别在于前面两个是操作字节流,后面两个是操作字符流。它们都会直接操作文件流,直接与OS底层交互。因此他们也被称为节点流。
注意使用这几个流的对象之后,需要关闭流对象,因为java垃圾回收器不会主动回收,只能由操作系统来回收。因为JVM 不是直接和文件打交道的,而是通过操作系统和文件打交道的,不过在Java7之后,可以在 try() 括号中打开流,最后程序会通知OS(操作系统)关闭流对象,不再需要显示地close。
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
从文件向程序冲写数据使用InputStream的FileInputStream,按字节数组读取
代码:

package com.sxt.io; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; /** * 四个步骤: 分段读取 文件字节输入流 * 1、创建源 * 2、选择流 * 3、操作 * 4、释放资源 * @author liuzeyu12a * */ public class IOTest03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1、创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); //2、选择流 InputStream is =null; try { is =new FileInputStream(src); //3、操作 (分段读取) byte[] flush = new byte[1024*10]; //缓冲容器 int len = -1; //接收长度 while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) { //字节数组-->字符串 (解码) String str = new String(flush,0,len); System.out.println(str); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4、释放资源 try { if(null!=is) { is.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
从程序向文件中写数据使用OutputStream的FileOutputStream,按字节数组写入
代码:

1 package com.sxt.io; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.OutputStream; 8 9 /** 10 * 文件字节输出流 11 *1、创建源 12 *2、选择流 13 *3、操作(写出内容) 14 *4、释放资源 15 * @author liuzeyu12a 16 * 17 */ 18 public class IOTest04 { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 //1、创建源 22 File dest = new File("dest.txt"); 23 //2、选择流 24 OutputStream os =null; 25 try { 26 os = new FileOutputStream(dest,true); 27 //3、操作(写出) 28 String msg ="IO is so easy "; 29 byte[] datas =msg.getBytes(); // 字符串-->字节数组(编码) 30 os.write(datas,0,datas.length); 31 os.flush(); 32 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 }catch (IOException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 }finally{ 37 //4、释放资源 38 try { 39 if (null != os) { 40 os.close(); 41 } 42 } catch (Exception e) { 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 47 }
综合以上两种文件操作,可以写一个文件拷贝的案例
代码:

