Map -- TreeMap
Posted wkcode
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Map -- TreeMap相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3310928.html
第1部分 TreeMap介绍
TreeMap 简介
TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的。
TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合。
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法。比如返回有序的key集合。
TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆。
TreeMap 实现了java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化。
TreeMap基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap的基本操作 containsKey、get、put 和 remove 的时间复杂度是 log(n) 。
另外,TreeMap是非同步的。 它的iterator 方法返回的迭代器是fail-fast的。
TreeMap的构造函数
// 默认构造函数。使用该构造函数,TreeMap中的元素按照自然排序进行排列。
TreeMap()
// 创建的TreeMap包含Map
TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> copyFrom)
// 指定Tree的比较器
TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator)
// 创建的TreeSet包含copyFrom
TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> copyFrom)
TreeMap的API

Entry<K, V> ceilingEntry(K key) K ceilingKey(K key) void clear() Object clone() Comparator<? super K> comparator() boolean containsKey(Object key) NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet() Entry<K, V> firstEntry() K firstKey() Entry<K, V> floorEntry(K key) K floorKey(K key) V get(Object key) NavigableMap<K, V> headMap(K to, boolean inclusive) SortedMap<K, V> headMap(K toExclusive) Entry<K, V> higherEntry(K key) K higherKey(K key) boolean isEmpty() Set<K> keySet() Entry<K, V> lastEntry() K lastKey() Entry<K, V> lowerEntry(K key) K lowerKey(K key) NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() Entry<K, V> pollFirstEntry() Entry<K, V> pollLastEntry() V put(K key, V value) V remove(Object key) int size() SortedMap<K, V> subMap(K fromInclusive, K toExclusive) NavigableMap<K, V> subMap(K from, boolean fromInclusive, K to, boolean toInclusive) NavigableMap<K, V> tailMap(K from, boolean inclusive) SortedMap<K, V> tailMap(K fromInclusive)
第2部分 TreeMap数据结构
java.lang.Object ? java.util.AbstractMap<K, V> ? java.util.TreeMap<K, V> public class TreeMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {}
TreeMap与Map关系如下图:
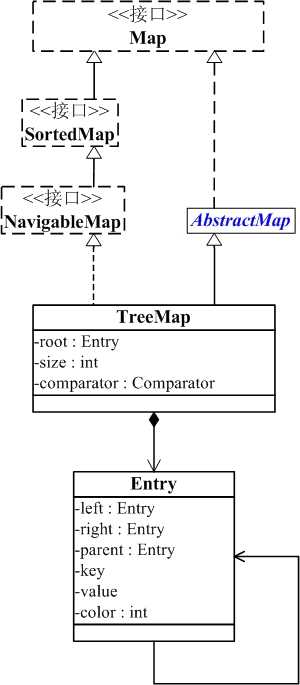
从图中可以看出:
(01) TreeMap实现继承于AbstractMap,并且实现了NavigableMap接口。
(02) TreeMap的本质是R-B Tree(红黑树),它包含几个重要的成员变量: root, size, comparator。
root 是红黑树的根节点。它是Entry类型,Entry是红黑树的节点,它包含了红黑树的6个基本组成成分:key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)。Entry节点根据key进行排序,Entry节点包含的内容为value。
红黑数排序时,根据Entry中的key进行排序;Entry中的key比较大小是根据比较器comparator来进行判断的。
size是红黑数中节点的个数。
第3部分 TreeMap源码解析(基于JDK1.6.0_45)

package java.util; public class TreeMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { // 比较器。用来给TreeMap排序 private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; // TreeMap是红黑树实现的,root是红黑书的根节点 private transient Entry<K,V> root = null; // 红黑树的节点总数 private transient int size = 0; // 记录红黑树的修改次数 private transient int modCount = 0; // 默认构造函数 public TreeMap() { comparator = null; } // 带比较器的构造函数 public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; } // 带Map的构造函数,Map会成为TreeMap的子集 public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = null; putAll(m); } // 带SortedMap的构造函数,SortedMap会成为TreeMap的子集 public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = m.comparator(); try { buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } } public int size() { return size; } // 返回TreeMap中是否保护“键(key)” public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return getEntry(key) != null; } // 返回TreeMap中是否保护"值(value)" public boolean containsValue(Object value) { // getFirstEntry() 是返回红黑树的第一个节点 // successor(e) 是获取节点e的后继节点 for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e)) if (valEquals(value, e.value)) return true; return false; } // 获取“键(key)”对应的“值(value)” public V get(Object key) { // 获取“键”为key的节点(p) Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key); // 若节点(p)为null,返回null;否则,返回节点对应的值 return (p==null ? null : p.value); } public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { return comparator; } // 获取第一个节点对应的key public K firstKey() { return key(getFirstEntry()); } // 获取最后一个节点对应的key public K lastKey() { return key(getLastEntry()); } // 将map中的全部节点添加到TreeMap中 public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> map) { // 获取map的大小 int mapSize = map.size(); // 如果TreeMap的大小是0,且map的大小不是0,且map是已排序的“key-value对” if (size==0 && mapSize!=0 && map instanceof SortedMap) { Comparator c = ((SortedMap)map).comparator(); // 如果TreeMap和map的比较器相等; // 则将map的元素全部拷贝到TreeMap中,然后返回! if (c == comparator || (c != null && c.equals(comparator))) { ++modCount; try { buildFromSorted(mapSize, map.entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } return; } } // 调用AbstractMap中的putAll(); // AbstractMap中的putAll()又会调用到TreeMap的put() super.putAll(map); } // 获取TreeMap中“键”为key的节点 final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { // 若“比较器”为null,则通过getEntryUsingComparator()获取“键”为key的节点 if (comparator != null) return getEntryUsingComparator(key); if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; // 将p设为根节点 Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key); // 若“p的key” < key,则p=“p的左孩子” if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; // 若“p的key” > key,则p=“p的左孩子” else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; // 若“p的key” = key,则返回节点p else return p; } return null; } // 获取TreeMap中“键”为key的节点(对应TreeMap的比较器不是null的情况) final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) { K k = (K) key; Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; if (cpr != null) { // 将p设为根节点 Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key); // 若“p的key” < key,则p=“p的左孩子” if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; // 若“p的key” > key,则p=“p的左孩子” else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; // 若“p的key” = key,则返回节点p else return p; } } return null; } // 获取TreeMap中不小于key的最小的节点; // 若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key大),就返回null final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) { Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = compare(key, p.key); // 情况一:若“p的key” > key。 // 若 p 存在左孩子,则设 p=“p的左孩子”; // 否则,返回p if (cmp < 0) { if (p.left != null) p = p.left; else return p; // 情况二:若“p的key” < key。 } else if (cmp > 0) { // 若 p 存在右孩子,则设 p=“p的右孩子” if (p.right != null) { p = p.right; } else { // 若 p 不存在右孩子,则找出 p 的后继节点,并返回 // 注意:这里返回的 “p的后继节点”有2种可能性:第一,null;第二,TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点。 // 理解这一点的核心是,getCeilingEntry是从root开始遍历的。 // 若getCeilingEntry能走到这一步,那么,它之前“已经遍历过的节点的key”都 > key。 // 能理解上面所说的,那么就很容易明白,为什么“p的后继节点”又2种可能性了。 Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent; Entry<K,V> ch = p; while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) { ch = parent; parent = parent.parent; } return parent; } // 情况三:若“p的key” = key。 } else return p; } return null; } // 获取TreeMap中不大于key的最大的节点; // 若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key小),就返回null // getFloorEntry的原理和getCeilingEntry类似,这里不再多说。 final Entry<K,V> getFloorEntry(K key) { Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = compare(key, p.key); if (cmp > 0) { if (p.right != null) p = p.right; else return p; } else if (cmp < 0) { if (p.left != null) { p = p.left; } else { Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent; Entry<K,V> ch = p; while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) { ch = parent; parent = parent.parent; } return parent; } } else return p; } return null; } // 获取TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点。 // 若不存在,就返回null。 // 请参照getCeilingEntry来对getHigherEntry进行理解。 final Entry<K,V> getHigherEntry(K key) { Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = compare(key, p.key); if (cmp < 0) { if (p.left != null) p = p.left; else return p; } else { if (p.right != null) { p = p.right; } else { Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent; Entry<K,V> ch = p; while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) { ch = parent; parent = parent.parent; } return parent; } } } return null; } // 获取TreeMap中小于key的最大的节点。 // 若不存在,就返回null。 // 请参照getCeilingEntry来对getLowerEntry进行理解。 