Huffman树及其编码(STL array实现)
Posted virgildevil
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Huffman树及其编码(STL array实现)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
这篇随笔主要是Huffman编码,构建哈夫曼树有各种各样的实现方法,如优先队列,数组构成的树等,但本质都是堆。
这里我用数组来存储数据,以堆的思想来构建一个哈弗曼树,并存入vector中,进而实现哈夫曼编码
步骤: 1生成哈夫曼树 (取最小权值树和次小权值树生成新树,排列后重新取树,不断重复)
2编码 (遵循左零右一的原则)
3解码(是编码的逆向,本文还未实现,日后有机会补充)
data.txt 测试数据:
|
5 |
结果:
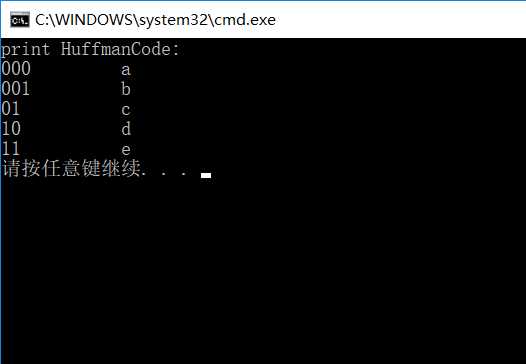
下面贴代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <fstream> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <array> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 #define ARR_SIZE 100 //缓冲区大小 10 11 typedef struct Tree 12 { 13 int freq; 14 char key = ‘�‘; 15 Tree *left, *right; 16 Tree() 17 { 18 freq = 0; 19 key = ‘�‘; 20 left = NULL; 21 right = NULL; 22 } 23 } Tree, *pTree; 24 union key_or_point 25 { 26 char key; 27 pTree point; 28 }; 29 enum infor_type 30 { 31 key_s, 32 point_s 33 }; 34 class infor 35 { 36 public: 37 int freq;//权值 38 key_or_point kp;//记录键值或者 新生成的树的地址 39 infor_type type;// 联合体key_or_point的类型由infor_type标志 40 infor() 41 { 42 freq = 0; 43 kp.key = NULL; 44 type = key_s; 45 } 46 }; 47 48 array<infor, ARR_SIZE> arr;//用来读取要处理的数据 49 vector<pTree> trees; //所有生成的树都放在vector里面 50 51 int num; //要处理的数据个数 52 53 bool cmp(infor a, infor b) 54 { 55 return a.freq > b.freq; 56 } 57 58 void Huffman() 59 { 60 //找出最小权值和次小权值 61 sort(&arr[0], &arr[num], cmp); 62 int cal = num - 1; 63 while (cal > 0) 64 { 65 66 pTree pta = new Tree(); 67 vector<pTree>::iterator it; 68 69 pTree ptl = new Tree(); 70 ptl->freq = arr[cal].freq; 71 // pt all 的左子树 72 if (arr[cal].type == point_s) 73 { 74 pta->left = arr[cal].kp.point;//如果存放的是地址,那么该树已入vector 75 //无需重复操作 76 } 77 else 78 { 79 ptl->key = arr[cal].kp.key; 80 trees.push_back(ptl); 81 it = trees.end() - 1; 82 pta->left = *it; 83 } 84 85 86 pTree ptr = new Tree(); 87 ptr->freq = arr[cal - 1].freq; 88 // pt all 的右子树 89 if (arr[cal - 1].type == point_s) 90 { 91 pta->right = arr[cal - 1].kp.point; //如果存放的是地址,那么该树已入vector 92 //无需重复操作 93 } 94 else 95 { 96 ptr->key = arr[cal - 1].kp.key; 97 trees.push_back(ptr); 98 it = trees.end() - 1; 99 pta->right = *it; 100 } 101 102 pta->freq = arr[cal].freq + arr[cal - 1].freq; 103 trees.push_back(pta);//pt all 本树 104 105 it = trees.end() - 1; 106 arr[cal - 1].kp.point = *it; 107 arr[cal - 1].type = point_s;//保存新生成树的地址 108 109 arr[cal - 1].freq = arr[cal - 1].freq + arr[cal ].freq; 110 //最小权值的树和次权值的树组成新树后,放回原数组 111 //新树的key_or_point此时类型变为point_s指针指向vector存放的位置 112 113 //第一次循环会有三棵树入vector,重新排列后,新树无需重复入vector 114 cal--; 115 sort(&arr[0], &arr[cal + 1], cmp); 116 117 } 118 119 } 120 121 void traversTree(pTree pt, string st = "") 122 { 123 //中序遍历二叉树 124 //遵循左0右1的原则 125 if (pt->left == NULL && pt->right == NULL) 126 { 127 cout.flags(ios::left); 128 cout.width(10); 129 cout << st.c_str() << " "; 130 cout << pt->key << endl; 131 return; 132 } 133 if (pt->left != NULL) 134 { 135 st += ‘0‘; 136 traversTree(pt->left, st); 137 st.pop_back();//从左边出来后要回退一个字符,避免进入右边时多出一个字符 138 } 139 140 if (pt->right != NULL) 141 { 142 st += ‘1‘; 143 traversTree(pt->right, st); 144 } 145 return ; 146 } 147 148 void printCode() 149 { 150 vector<pTree>::iterator it; 151 it = trees.end() - 1; 152 pTree pt = *it; //取出最顶端的树 153 cout << "print HuffmanCode:" << endl; 154 traversTree(pt); 155 } 156 int main() 157 { 158 ifstream filein("data.txt"); 159 cin.rdbuf(filein.rdbuf());//重定向输入 160 cin >> num;//要处理的数据个数 161 for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) 162 { 163 cin >> arr[i].freq; 164 } 165 for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) 166 { 167 cin >> arr[i].kp.key; 168 } 169 Huffman(); 170 printCode(); 171 return 0; 172 }
分析:
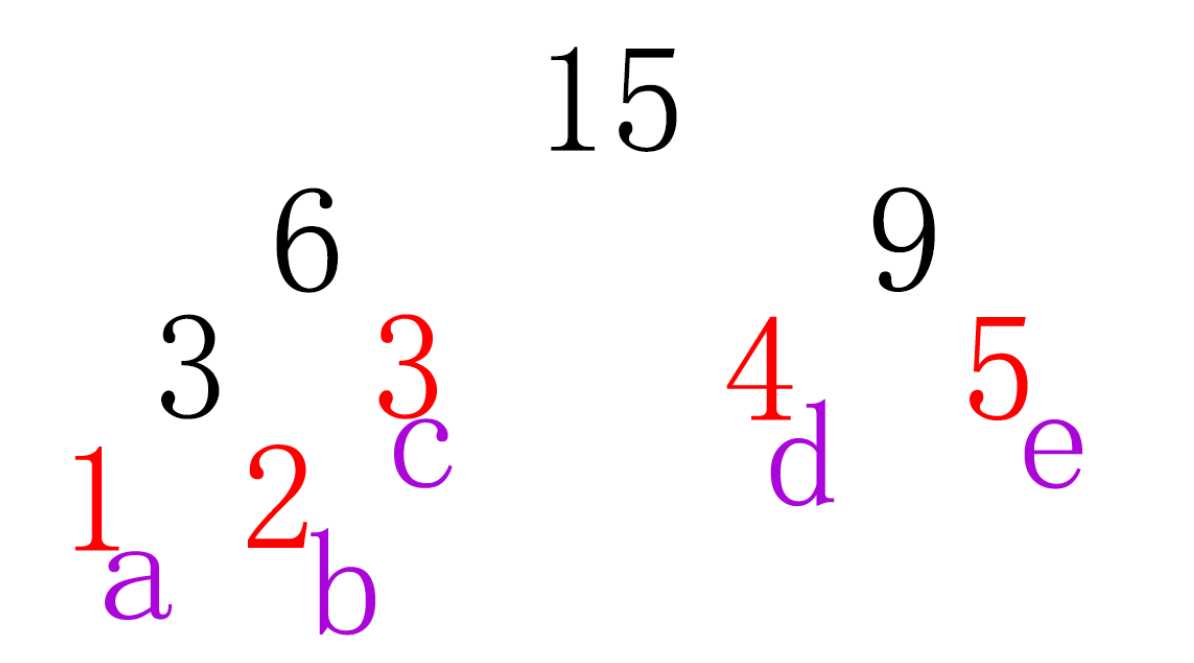
这是以上测试数据生成的树的情况。
只有叶子节点表示有效的符号,所以遍历树时返回条件是叶子节点(如果是叶子节点则返回)
总结:
1 编程时用的一些小技巧总结:
1.1 输出调试信息:可以采用如下方式
#ifdef DEBUG
cout调试信息....
#endif
1.2 联合体union需要取得类型时,可以加一个enum来记录和标志uninon的类型
2 编程方法反思:
可以看到源码中用到了两次sort,这是省事的做法了。
目前想到的改进的方法是用二分插入(数据已经排序)
对比起来,我觉得优先队列的方式更易懂且效率更高,但此文也算是一次小探索,值得记录下来
3 感想:
本人入园第一次随笔,如有不足或错误,还望指出。
以上
以上是关于Huffman树及其编码(STL array实现)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章