1 package com.sxt.io; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 6 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 7 import java.io.IOException; 8 import java.io.InputStream; 9 import java.io.OutputStream; 10 11 /** 12 * 文件拷贝:文件字节输入、输出流 13 * 14 * @author liuzeyu12a 15 * 16 */ 17 public class Copy { 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 copy("src/com/sxt/io/Copy.java","copy.txt"); 21 } 22 /** 23 * 文件的拷贝 24 * 思考: 利用递归 制作文件夹的拷贝 25 * @param srcPath 26 * @param destPath 27 */ 28 public static void copy(String srcPath,String destPath) { 29 //1、创建源 30 File src = new File(srcPath); //源头 31 File dest = new File(destPath);//目的地 32 //2、选择流 33 InputStream is =null; 34 OutputStream os =null; 35 try { 36 is =new FileInputStream(src); 37 os = new FileOutputStream(dest); 38 //3、操作 (分段读取) 39 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; //缓冲容器 40 int len = -1; //接收长度 41 while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) { 42 os.write(flush,0,len); //分段写出 43 } 44 os.flush(); 45 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 }catch (IOException e) { 48 e.printStackTrace(); 49 }finally{ 50 //4、释放资源 分别关闭 先打开的后关闭 51 try { 52 if (null != os) { 53 os.close(); 54 } 55 } catch (IOException e) { 56 e.printStackTrace(); 57 } 58 59 try { 60 if(null!=is) { 61 is.close(); 62 } 63 } catch (IOException e) { 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } 66 } 67 } 68 public static void copy2(String srcPath,String destPath) { 69 //1、创建源 70 File src = new File(srcPath); //源头 71 File dest = new File(destPath);//目的地 72 //2、选择流 73 try(InputStream is=new FileInputStream(src); 74 OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(dest); ) { 75 //3、操作 (分段读取) 76 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; //缓冲容器 77 int len = -1; //接收长度 78 while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) { 79 os.write(flush,0,len); //分段写出 80 } 81 os.flush(); 82 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { 83 e.printStackTrace(); 84 }catch (IOException e) { 85 e.printStackTrace(); 86 } 87 } 88 }
3、字符输入流 Reader
在上面的继承关系图中可以看出:
Reader 是所有的输入字符流的父类,它是一个抽象类。
* CharReader、StringReader 是两种基本的介质流,它们分别将Char 数组、String中读取数据。PipedReader 是从与其它线程共用的管道中读取数据。
* BufferedReader 很明显就是一个装饰器,它和其子类负责装饰其它Reader 对象。
* FilterReader 是所有自定义具体装饰流的父类,其子类PushbackReader 对Reader 对象进行装饰,会增加一个行号。
* InputStreamReader 是一个连接字节流和字符流的桥梁,它将字节流转变为字符流。FileReader 可以说是一个达到此功能、常用的工具类,在其源代码中明显使用了将FileInputStream 转变为Reader 的方法。
我们可以从这个类中得到一定的技巧。
* Reader 中各个类的用途和使用方法基本和InputStream 中的类使用一致。后面会有Reader 与InputStream 的对应关系。
为了人为操作方便,我们一般只对字符敏感,所以使用FileReader/FileWriter操作字符会更加方便。
4、字符输出流Writer
在上面的关系图中可以看出:
Writer 是所有的输出字符流的父类,它是一个抽象类。
* CharArrayWriter、StringWriter 是两种基本的介质流,它们分别向Char 数组、String 中写入数据。PipedWriter 是向与其它线程共用的管道中写入数据,
* BufferedWriter 是一个装饰器为Writer 提供缓冲功能。
* PrintWriter 和PrintStream 极其类似,功能和使用也非常相似。
* OutputStreamWriter 是OutputStream 到Writer 转换的桥梁,它的子类FileWriter 其实就是一个实现此功能的具体类(具体可以研究一下SourceCode)。功能和使用和OutputStream 极其类似,后面会有它们的对应图。
- 文件流:FileReader/FileWriter
从文件向程序冲写数据使用Reader的FileReader,按字符数组读取

package com.sxt.io; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; /** * 四个步骤: 分段读取 文件字符输入流 * 1、创建源 * 2、选择流 * 3、操作 * 4、释放资源 * * @author liuzeyu12a * */ public class IOTest05 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1、创建源 File src = new File("abc.txt"); //2、选择流 Reader reader =null; try { reader =new FileReader(src); //3、操作 (分段读取) char[] flush = new char[1024]; //缓冲容器 int len = -1; //接收长度 while((len=reader.read(flush))!=-1) { //字符数组-->字符串 String str = new String(flush,0,len); System.out.println(str); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4、释放资源 try { if(null!=reader) { reader.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
从文件向程序冲写数据使用Writer的FileWriter,按字符数组写出

1 package com.sxt.io; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileWriter; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.Writer; 8 9 /** 10 * 文件字符输出流 11 *1、创建源 12 *2、选择流 13 *3、操作(写出内容) 14 *4、释放资源 15 * @author liuzeyu12a 16 * 17 */ 18 public class IOTest06 { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 //1、创建源 22 File dest = new File("dest.txt"); 23 //2、选择流 24 Writer writer =null; 25 try { 26 writer = new FileWriter(dest); 27 //3、操作(写出) 28 //写法一 29 // String msg ="IO is so easy 尚学堂欢迎你"; 30 // char[] datas =msg.toCharArray(); // 字符串-->字符数组 31 // writer.write(datas,0,datas.length); 32 //写法二 33 /*String msg ="IO is so easy 尚学堂欢迎你"; 34 writer.write(msg); 35 writer.write("add"); 36 writer.flush();*/ 37 38 //写法三 39 writer.append("IO is so easy ").append("尚学堂欢迎你"); 40 writer.flush(); 41 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 }catch (IOException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 }finally{ 46 //4、释放资源 47 try { 48 if (null != writer) { 49 writer.close(); 50 } 51 } catch (Exception e) { 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 }
5、另外我们再介绍两个字节流类,是为了操作字节方便所引入,分别是ByteArrayInputStream / ByteArrayOutputStream
之前我们操作的源头都是来自了文件File ,现在我们将源头换成电脑中的一块内存,或者网络(服务器)上的一块内存,用字节数组表示。操作内存,这个时候JVM 就可以直接访问了,不用再经过操作系统了,此时的资源就有GC来回收了,可以不用手动关闭了。
所有的对象都可以转成字节数组,转成字节数组后,在内存中就以二进制存在,方便网络上的数据传输。
程序向内存中的字节数组读取数据ByteArrayInputStream