final Entry<K,V> getLowerEntry(K key) { Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = compare(key, p.key); if (cmp > 0) { if (p.right != null) p = p.right; else return p; } else { if (p.left != null) { p = p.left; } else { Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent; Entry<K,V> ch = p; while (parent != null && ch == parent.left) { ch = parent; parent = parent.parent; } return parent; } } } return null; } // 将“key, value”添加到TreeMap中 // 理解TreeMap的前提是掌握“红黑树”。 // 若理解“红黑树中添加节点”的算法,则很容易理解put。 public V put(K key, V value) { Entry<K,V> t = root; // 若红黑树为空,则插入根节点 if (t == null) { // TBD: // 5045147: (coll) Adding null to an empty TreeSet should // throw NullPointerException // // compare(key, key); // type check root = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; // 在二叉树(红黑树是特殊的二叉树)中,找到(key, value)的插入位置。 // 红黑树是以key来进行排序的,所以这里以key来进行查找。 if (cpr != null) { do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } // 新建红黑树的节点(e) Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, parent); if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; // 红黑树插入节点后,不再是一颗红黑树; // 这里通过fixAfterInsertion的处理,来恢复红黑树的特性。 fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; modCount++; return null; } // 删除TreeMap中的键为key的节点,并返回节点的值 public V remove(Object key) { // 找到键为key的节点 Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key); if (p == null) return null; // 保存节点的值 V oldValue = p.value; // 删除节点 deleteEntry(p); return oldValue; } // 清空红黑树 public void clear() { modCount++; size = 0; root = null; } // 克隆一个TreeMap,并返回Object对象 public Object clone() { TreeMap<K,V> clone = null; try { clone = (TreeMap<K,V>) super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { throw new InternalError(); } // Put clone into "virgin" state (except for comparator) clone.root = null; clone.size = 0; clone.modCount = 0; clone.entrySet = null; clone.navigableKeySet = null; clone.descendingMap = null; // Initialize clone with our mappings try { clone.buildFromSorted(size, entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } return clone; } // 获取第一个节点(对外接口)。 public Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() { return exportEntry(getFirstEntry()); } // 获取最后一个节点(对外接口)。 public Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() { return exportEntry(getLastEntry()); } // 获取第一个节点,并将改节点从TreeMap中删除。 public Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() { // 获取第一个节点 Entry<K,V> p = getFirstEntry(); Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(p); // 删除第一个节点 if (p != null) deleteEntry(p); return result; } // 获取最后一个节点,并将改节点从TreeMap中删除。 public Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() { // 获取最后一个节点 Entry<K,V> p = getLastEntry(); Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(p); // 删除最后一个节点 if (p != null) deleteEntry(p); return result; } // 返回小于key的最大的键值对,没有的话返回null public Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(getLowerEntry(key)); } // 返回小于key的最大的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null public K lowerKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(getLowerEntry(key)); } // 返回不大于key的最大的键值对,没有的话返回null public Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(getFloorEntry(key)); } // 返回不大于key的最大的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null public K floorKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(getFloorEntry(key)); } // 返回不小于key的最小的键值对,没有的话返回null public Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(getCeilingEntry(key)); } // 返回不小于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null public K ceilingKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(getCeilingEntry(key)); } // 返回大于key的最小的键值对,没有的话返回null public Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(getHigherEntry(key)); } // 返回大于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null public K higherKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(getHigherEntry(key)); } // TreeMap的红黑树节点对应的集合 private transient EntrySet entrySet = null; // KeySet为KeySet导航类 private transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySet = null; // descendingMap为键值对的倒序“映射” private transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap = null; // 返回TreeMap的“键的集合” public Set<K> keySet() { return navigableKeySet(); } // 获取“可导航”的Key的集合 // 实际上是返回KeySet类的对象。 public NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() { KeySet<K> nks = navigableKeySet; return (nks != null) ? nks : (navigableKeySet = new KeySet(this)); } // 返回“TreeMap的值对应的集合” public Collection<V> values() { Collection<V> vs = values; return (vs != null) ? vs : (values = new Values()); } // 获取TreeMap的Entry的集合,实际上是返回EntrySet类的对象。 public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { EntrySet es = entrySet; return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet()); } // 获取TreeMap的降序Map // 实际上是返回DescendingSubMap类的对象 public NavigableMap<K, V> descendingMap() { NavigableMap<K, V> km = descendingMap; return (km != null) ? km : (descendingMap = new DescendingSubMap(this, true, null, true, true, null, true)); } // 获取TreeMap的子Map // 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) { return new AscendingSubMap(this, false, fromKey, fromInclusive, false, toKey, toInclusive); } // 获取“Map的头部” // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) { return new AscendingSubMap(this, true, null, true, false, toKey, inclusive); } // 获取“Map的尾部”。 // 范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive) { return new AscendingSubMap(this, false, fromKey, inclusive, true, null, true); } // 获取“子Map”。 // 范围是从fromKey(包括) 到 toKey(不包括) public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) { return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false); } // 获取“Map的头部”。 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey(不包括) public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) { return headMap(toKey, false); } // 获取“Map的尾部”。 // 范围是从 fromKey(包括) 到 最后一个节点 public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) { return tailMap(fromKey, true); } // ”TreeMap的值的集合“对应的类,它集成于AbstractCollection class Values extends AbstractCollection<V> { // 返回迭代器 public Iterator<V> iterator() { return new ValueIterator(getFirstEntry()); } // 返回个数 public int size() { return TreeMap.this.size(); } // "TreeMap的值的集合"中是否包含"对象o" public boolean contains(Object o) { return TreeMap.this.containsValue(o); } // 删除"TreeMap的值的集合"中的"对象o" public boolean remove(Object o) { for (Entry<K,V> e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e)) { if (valEquals(e.getValue(), o)) { deleteEntry(e); return true; } } return false; } // 清空删除"TreeMap的值的集合" public void clear() { TreeMap.this.clear(); } } // EntrySet是“TreeMap的所有键值对组成的集合”, // EntrySet集合的单位是单个“键值对”。 class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> { public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { return new EntryIterator(getFirstEntry()); } // EntrySet中是否包含“键值对Object” public boolean contains(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o; V value = entry.getValue(); Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey()); return p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value); } // 删除EntrySet中的“键值对Object” public boolean remove(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o; V value = entry.getValue(); Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(entry.getKey()); if (p != null && valEquals(p.getValue(), value)) { deleteEntry(p); return true; } return false; } // 返回EntrySet中元素个数 public int size() { return TreeMap.this.size(); } // 清空EntrySet public void clear() { TreeMap.this.clear(); } } // 返回“TreeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(顺序)” Iterator<K> keyIterator() { return new KeyIterator(getFirstEntry()); } // 返回“TreeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(逆序)” Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() { return new DescendingKeyIterator(getLastEntry()); } // KeySet是“TreeMap中所有的KEY组成的集合” // KeySet继承于AbstractSet,而且实现了NavigableSet接口。 