java bio总结
Posted kyleinjava
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java bio总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
、同步异步、阻塞非阻塞(目前不是很清楚,这篇博客写完后,后续进行处理)
1.同步和异步:关注的是消息的通讯机制,
同步:发起调用后,如果没有得到结果,该调用是不会返回的;该调用者会主动等待调用返回。
异步:发起调用后,调用立刻返回,但并不是返回的结果;也就是说调用者并不会立刻得到结果,而是被调用者通知调用者,或者通过回调函数处理这个调用。
2.阻塞和非阻塞:指的是程序等待调用结果时的状态。只有同步才会有阻塞和非阻塞的概念。
阻塞:发起调用后当前线程会被挂起,直到有返回
非阻塞:发起调用后,当前线程不会被挂起,而是继续执行。
二、io流的分类
1.输入流、输出流:根据流是否流向处理器来确定是输入流还是输出流。
2.字节流、字符流:字节流读到的数据不会进行任何处理;字符流读取到的二进制数据会根据相应的编码进行转换为字符,字符流=字节流+解码。
三、io流类结构图
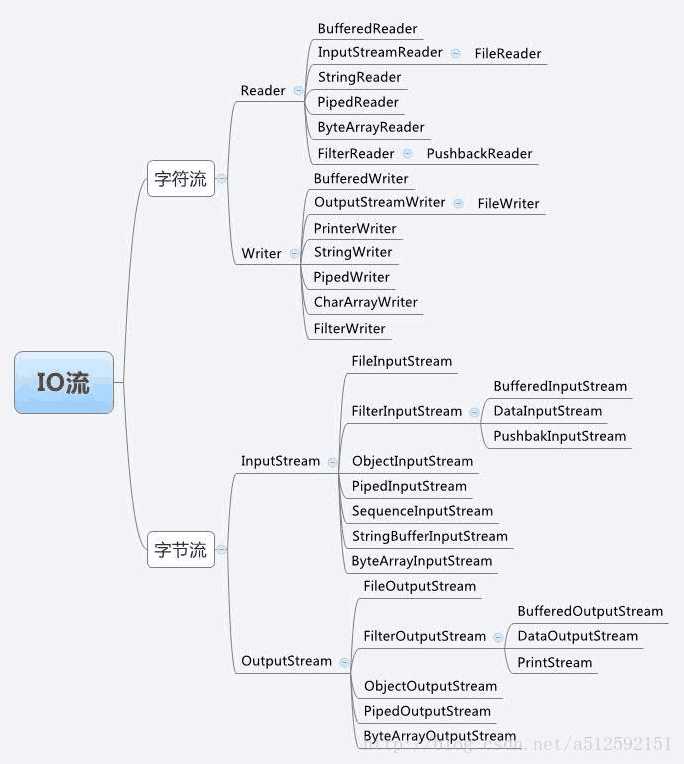

四、常用功能
注意一点:使用完io后,一定要关闭流
1.io流对文件进行读取
/** * 字符流读写文本文件 * 在使用io读写文本文件的时候一定要记住关闭流 */ public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { ReadFile(new File("E:/b.txt")); WriteFile(new File("E:/c.txt")); } public static void ReadFile(File file){ FileReader fr = null; BufferedReader br = null; InputStreamReader isr = null; try { System.out.println("\\r\\n========自己定义缓冲数组来读取文件================"); fr = new FileReader(file); char[] buffer1 = new char[3]; int len1 = 0; while((len1 = fr.read(buffer1)) != -1){ System.out.print(new String(buffer1,0,len1)); } System.out.println("\\r\\n========使用缓冲流来读取文件================"); br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); String temp = ""; while((temp = br.readLine()) != null){ System.out.println(temp); } System.out.println("\\r\\n========使用转换流来读取文件==========="); isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file),"utf-8"); char[] buffer2 = new char[1]; int len2 = 0; while((len2 = isr.read(buffer2)) != -1 ){ System.out.print(new String(buffer2,0,len2)); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { br.close(); isr.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void WriteFile(File file){ FileOutputStream fos = null; FileWriter fw = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { //========使用字节流写入文件=========== fos = new FileOutputStream(file); fos.write("测试写入文件abc123。。".getBytes()); fos.write("测试是否叠加".getBytes()); fos.flush(); //========使用字符流写入文件=========== fw = new FileWriter(file,true); fw.write("\\r\\n========使用字符流写入文件==========="); fw.write("这是用FileWriter写入的数据 "); fw.flush(); //========使用缓冲流写入文件=========== //FileWriter默认是会覆盖上一次的数据,所以在新建的时候要将是否追加参数设置为true bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file,true)); bw.newLine(); bw.write("使用缓冲流写入"); bw.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NumberFormatException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { bw.close(); fw.close(); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
2.字节流对文件进行复制
/** * 字节流对文件进行复制 * */ public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { copy(); } public static void copy(){ FileInputStream fis = null; FileOutputStream fos = null; try{ fis = new FileInputStream("E:/a.txt"); fos = new FileOutputStream("E:/b.txt"); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];//使用数组进行缓冲,提高io速度 int len = 0; while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){ fos.write(buffer, 0, len); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
五、IO流使用的一些细节
1.IO流中,缓冲类都是Buffered*类,其并不具备读写能力,只是内部维护了一个8kb的数组,只有在调用了close()和flush()或者字节数组已经满了才会将数据写入到硬盘。提高了文件的读写效率。
2.文件输出流,目标文件如果不存在,则会创建文件。其write方法默认清空文件内容,再写入内容,需要在构造方法中设置才能成功。
3.FileOutputStream 参数为int时,只会把低8位写出,剩余24位丢弃。
4.转换流的作用就是将字节流转换为字符流,并可以按照指定的编码对数据进行读写。
以上是关于java bio总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章