1 package com.sxt.io; 2 3 import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 import java.io.InputStream; 7 8 /** 9 * 四个步骤:字节数组输入流 10 * 1、创建源 : 字节数组 不要太大 11 * 2、选择流 12 * 3、操作 13 * 4、释放资源: 可以不用处理 14 * 15 * @author liuzeyu12a 16 * 17 */ 18 public class IOTest07 { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 //1、创建源 22 byte[] src = "talk is cheap show me the code".getBytes(); 23 //2、选择流 24 InputStream is =null; 25 try { 26 is =new ByteArrayInputStream(src); 27 //3、操作 (分段读取) 28 byte[] flush = new byte[5]; //缓冲容器 29 int len = -1; //接收长度 30 while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) { 31 //字节数组-->字符串 (解码) 32 String str = new String(flush,0,len); 33 System.out.println(str); 34 } 35 36 } catch (IOException e) { 37 e.printStackTrace(); 38 }finally { 39 //4、释放资源 40 try { 41 if(null!=is) { 42 is.close(); 43 } 44 } catch (IOException e) { 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 50 }
程序向内存中写数据后,再从内存中使用toByteArray()方法得到字节数组

package com.sxt.io; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; /** * 字节数组输出流 ByteArrayOutputStream *1、创建源 : 内部维护 *2、选择流 : 不关联源 *3、操作(写出内容) *4、释放资源 :可以不用 * * 获取数据: toByteArray() * @author liuzeyu12a * */ public class IOTest08 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1、创建源 byte[] dest =null; //2、选择流 (新增方法) ByteArrayOutputStream baos =null; try { baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //3、操作(写出) String msg ="show me the code"; byte[] datas =msg.getBytes(); // 字符串-->字节数组(编码) baos.write(datas,0,datas.length); baos.flush(); //获取数据 dest = baos.toByteArray(); System.out.println(dest.length +"-->"+new String(dest,0,baos.size())); }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //4、释放资源 try { if (null != baos) { baos.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { } } } }
这里要注意的是ByteArrayOutputStream使用的是子类新增的方法,幷没有发生多态。当我们程序向内存中写数据时,写多大的内存是有内存自己分配的,所以可以不能加目的地,并且要注意写入的数据不能太大。
6、一个综合的案例,实现图片读取到字节数组,再由字节数组写出到图片,其实就是图片的拷贝。
分析:
由文件到程序,再有程序到字节数组,必须经过程序这个中间站.
图片到字节数组:
图片到程序 FileInputStream
程序到字节数组 ByteArrayOutputStream
字节数组到图片:
字节数组程序 ByteArrayInputStream
程序到文件 FileOutputStream
代码实现:

1 package com.sxt.io; 2 3 import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; 4 import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; 5 import java.io.File; 6 import java.io.FileInputStream; 7 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 8 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 9 import java.io.IOException; 10 import java.io.InputStream; 11 import java.io.OutputStream; 12 13 /** 14 *1、 图片读取到字节数组 15 *2、 字节数组写出到文件 16 * @author liuzeyu12a 17 * 18 */ 19 public class IOTest09 { 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) { 22 //图片转成字节数组 23 byte[] datas = fileToByteArray("p.png"); 24 System.out.println(datas.length); 25 byteArrayToFile(datas,"p-byte.png"); 26 } 27 /** 28 * 1、图片读取到字节数组 29 * 1)、图片到程序 FileInputStream 30 * 2)、程序到字节数组 ByteArrayOutputStream 31 */ 32 public static byte[] fileToByteArray(String filePath) { 33 //1、创建源与目的地 34 File src = new File(filePath); 35 byte[] dest =null; 36 //2、选择流 37 InputStream is =null; 38 ByteArrayOutputStream baos =null; 39 try { 40 is =new FileInputStream(src); 41 baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 42 //3、操作 (分段读取) 43 byte[] flush = new byte[1024*10]; //缓冲容器 44 int len = -1; //接收长度 45 while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) { 46 baos.write(flush,0,len); //写出到字节数组中 47 } 48 baos.flush(); 49 return baos.toByteArray(); 50 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 51 e.printStackTrace(); 52 } catch (IOException e) { 53 e.printStackTrace(); 54 }finally { 55 //4、释放资源 56 try { 57 if(null!=is) { 58 is.close(); 59 } 60 } catch (IOException e) { 61 e.printStackTrace(); 62 } 63 } 64 return null; 65 } 66 /** 67 * 2、字节数组写出到图片 68 * 1)、字节数组到程序 ByteArrayInputStream 69 * 2)、程序到文件 FileOutputStream 70 */ 71 public static void byteArrayToFile(byte[] src,String filePath) { 72 //1、创建源 73 File dest = new File(filePath); 74 //2、选择流 75 InputStream is =null; 76 OutputStream os =null; 77 try { 78 is =new ByteArrayInputStream(src); 79 os = new FileOutputStream(dest); 80 //3、操作 (分段读取) 81 byte[] flush = new byte[5]; //缓冲容器 82 int len = -1; //接收长度 83 while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) { 84 os.write(flush,0,len); //写出到文件 85 } 86 os.flush(); 87 } catch (IOException e) { 88 e.printStackTrace(); 89 }finally { 90 //4、释放资源 91 try { 92 if (null != os) { 93 os.close(); 94 } 95 } catch (Exception e) { 96 } 97 } 98 } 99 }
在jdk7 以后我们可以使用try...with对流的关闭操作进行简化
将以上代码进行封装简化

1 package com.sxt.io; 2 3 import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; 4 import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; 5 import java.io.Closeable; 6 import java.io.FileInputStream; 7 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 8 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 9 import java.io.IOException; 10 import java.io.InputStream; 11 import java.io.OutputStream; 12 13 /** 14 * try ...with...resource 15 * @author liuzeyu12a 16 * 17 */ 18 public class FileUtils2 { 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 //文件到文件 22 try { 23 InputStream is = new FileInputStream("abc.txt"); 24 OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("abc-copy.txt"); 25 copy(is,os); 26 } catch (IOException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 //文件到字节数组 31 byte[] datas = null; 32 try { 33 InputStream is = new FileInputStream("p.png"); 34 ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 35 copy(is,os); 36 datas = os.toByteArray(); 37 System.out.println(datas.length); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 //字节数组到文件 42 try { 43 InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(datas); 44 OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("p-copy.png"); 45 copy(is,os); 46 } catch (IOException e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 } 49 } 50 /** 51 * 对接输入输出流 52 * try ...with...resource 53 * @param is 54 * @param os 55 */ 56 public static void copy(InputStream is,OutputStream os) { 57 try(is;os) { 58 //3、操作 (分段读取) 59 byte[] flush = new byte[1024]; //缓冲容器 60 int len = -1; //接收长度 61 while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1) { 62 os.write(flush,0,len); //分段写出 63 } 64 os.flush(); 65 }catch(FileNotFoundException e) { 66 e.printStackTrace(); 67 }catch (IOException e) { 68 e.printStackTrace(); 69 } 70 } 71 }
部分图片文字参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/runningTurtle/p/7088125.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoyanjun/p/6292384.html
以上是关于IO流的输入输出的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