static final class KeySet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements NavigableSet<E> { // NavigableMap成员,KeySet是通过NavigableMap实现的 private final NavigableMap<E, Object> m; KeySet(NavigableMap<E,Object> map) { m = map; } // 升序迭代器 public Iterator<E> iterator() { // 若是TreeMap对象,则调用TreeMap的迭代器keyIterator() // 否则,调用TreeMap子类NavigableSubMap的迭代器keyIterator() if (m instanceof TreeMap) return ((TreeMap<E,Object>)m).keyIterator(); else return (Iterator<E>)(((TreeMap.NavigableSubMap)m).keyIterator()); } // 降序迭代器 public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() { // 若是TreeMap对象,则调用TreeMap的迭代器descendingKeyIterator() // 否则,调用TreeMap子类NavigableSubMap的迭代器descendingKeyIterator() if (m instanceof TreeMap) return ((TreeMap<E,Object>)m).descendingKeyIterator(); else return (Iterator<E>)(((TreeMap.NavigableSubMap)m).descendingKeyIterator()); } public int size() { return m.size(); } public boolean isEmpty() { return m.isEmpty(); } public boolean contains(Object o) { return m.containsKey(o); } public void clear() { m.clear(); } public E lower(E e) { return m.lowerKey(e); } public E floor(E e) { return m.floorKey(e); } public E ceiling(E e) { return m.ceilingKey(e); } public E higher(E e) { return m.higherKey(e); } public E first() { return m.firstKey(); } public E last() { return m.lastKey(); } public Comparator<? super E> comparator() { return m.comparator(); } public E pollFirst() { Map.Entry<E,Object> e = m.pollFirstEntry(); return e == null? null : e.getKey(); } public E pollLast() { Map.Entry<E,Object> e = m.pollLastEntry(); return e == null? null : e.getKey(); } public boolean remove(Object o) { int oldSize = size(); m.remove(o); return size() != oldSize; } public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) { return new TreeSet<E>(m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive, toElement, toInclusive)); } public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) { return new TreeSet<E>(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive)); } public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) { return new TreeSet<E>(m.tailMap(fromElement, inclusive)); } public SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) { return subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false); } public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) { return headSet(toElement, false); } public SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) { return tailSet(fromElement, true); } public NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() { return new TreeSet(m.descendingMap()); } } // 它是TreeMap中的一个抽象迭代器,实现了一些通用的接口。 abstract class PrivateEntryIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> { // 下一个元素 Entry<K,V> next; // 上一次返回元素 Entry<K,V> lastReturned; // 期望的修改次数,用于实现fast-fail机制 int expectedModCount; PrivateEntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) { expectedModCount = modCount; lastReturned = null; next = first; } public final boolean hasNext() { return next != null; } // 获取下一个节点 final Entry<K,V> nextEntry() { Entry<K,V> e = next; if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); next = successor(e); lastReturned = e; return e; } // 获取上一个节点 final Entry<K,V> prevEntry() { Entry<K,V> e = next; if (e == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); next = predecessor(e); lastReturned = e; return e; } // 删除当前节点 public void remove() { if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); // 这里重点强调一下“为什么当lastReturned的左右孩子都不为空时,要将其赋值给next”。 // 目的是为了“删除lastReturned节点之后,next节点指向的仍然是下一个节点”。 // 根据“红黑树”的特性可知: // 当被删除节点有两个儿子时。那么,首先把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。 // 这意味着“当被删除节点有两个儿子时,删除当前节点之后,‘新的当前节点‘实际上是‘原有的后继节点(即下一个节点)’”。 // 而此时next仍然指向"新的当前节点"。也就是说next是仍然是指向下一个节点;能继续遍历红黑树。 if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null) next = lastReturned; deleteEntry(lastReturned); expectedModCount = modCount; lastReturned = null; } } // TreeMap的Entry对应的迭代器 final class EntryIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> { EntryIterator(Entry<K,V> first) { super(first); } public Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextEntry(); } } // TreeMap的Value对应的迭代器 final class ValueIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<V> { ValueIterator(Entry<K,V> first) { super(first); } public V next() { return nextEntry().value; } } // reeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(顺序) final class KeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> { KeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) { super(first); } public K next() { return nextEntry().key; } } // TreeMap的KEY组成的迭代器(逆序) final class DescendingKeyIterator extends PrivateEntryIterator<K> { DescendingKeyIterator(Entry<K,V> first) { super(first); } public K next() { return prevEntry().key; } } // 比较两个对象的大小 final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) { return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2) : comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2); } // 判断两个对象是否相等 final static boolean valEquals(Object o1, Object o2) { return (o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2)); } // 返回“Key-Value键值对”的一个简单拷贝(AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>对象) // 可用来读取“键值对”的值 static <K,V> Map.Entry<K,V> exportEntry(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) { return e == null? null : new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>(e); } // 若“键值对”不为null,则返回KEY;否则,返回null static <K,V> K keyOrNull(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) { return e == null? null : e.key; } // 若“键值对”不为null,则返回KEY;否则,抛出异常 static <K> K key(Entry<K,?> e) { if (e==null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return e.key; } // TreeMap的SubMap,它一个抽象类,实现了公共操作。 // 它包括了"(升序)AscendingSubMap"和"(降序)DescendingSubMap"两个子类。 static abstract class NavigableSubMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements NavigableMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable { // TreeMap的拷贝 final TreeMap<K,V> m; // lo是“子Map范围的最小值”,hi是“子Map范围的最大值”; // loInclusive是“是否包含lo的标记”,hiInclusive是“是否包含hi的标记” // fromStart是“表示是否从第一个节点开始计算”, // toEnd是“表示是否计算到最后一个节点 ” final K lo, hi; final boolean fromStart, toEnd; final boolean loInclusive, hiInclusive; // 构造函数 NavigableSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m, boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive, boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) { if (!fromStart && !toEnd) { if (m.compare(lo, hi) > 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey > toKey"); } else { if (!fromStart) // type check m.compare(lo, lo); if (!toEnd) m.compare(hi, hi); } this.m = m; this.fromStart = fromStart; this.lo = lo; this.loInclusive = loInclusive; this.toEnd = toEnd; this.hi = hi; this.hiInclusive = hiInclusive; } // 判断key是否太小 final boolean tooLow(Object key) { // 若该SubMap不包括“起始节点”, // 并且,“key小于最小键(lo)”或者“key等于最小键(lo),但最小键却没包括在该SubMap内” // 则判断key太小。其余情况都不是太小! if (!fromStart) { int c = m.compare(key, lo); if (c < 0 || (c == 0 && !loInclusive)) return true; } return false; } // 判断key是否太大 final boolean tooHigh(Object key) { // 若该SubMap不包括“结束节点”, // 并且,“key大于最大键(hi)”或者“key等于最大键(hi),但最大键却没包括在该SubMap内” // 则判断key太大。其余情况都不是太大! if (!toEnd) { int c = m.compare(key, hi); if (c > 0 || (c == 0 && !hiInclusive)) return true; } return false; } // 判断key是否在“lo和hi”开区间范围内 final boolean inRange(Object key) { return !tooLow(key) && !tooHigh(key); } // 判断key是否在封闭区间内 final boolean inClosedRange(Object key) { return (fromStart || m.compare(key, lo) >= 0) && (toEnd || m.compare(hi, key) >= 0); } // 判断key是否在区间内, inclusive是区间开关标志 final boolean inRange(Object key, boolean inclusive) { return inclusive ? inRange(key) : inClosedRange(key); } // 返回最低的Entry final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowest() { // 若“包含起始节点”,则调用getFirstEntry()返回第一个节点 // 否则的话,若包括lo,则调用getCeilingEntry(lo)获取大于/等于lo的最小的Entry; // 否则,调用getHigherEntry(lo)获取大于lo的最小Entry TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = (fromStart ? m.getFirstEntry() : (loInclusive ? m.getCeilingEntry(lo) : m.getHigherEntry(lo))); return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e; } // 返回最高的Entry final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighest() { // 若“包含结束节点”,则调用getLastEntry()返回最后一个节点 // 否则的话,若包括hi,则调用getFloorEntry(hi)获取小于/等于hi的最大的Entry; // 否则,调用getLowerEntry(hi)获取大于hi的最大Entry TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = (toEnd ? m.getLastEntry() : (hiInclusive ? m.getFloorEntry(hi) : m.getLowerEntry(hi))); return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e; } // 返回"大于/等于key的最小的Entry" final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absCeiling(K key) { // 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于/等于key的最小Entry” // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了! if (tooLow(key)) return absLowest(); // 获取“大于/等于key的最小Entry” TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getCeilingEntry(key); return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e; } // 返回"大于key的最小的Entry" final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHigher(K key) { // 只有在“key太小”的情况下,absLowest()返回的Entry才是“大于key的最小Entry” // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“起始节点”时,absLowest()返回的是最小Entry了,而不一定是“大于key的最小Entry”! if (tooLow(key)) return absLowest(); // 获取“大于key的最小Entry” TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getHigherEntry(key); return (e == null || tooHigh(e.key)) ? null : e; } // 返回"小于/等于key的最大的Entry" final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absFloor(K key) { // 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于/等于key的最大Entry” // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了! if (tooHigh(key)) return absHighest(); // 获取"小于/等于key的最大的Entry" TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getFloorEntry(key); return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e; } // 返回"小于key的最大的Entry" final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLower(K key) { // 只有在“key太大”的情况下,(absHighest)返回的Entry才是“小于key的最大Entry” // 其它情况下不行。例如,当包含“结束节点”时,absHighest()返回的是最大Entry了,而不一定是“小于key的最大Entry”! if (tooHigh(key)) return absHighest(); // 获取"小于key的最大的Entry" TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = m.getLowerEntry(key); return (e == null || tooLow(e.key)) ? null : e; } // 返回“大于最大节点中的最小节点”,不存在的话,返回null final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absHighFence() { return (toEnd ? null : (hiInclusive ? m.getHigherEntry(hi) : m.getCeilingEntry(hi))); } // 返回“小于最小节点中的最大节点”,不存在的话,返回null final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> absLowFence() { return (fromStart ? null : (loInclusive ? m.getLowerEntry(lo) : m.getFloorEntry(lo))); } // 下面几个abstract方法是需要NavigableSubMap的实现类实现的方法 abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest(); abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest(); abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key); abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key); abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key); abstract TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key); // 返回“顺序”的键迭代器 abstract Iterator<K> keyIterator(); // 返回“逆序”的键迭代器 abstract Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator(); // 返回SubMap是否为空。空的话,返回true,否则返回false public boolean isEmpty() { return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.isEmpty() : entrySet().isEmpty(); } // 返回SubMap的大小 public int size() { return (fromStart && toEnd) ? m.size() : entrySet().size(); } // 返回SubMap是否包含键key public final boolean containsKey(Object key) { return inRange(key) && m.containsKey(key); } // 将key-value 插入SubMap中 public final V put(K key, V value) { if (!inRange(key)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("key out of range"); return m.put(key, value); } // 获取key对应值 public final V get(Object key) { return !inRange(key)? null : m.get(key); } // 删除key对应的键值对 public final V remove(Object key) { return !inRange(key)? null : m.remove(key); } // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键值对” public final Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(subCeiling(key)); } // 获取“大于/等于key的最小键” public final K ceilingKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(subCeiling(key)); } // 获取“大于key的最小键值对” public final Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(subHigher(key)); } // 获取“大于key的最小键” public final K higherKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(subHigher(key)); } // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键值对” public final Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(subFloor(key)); } // 获取“小于/等于key的最大键” public final K floorKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(subFloor(key)); } // 获取“小于key的最大键值对” public final Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key) { return exportEntry(subLower(key)); } // 获取“小于key的最大键” public final K lowerKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(subLower(key)); } // 获取"SubMap的第一个键" public final K firstKey() { return key(subLowest()); } // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键" public final K lastKey() { return key(subHighest()); } // 获取"SubMap的第一个键值对" public final Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() { return exportEntry(subLowest()); } // 获取"SubMap的最后一个键值对" public final Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() { return exportEntry(subHighest()); } // 返回"SubMap的第一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对 public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subLowest(); Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e); if (e != null) m.deleteEntry(e); return result; } // 返回"SubMap的最后一个键值对",并从SubMap中删除改键值对 public final Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = subHighest(); Map.Entry<K,V> result = exportEntry(e); if (e != null) m.deleteEntry(e); return result; } // Views transient NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMapView = null; transient EntrySetView entrySetView = null; transient KeySet<K> navigableKeySetView = null; // 返回NavigableSet对象,实际上返回的是当前对象的"Key集合"。 public final NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet() { KeySet<K> nksv = navigableKeySetView; return (nksv != null) ? nksv : (navigableKeySetView = new TreeMap.KeySet(this)); } // 返回"Key集合"对象 public final Set<K> keySet() { return navigableKeySet(); } // 返回“逆序”的Key集合 public NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet() { return descendingMap().navigableKeySet(); } // 排列fromKey(包含) 到 toKey(不包含) 的子map public final SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) { return subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, false); } // 返回当前Map的头部(从第一个节点 到 toKey, 不包括toKey) public final SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) { return headMap(toKey, false); } // 返回当前Map的尾部[从 fromKey(包括fromKeyKey) 到 最后一个节点] public final SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) { return tailMap(fromKey, true); } // Map的Entry的集合 abstract class EntrySetView extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> { private transient int size = -1, sizeModCount; // 获取EntrySet的大小 public int size() { // 若SubMap是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则SubMap大小就是原TreeMap的大小 if (fromStart && toEnd) return m.size(); // 若SubMap不是从“开始节点”到“结尾节点”,则调用iterator()遍历EntrySetView中的元素 if (size == -1 || sizeModCount != m.modCount) { sizeModCount = m.modCount; size = 0; Iterator i = iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { size++; i.next(); } } return size; } // 判断EntrySetView是否为空 public boolean isEmpty() { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> n = absLowest(); return n == null || tooHigh(n.key); } // 判断EntrySetView是否包含Object public boolean contains(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o; K key = entry.getKey(); if (!inRange(key)) return false; TreeMap.Entry node = m.getEntry(key); return node != null && valEquals(node.getValue(), entry.getValue()); } // 从EntrySetView中删除Object public boolean remove(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o; K key = entry.getKey(); if (!inRange(key)) return false; TreeMap.Entry<K,V> node = m.getEntry(key); if (node!=null && valEquals(node.getValue(),entry.getValue())){ m.deleteEntry(node); return true; } return false; } } // SubMap的迭代器 abstract class SubMapIterator<T> implements Iterator<T> { // 上一次被返回的Entry TreeMap.Entry<K,V> lastReturned; // 指向下一个Entry TreeMap.Entry<K,V> next; // “栅栏key”。根据SubMap是“升序”还是“降序”具有不同的意义 final K fenceKey; int expectedModCount; // 构造函数 SubMapIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first, TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) { // 每创建一个SubMapIterator时,保存修改次数 // 若后面发现expectedModCount和modCount不相等,则抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。 // 这就是所说的fast-fail机制的原理! expectedModCount = m.modCount; lastReturned = null; next = first; fenceKey = fence == null ? null : fence.key; } // 是否存在下一个Entry public final boolean hasNext() { return next != null && next.key != fenceKey; } // 返回下一个Entry final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> nextEntry() { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next; if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey) throw new NoSuchElementException(); if (m.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); // next指向e的后继节点 next = successor(e); lastReturned = e; return e; } // 返回上一个Entry final TreeMap.Entry<K,V> prevEntry() { TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e = next; if (e == null || e.key == fenceKey) throw new NoSuchElementException(); if (m.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); // next指向e的前继节点 next = predecessor(e); lastReturned = e; return e; } // 删除当前节点(用于“升序的SubMap”)。 // 删除之后,可以继续升序遍历;红黑树特性没变。 final void removeAscending() { if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (m.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); // 这里重点强调一下“为什么当lastReturned的左右孩子都不为空时,要将其赋值给next”。 // 目的是为了“删除lastReturned节点之后,next节点指向的仍然是下一个节点”。 // 根据“红黑树”的特性可知: // 当被删除节点有两个儿子时。那么,首先把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。 // 这意味着“当被删除节点有两个儿子时,删除当前节点之后,‘新的当前节点‘实际上是‘原有的后继节点(即下一个节点)’”。 // 而此时next仍然指向"新的当前节点"。也就是说next是仍然是指向下一个节点;能继续遍历红黑树。 if (lastReturned.left != null && lastReturned.right != null) next = lastReturned; m.deleteEntry(lastReturned); lastReturned = null; expectedModCount = m.modCount; } // 删除当前节点(用于“降序的SubMap”)。 // 删除之后,可以继续降序遍历;红黑树特性没变。 final void removeDescending() { if (lastReturned == null) throw new IllegalStateException(); if (m.modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); m.deleteEntry(lastReturned); lastReturned = null; expectedModCount = m.modCount; } } // SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator final class SubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> { SubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first, TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) { super(first, fence); } // 获取下一个节点(升序) public Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextEntry(); } // 删除当前节点(升序) public void remove() { removeAscending(); } } // SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持升序操作,继承于SubMapIterator final class SubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> { SubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> first, TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) { super(first, fence); } // 获取下一个节点(升序) public K next() { return nextEntry().key; } // 删除当前节点(升序) public void remove() { removeAscending(); } } // 降序SubMap的Entry迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator final class DescendingSubMapEntryIterator extends SubMapIterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> { DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last, TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) { super(last, fence); } // 获取下一个节点(降序) public Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return prevEntry(); } // 删除当前节点(降序) public void remove() { removeDescending(); } } // 降序SubMap的Key迭代器,它只支持降序操作,继承于SubMapIterator final class DescendingSubMapKeyIterator extends SubMapIterator<K> { DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> last, TreeMap.Entry<K,V> fence) { super(last, fence); } // 获取下一个节点(降序) public K next() { return prevEntry().key; } // 删除当前节点(降序) public void remove() { removeDescending(); } } } // 升序的SubMap,继承于NavigableSubMap static final class AscendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866124060L; // 构造函数 AscendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m, boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive, boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) { super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive); } // 比较器 public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { return m.comparator(); } // 获取“子Map”。 // 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) { if (!inRange(fromKey, fromInclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range"); if (!inRange(toKey, toInclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range"); return new AscendingSubMap(m, false, fromKey, fromInclusive, false, toKey, toInclusive); } // 获取“Map的头部”。 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) { if (!inRange(toKey, inclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range"); return new AscendingSubMap(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, false, toKey, inclusive); } // 获取“Map的尾部”。 // 范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive){ if (!inRange(fromKey, inclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range"); return new AscendingSubMap(m, false, fromKey, inclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive); } // 获取对应的降序Map public NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() { NavigableMap<K,V> mv = descendingMapView; return (mv != null) ? mv : (descendingMapView = new DescendingSubMap(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive)); } // 返回“升序Key迭代器” Iterator<K> keyIterator() { return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence()); } // 返回“降序Key迭代器” Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() { return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence()); } // “升序EntrySet集合”类 // 实现了iterator() final class AscendingEntrySetView extends EntrySetView { public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { return new SubMapEntryIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence()); } } // 返回“升序EntrySet集合” public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { EntrySetView es = entrySetView; return (es != null) ? es : new AscendingEntrySetView(); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absLowest(); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absHighest(); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absCeiling(key); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absHigher(key); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absFloor(key); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absLower(key); } } // 降序的SubMap,继承于NavigableSubMap // 相比于升序SubMap,它的实现机制是将“SubMap的比较器反转”! static final class DescendingSubMap<K,V> extends NavigableSubMap<K,V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = 912986545866120460L; DescendingSubMap(TreeMap<K,V> m, boolean fromStart, K lo, boolean loInclusive, boolean toEnd, K hi, boolean hiInclusive) { super(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive); } // 反转的比较器:是将原始比较器反转得到的。 private final Comparator<? super K> reverseComparator = Collections.reverseOrder(m.comparator); // 获取反转比较器 public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { return reverseComparator; } // 获取“子Map”。 // 范围是从fromKey 到 toKey;fromInclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记,toInclusive是是否包含toKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive) { if (!inRange(fromKey, fromInclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range"); if (!inRange(toKey, toInclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range"); return new DescendingSubMap(m, false, toKey, toInclusive, false, fromKey, fromInclusive); } // 获取“Map的头部”。 // 范围从第一个节点 到 toKey, inclusive是是否包含toKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive) { if (!inRange(toKey, inclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("toKey out of range"); return new DescendingSubMap(m, false, toKey, inclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive); } // 获取“Map的尾部”。 // 范围是从 fromKey 到 最后一个节点,inclusive是是否包含fromKey的标记 public NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive){ if (!inRange(fromKey, inclusive)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromKey out of range"); return new DescendingSubMap(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, false, fromKey, inclusive); } // 获取对应的降序Map public NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap() { NavigableMap<K,V> mv = descendingMapView; return (mv != null) ? mv : (descendingMapView = new AscendingSubMap(m, fromStart, lo, loInclusive, toEnd, hi, hiInclusive)); } // 返回“升序Key迭代器” Iterator<K> keyIterator() { return new DescendingSubMapKeyIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence()); } // 返回“降序Key迭代器” Iterator<K> descendingKeyIterator() { return new SubMapKeyIterator(absLowest(), absHighFence()); } // “降序EntrySet集合”类 // 实现了iterator() final class DescendingEntrySetView extends EntrySetView { public Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() { return new DescendingSubMapEntryIterator(absHighest(), absLowFence()); } } // 返回“降序EntrySet集合” public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { EntrySetView es = entrySetView; return (es != null) ? es : new DescendingEntrySetView(); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLowest() { return absHighest(); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHighest() { return absLowest(); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subCeiling(K key) { return absFloor(key); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subHigher(K key) { return absLower(key); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subFloor(K key) { return absCeiling(key); } TreeMap.Entry<K,V> subLower(K key) { return absHigher(key); } } // SubMap是旧版本的类,新的Java中没有用到。 private class SubMap extends AbstractMap<K,V> implements SortedMap<K,V>, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6520786458950516097L; private boolean fromStart = false, toEnd = false; private K fromKey, toKey; private Object readResolve() { return new AscendingSubMap(TreeMap.this, fromStart, fromKey, true, toEnd, toKey, false); } public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { throw new InternalError(); } public K lastKey() { throw new InternalError(); } public K firstKey() { throw new InternalError(); } public SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); } public SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey) { throw new InternalError(); } public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey) { throw new InternalError(); } public Comparator<? super K> comparator() { throw new InternalError(); } } // 红黑树的节点颜色--红色 private static final boolean RED = false; // 红黑树的节点颜色--黑色 private static final boolean BLACK = true; // “红黑树的节点”对应的类。 // 包含了 key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色) static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { // 键 K key; // 值 V value; // 左孩子 Entry<K,V> left = null; // 右孩子 Entry<K,V> right = null; // 父节点 Entry<K,V> parent; // 当前节点颜色 boolean color = BLACK; // 构造函数 Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.parent = parent; } // 返回“键” public K getKey() { return key; } // 返回“值” public V getValue() { return value; } // 更新“值”,返回旧的值 public V setValue(V value) { V oldValue = this.value; this.value = value; return oldValue; } // 判断两个节点是否相等的函数,覆盖equals()函数。 // 若两个节点的“key相等”并且“value相等”,则两个节点相等 public boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o; return valEquals(key,e.getKey()) && valEquals(value,e.getValue()); } // 覆盖hashCode函数。 public int hashCode() { int keyHash = (key==null ? 0 : key.hashCode()); int valueHash = (value==null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); return keyHash ^ valueHash; } // 覆盖toString()函数。 public String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } } // 返回“红黑树的第一个节点” final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() { Entry<K,V> p = root; if (p != null) while (p.left != null) p = p.left; return p; } // 返回“红黑树的最后一个节点” final Entry<K,V> getLastEntry() { Entry<K,V> p = root; if (p != null) while (p.right != null) p = p.right; return p; } // 返回“节点t的后继节点” static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) { if (t == null) return null; else if (t.right != null) { Entry<K,V> p = t.right; while (p.left != null) p = p.left; return p; } else { Entry<K,V> p = t.parent; Entry<K,V> ch = t; while (p != null && ch == p.right) { ch = p; p = p.parent; } return p; } } // 返回“节点t的前继节点” static <K,V> Entry<K,V> predecessor(Entry<K,V> t) { if (t == null) return null; else if (t.left != null) { Entry<K,V> p = t.left; while (p.right != null) p = p.right; return p; } else { Entry<K,V> p = t.parent; Entry<K,V> ch = t; while (p != null && ch == p.left) { ch = p; p = p.parent; } return p; } } // 返回“节点p的颜色” // 根据“红黑树的特性”可知:空节点颜色是黑色。 private static <K,V> boolean colorOf(Entry<K,V> p) { return (p == null ? BLACK : p.color); } // 返回“节点p的父节点” private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> parentOf(Entry<K,V> p) { return (p == null ? null: p.parent); } // 设置“节点p的颜色为c” private static <K,V> void setColor(Entry<K,V> p, boolean c) { if (p != null) p.color = c; } // 设置“节点p的左孩子” private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> leftOf(Entry<K,V> p) { return (p == null) ? null: p.left; } // 设置“节点p的右孩子” private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> rightOf(Entry<K,V> p) { return (p == null) ? null: p.right; } // 对节点p执行“左旋”操作 private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> r = p.right; p.right = r.left; if (r.left != null) r.left.parent = p; r.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = r; else if (p.parent.left == p) p.parent.left = r; else p.parent.right = r; r.left = p; p.parent = r; } } // 对节点p执行“右旋”操作 private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) { if (p != null) { Entry<K,V> l = p.left; p.left = l.right; if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p; l.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = l; else if (p.parent.right == p) p.parent.right = l; else p.parent.left = l; l.right = p; p.parent = l; } } // 插入之后的修正操作。 // 目的是保证:红黑树插入节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树 private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) { x.color = RED; while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) { if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) { Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateLeft(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } else { Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x))); if (colorOf(y) == RED) { setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(y, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); x = parentOf(parentOf(x)); } else { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { x = parentOf(x); rotateRight(x); } setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x))); } } } root.color = BLACK; } // 删除“红黑树的节点p” private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) { modCount++; size--; // If strictly internal, copy successor‘s element to p and then make p // point to successor. if (p.left != null && p.right != null) { Entry<K,V> s = successor (p); p.key = s.key; p.value = s.value; p = s; } // p has 2 children // Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists. Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right); if (replacement != null) { // Link replacement to parent replacement.parent = p.parent; if (p.parent == null) root = replacement; else if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = replacement; else p.parent.right = replacement; // Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion. p.left = p.right = p.parent = null; // Fix replacement if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(replacement); } else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node. root = null; } else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink. if (p.color == BLACK) fixAfterDeletion(p); if (p.parent != null) { if (p == p.parent.left) p.parent.left = null; else if (p == p.parent.right) p.parent.right = null; p.parent = null; } } } // 删除之后的修正操作。 // 目的是保证:红黑树删除节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树 private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) { while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) { if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { setColor(sib, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(x), RED); rotateLeft(parentOf(x)); sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); } if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(sib, RED); x = parentOf(x); } else { if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK); setColor(sib, RED); rotateRight(sib); sib = rightOf(parentOf(x)); } setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x))); setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK); rotateLeft(parentOf(x)); x = root; } } else { // symmetric Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); if (colorOf(sib) == RED) { setColor(sib, BLACK); setColor(parentOf(x), RED); rotateRight(parentOf(x)); sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); } if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK && colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(sib, RED); x = parentOf(x); } else { if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) { setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK); setColor(sib, RED); rotateLeft(sib); sib = leftOf(parentOf(x)); } setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x))); setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK); setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK); rotateRight(parentOf(x)); x = root; } } } setColor(x, BLACK); } private static final long serialVersionUID = 919286545866124006L; // java.io.Serializable的写入函数 // 将TreeMap的“容量,所有的Entry”都写入到输出流中 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException { // Write out the Comparator and any hidden stuff s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size (number of Mappings) s.writeInt(size); // Write out keys and values (alternating) for (Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) { Map.Entry<K,V> e = i.next(); s.writeObject(e.getKey()); s.writeObject(e.getValue()); } } // java.io.Serializable的读取函数:根据写入方式读出 // 先将TreeMap的“容量、所有的Entry”依次读出 private void readObject(final java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // Read in the Comparator and any hidden stuff s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in size int size = s.readInt(); buildFromSorted(size, null, s, null); } // 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap private void buildFromSorted(int size, Iterator it, java.io.ObjectInputStream str, V defaultVal) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { this.size = size; root = buildFromSorted(0, 0, size-1, computeRedLevel(size), it, str, defaultVal); } // 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap // 将map中的元素逐个添加到TreeMap中,并返回map的中间元素作为根节点。 private final Entry<K,V> buildFromSorted(int level, int lo, int hi, int redLevel, Iterator it, java.io.ObjectInputStream str, V defaultVal) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { if (hi < lo) return null; // 获取中间元素 int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; Entry<K,V> left = null; // 若lo小于mid,则递归调用获取(middel的)左孩子。 if (lo < mid) left = buildFromSorted(level+1, lo, mid - 1, redLevel, it, str, defaultVal); // 获取middle节点对应的key和value K key; V value; if (it != null) { if (defaultVal==null) { Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>)it.next(); key = entry.getKey(); value = entry.getValue(); } else { key = (K)it.next(); value = defaultVal; } } else { // use stream key = (K) str.readObject(); value = (defaultVal != null ? defaultVal : (V) str.readObject()); } // 创建middle节点 Entry<K,V> middle = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null); // 若当前节点的深度=红色节点的深度,则将节点着色为红色。 if (level == redLevel) middle.color = RED; // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子 if (left != null) { middle.left = left; left.parent = middle; } if (mid < hi) { // 递归调用获取(middel的)右孩子。 Entry<K,V> right = buildFromSorted(level+1, mid+1, hi, redLevel, it, str, defaultVal); // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子 middle.right = right; right.parent = middle; } return middle; } // 计算节点树为sz的最大深度,也是红色节点的深度值。 private static int computeRedLevel(int sz) { int level = 0; for (int m = sz - 1; m >= 0; m = m / 2 - 1) level++; return level; } }
说明:
在详细介绍TreeMap的代码之前,我们先建立一个整体概念。
TreeMap是通过红黑树实现的,TreeMap存储的是key-value键值对,TreeMap的排序是基于对key的排序。
TreeMap提供了操作“key”、“key-value”、“value”等方法,也提供了对TreeMap这颗树进行整体操作的方法,如获取子树、反向树。
后面的解说内容分为几部分,
首先,介绍TreeMap的核心,即红黑树相关部分;
然后,介绍TreeMap的主要函数;
再次,介绍TreeMap实现的几个接口;
最后,补充介绍TreeMap的其它内容。
第3.1部分 TreeMap的红黑树相关内容
TreeMap中于红黑树相关的主要函数有:
1 数据结构
1.1 红黑树的节点颜色--红色
private static final boolean RED = false;
1.2 红黑树的节点颜色--黑色
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
1.3 “红黑树的节点”对应的类。
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { ... }
Entry包含了6个部分内容:key(键)、value(值)、left(左孩子)、right(右孩子)、parent(父节点)、color(颜色)
Entry节点根据key进行排序,Entry节点包含的内容为value。
2 相关操作
2.1 左旋
private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) { ... }
2.2 右旋
private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) { ... }
2.3 插入操作
public V put(K key, V value) { ... }
2.4 插入修正操作
红黑树执行插入操作之后,要执行“插入修正操作”。
目的是:保红黑树在进行插入节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树
private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) { ... }
2.5 删除操作
private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) { ... }
2.6 删除修正操作
红黑树执行删除之后,要执行“删除修正操作”。
目的是保证:红黑树删除节点之后,仍然是一颗红黑树
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) { ... }
第3.2部分 TreeMap的构造函数
1 默认构造函数
使用默认构造函数构造TreeMap时,使用java的默认的比较器比较Key的大小,从而对TreeMap进行排序。
public TreeMap() { comparator = null; }
2 带比较器的构造函数
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; }
3 带Map的构造函数,Map会成为TreeMap的子集
public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = null; putAll(m); }
该构造函数会调用putAll()将m中的所有元素添加到TreeMap中。putAll()源码如下:
public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> e : m.entrySet()) put(e.getKey(), e.getValue()); }
从中,我们可以看出putAll()就是将m中的key-value逐个的添加到TreeMap中。
4 带SortedMap的构造函数,SortedMap会成为TreeMap的子集
public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = m.comparator(); try { buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } }
该构造函数不同于上一个构造函数,在上一个构造函数中传入的参数是Map,Map不是有序的,所以要逐个添加。
而该构造函数的参数是SortedMap是一个有序的Map,我们通过buildFromSorted()来创建对应的Map。
buildFromSorted涉及到的代码如下:

// 根据已经一个排好序的map创建一个TreeMap // 将map中的元素逐个添加到TreeMap中,并返回map的中间元素作为根节点。 private final Entry<K,V> buildFromSorted(int level, int lo, int hi, int redLevel, Iterator it, java.io.ObjectInputStream str, V defaultVal) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { if (hi < lo) return null; // 获取中间元素 int mid = (lo + hi) / 2; Entry<K,V> left = null; // 若lo小于mid,则递归调用获取(middel的)左孩子。 if (lo < mid) left = buildFromSorted(level+1, lo, mid - 1, redLevel, it, str, defaultVal); // 获取middle节点对应的key和value K key; V value; if (it != null) { if (defaultVal==null) { Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>)it.next(); key = entry.getKey(); value = entry.getValue(); } else { key = (K)it.next(); value = defaultVal; } } else { // use stream key = (K) str.readObject(); value = (defaultVal != null ? defaultVal : (V) str.readObject()); } // 创建middle节点 Entry<K,V> middle = new Entry<K,V>(key, value, null); // 若当前节点的深度=红色节点的深度,则将节点着色为红色。 if (level == redLevel) middle.color = RED; // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子 if (left != null) { middle.left = left; left.parent = middle; } if (mid < hi) { // 递归调用获取(middel的)右孩子。 Entry<K,V> right = buildFromSorted(level+1, mid+1, hi, redLevel, it, str, defaultVal); // 设置middle为left的父亲,left为middle的左孩子 middle.right = right; right.parent = middle; } return middle; }
要理解buildFromSorted,重点说明以下几点:
第一,buildFromSorted是通过递归将SortedMap中的元素逐个关联。
第二,buildFromSorted返回middle节点(中间节点)作为root。
第三,buildFromSorted添加到红黑树中时,只将level == redLevel的节点设为红色。第level级节点,实际上是buildFromSorted转换成红黑树后的最底端(假设根节点在最上方)的节点;只将红黑树最底端的阶段着色为红色,其余都是黑色。
第3.3部分 TreeMap的Entry相关函数
TreeMap的 firstEntry()、 lastEntry()、 lowerEntry()、 higherEntry()、 floorEntry()、 ceilingEntry()、 pollFirstEntry() 、 pollLastEntry() 原理都是类似的;下面以firstEntry()来进行详细说明
我们先看看firstEntry()和getFirstEntry()的代码:
public Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() { return exportEntry(getFirstEntry()); } final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() { Entry<K,V> p = root; if (p != null) while (p.left != null) p = p.left; return p; }
从中,我们可以看出 firstEntry() 和 getFirstEntry() 都是用于获取第一个节点。
但是,firstEntry() 是对外接口; getFirstEntry() 是内部接口。而且,firstEntry() 是通过 getFirstEntry() 来实现的。那为什么外界不能直接调用 getFirstEntry(),而需要多此一举的调用 firstEntry() 呢?
先告诉大家原因,再进行详细说明。这么做的目的是:防止用户修改返回的Entry。getFirstEntry()返回的Entry是可以被修改的,但是经过firstEntry()返回的Entry不能被修改,只可以读取Entry的key值和value值。下面我们看看到底是如何实现的。
(01) getFirstEntry()返回的是Entry节点,而Entry是红黑树的节点,它的源码如下:
// 返回“红黑树的第一个节点” final Entry<K,V> getFirstEntry() { Entry<K,V> p = root; if (p != null) while (p.left != null) p = p.left; return p; }
从中,我们可以调用Entry的getKey()、getValue()来获取key和value值,以及调用setValue()来修改value的值。
(02) firstEntry()返回的是exportEntry(getFirstEntry())。下面我们看看exportEntry()干了些什么?
static <K,V> Map.Entry<K,V> exportEntry(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) { return e == null? null : new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V>(e); }
实际上,exportEntry() 是新建一个AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry类型的对象,并返回。
SimpleImmutableEntry的实现在AbstractMap.java中,下面我们看看AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry是如何实现的,代码如下:

public static class SimpleImmutableEntry<K,V> implements Entry<K,V>, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7138329143949025153L; private final K key; private final V value; public SimpleImmutableEntry(K key, V value) { this.key = key; this.value = value; } public SimpleImmutableEntry(Entry<? extends K, ? extends V> entry) { this.key = entry.getKey(); this.value = entry.getValue(); } public K getKey() { return key; } public V getValue() { return value; } public V setValue(V value) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } public boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o; return eq(key, e.getKey()) && eq(value, e.getValue()); } public int hashCode() { return (key == null ? 0 : key.hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); } public String toString() { return key + "=" + value; } }
从中,我们可以看出SimpleImmutableEntry实际上是简化的key-value节点。
它只提供了getKey()、getValue()方法类获取节点的值;但不能修改value的值,因为调用 setValue() 会抛出异常UnsupportedOperationException();
再回到我们之前的问题:那为什么外界不能直接调用 getFirstEntry(),而需要多此一举的调用 firstEntry() 呢?
现在我们清晰的了解到:
(01) firstEntry()是对外接口,而getFirstEntry()是内部接口。
(02) 对firstEntry()返回的Entry对象只能进行getKey()、getValue()等读取操作;而对getFirstEntry()返回的对象除了可以进行读取操作之后,还可以通过setValue()修改值。
第3.4部分 TreeMap的key相关函数
TreeMap的firstKey()、lastKey()、lowerKey()、higherKey()、floorKey()、ceilingKey()原理都是类似的;下面以ceilingKey()来进行详细说明
ceilingKey(K key)的作用是“返回大于/等于key的最小的键值对所对应的KEY,没有的话返回null”,它的代码如下:
public K ceilingKey(K key) { return keyOrNull(getCeilingEntry(key)); }
ceilingKey()是通过getCeilingEntry()实现的。keyOrNull()的代码很简单,它是获取节点的key,没有的话,返回null。
static <K,V> K keyOrNull(TreeMap.Entry<K,V> e) { return e == null? null : e.key; }
getCeilingEntry(K key)的作用是“获取TreeMap中大于/等于key的最小的节点,若不存在(即TreeMap中所有节点的键都比key小),就返回null”。它的实现代码如下:

final Entry<K,V> getCeilingEntry(K key) { Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = compare(key, p.key); // 情况一:若“p的key” > key。 // 若 p 存在左孩子,则设 p=“p的左孩子”; // 否则,返回p if (cmp < 0) { if (p.left != null) p = p.left; else return p; // 情况二:若“p的key” < key。 } else if (cmp > 0) { // 若 p 存在右孩子,则设 p=“p的右孩子” if (p.right != null) { p = p.right; } else { // 若 p 不存在右孩子,则找出 p 的后继节点,并返回 // 注意:这里返回的 “p的后继节点”有2种可能性:第一,null;第二,TreeMap中大于key的最小的节点。 // 理解这一点的核心是,getCeilingEntry是从root开始遍历的。 // 若getCeilingEntry能走到这一步,那么,它之前“已经遍历过的节点的key”都 > key。 // 能理解上面所说的,那么就很容易明白,为什么“p的后继节点”有2种可能性了。 Entry<K,V> parent = p.parent; Entry<K,V> ch = p; while (parent != null && ch == parent.right) { ch = parent; parent = parent.parent; } return parent; } // 情况三:若“p的key” = key。 } else return p; } return null; }
中间部分和HashMap类似
第3.9部分 TreeMap实现的NavigableMap接口
1 反向TreeMap
descendingMap() 的作用是返回当前TreeMap的反向的TreeMap。所谓反向,就是排序顺序和原始的顺序相反。
我们已经知道TreeMap是一颗红黑树,而红黑树是有序的。
TreeMap的排序方式是通过比较器,在创建TreeMap的时候,若指定了比较器,则使用该比较器;否则,就使用Java的默认比较器。
而获取TreeMap的反向TreeMap的原理就是将比较器反向即可!
第3.10部分 TreeMap其它函数
1 顺序遍历和逆序遍历
TreeMap的顺序遍历和逆序遍历原理非常简单。
由于TreeMap中的元素是从小到大的顺序排列的。因此,顺序遍历,就是从第一个元素开始,逐个向后遍历;而倒序遍历则恰恰相反,它是从最后一个元素开始,逐个往前遍历。
我们可以通过 keyIterator() 和 descendingKeyIterator()来说明!
keyIterator()的作用是返回顺序的KEY的集合,
descendingKeyIterator()的作用是返回逆序的KEY的集合。
以上是关于Map -- TreeMap的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
